Abstract
Background
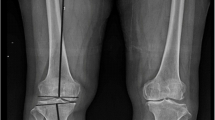
Posterior tibial slope (PTS) is an important factor affecting postoperative range of motion (ROM) following total knee arthroplasty (TKA). Metaphysio-diaphyseal angle (MDA) is a new entity defined as angle between proximal anatomical axis and metaphyseal axis of tibia. This study was undertaken to determine PTS in Indian patients and find its correlation with MDA of tibia. Accuracy of extramedullary jigs and the influence of MDA on the accuracy was also evaluated. This study is a retrospective analysis of prospectively collected data in a tertiary healthcare center.
Materials and Methods
Data of 100 consecutive patients undergoing TKA in a single center by a single surgeon was analyzed. Posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) substituting TKA was done with same jig to achieve different PTS in different patients. MDA, preoperative PTS and postoperative PTS were calculated. The data was analyzed using appropriate statistical analysis.
Results
Mean preoperative PTS was 11.64° and mean MDA was 23.76° with a strong correlation between them (Pearson’s coefficient 0.72). Extramedullary jigs were accurate in 53% cases. In remaining 47%, postoperative PTS was less than planned PTS in 30%, and more in 17%. Mean postoperative PTS was 2.54°. In patients with MDA <20°, postoperative PTS was significantly less (P = 0.0176) compared with those with MDA 20.
Conclusions
The study establishes the positive correlation between MDA and PTS in Indians; and that MDA is an independent factor affecting accuracy of extramedullary jigs in TKA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rodricks DJ, Patil S, Pulido P, Colwell CW Jr. Press-fit condylar design total knee arthroplasty. Fourteen to seventeen-year followup. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2007;89:89–95.
Vessely MB, Whaley AL, Harmsen WS, Schleck CD, Berry DJ. The chitranjan ranawat award: Long term survivorship and failure modes of 1000 cemented condylar total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2006;452:28–34.
Kettelkamp DB. Gait characteristics of the knee: Normal, abnormal, and post reconstruction. In: American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons: Symposium on reconstructive surgery of the knee. St Louis: CV Mosby; 1976. p. 47.
Laubenthal KN, Smidt GL, Kettelkamp DB. A quantitative analysis of knee motion during activities of daily living. Phys Ther 1972;52:34–43.
Kim JM, Moon MS. Squatting following total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1995;313:177–86.
Khattak MJ, Umer M, Davis ET, Habib M, Ahmed M. Lower limb alignment and posterior tibia slope in Pakistanis: A radiographic study. J Orthop Surg 2010;18:22–5.
Chiu KY, Zhang SD, Zhang GH. Posterior slope of tibial plateau in Chinese. J Arthroplasty 2000;15:224–7.
Yoo JH, Chang CB, Shin KS, Seong SC, Kim TK. Anatomical references to assess the posterior tibial slope in total knee arthroplasty: A comparison of 5 anatomical axes. J Arthroplasty 2008;23:586–92.
Massin P, Gournay A. Optimization of the posterior condylar offset, tibial slope, and condylar roll-back in total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26:124–30.
Yoga R, Sivapathasundaram N, Suresh C. Posterior slope of the Tibia Plateau in Malaysian patients undergoing total knee replacement. Malays Orthop J 2009;3:78–80.
Didia BC, Jaja BN. Posterior slope of tibial plateau in adult Nigerian subjects. Int J Morphol 2009;27:201–4.
Han HS, Chang CB, Seong SC, Lee S, Lee MC. Evaluation of anatomic references for tibial alignment in total knee replacement. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 2008;16:373–7.
Hashemi J, Chandrashekar N, Gill B, Beynnon BD, Slauterbeck JR, Schutt RC Jr, et al. The geometry of the tibial plateau and its influence on the biomechanics of the tibiofemoral joint. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2008;90:2724–34.
Yue B, Varadarajan KM, Ai S, Tang T, Rubash HE, Li G. Differences of knee anthropometry between chinese and white men and women. J Arthroplasty 2011;26:124–30.
Kansara D, Markel DC. The effect of posterior tibial slope on range of motion after total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2006;21:809–13.
Merchant AC, Arendt EA, Dye SF, Fredericson M, Grelsamer RP, Leadbetter WB, et al. The female knee: Anatomic variations and the female-specific total knee design. Clin Orthop Relat Res 2008;466:3059–65.
Dargel J, Michael JW, Feiser J, Ivo R, Koebke J. Human knee joint anatomy revisited: Morphometry in the light of sex-specific total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 2011;26:346–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohanty, S.S., Rao, N.N., Dash, K.K. et al. Correlation of posterior tibial slope with metaphysiodiaphyseal angle in total knee arthroplasty: A radiological study. IJOO 47, 67–71 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106910
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106910