Abstract
Background
The presence of extra articular deformities either in the femur or the tibia with arthritis of the knee makes total knee arthroplasty (TKA) technically demanding. The purpose of this study is to report outcomes with Total Knee Arthroplasty in patients with arthritis of the knee associated with extra articular deformity by intraarticular resection and soft tissue balancing.
Materials and Methods
Thirty six knees (32 patients) who had arthritis of the knee associated with extra articular deformity, underwent total knee arthroplasty between 1999 and 2006 were included in this retrospective analysis. All patients had intraarticular resection with soft tissue balancing to correct the deformity. Full length weight bearing anteroposterior X-rays, Knee society scores, and Knee range of motion was recorded pre- and postoperatively.
Results
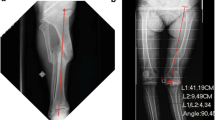
The mean period of followup was 85 months (range 42–120 months). The deformities amenable to correction by intraarticular resection in our series were Femur- Coronal plane 11°–18° (mean 16.2°) Saggital plane 0°-15° (mean 10.1°) Tibia - Coronal plane 12°-24° (mean 21°). There was an improvement in the range of motion from mean of 54° preoperatively to 114° postoperatively (P value <0.05). The Knee Society- Knee Score improved from 37 points to 85 points postoperatively (P value <0.05). The functional score improved from a mean value of 19 to a mean of 69.5 at followup (P <0.01). The preoperative hip knee ankle angle in the coronal plane improved from a mean of 14° ±2° varus (26° varus to 4° valgus) to a mean of 2° ±0.6° varus (6° varus to 2° valgus).
Conclusion
With a good preoperative planning and templating, intraarticular bone resection and good soft tissue balancing both in flexion and extension, correction would be possible in majority of extraarticular deformities.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotke PA, Ecker ML. Influence of positioning of prosthesis in total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1977;59:77–9.
Insall JN, Dorr LD, Scott RD, Scott WN. Rationale of the Knee Society Clinical Rating System. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1989;248:13–4.
Lonner JH, Siliski JM, Lotke PA. Simultaneous femoral osteotomy and total knee arthroplasty for treatment of osteoarthritis associated with severe extra articular deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2000;82:342–8.
Wang JW, Wang CJ. Total knee arthroplasty for arthritis of the knee with extra articular deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 2002;84:1769–74.
Moreland JR, Bassett LW, Hanker GJ. Radiographic analysis of the axial alignment of the lower extremity. J Bone Joint Surg Am 1987;69:745–9.
Wolff AM, Hungerford DS, Pepe CL. The effect of extra articular varus and valgus deformity on total knee arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1991;271:35–51.
Clayton ML, Thompson TR, Mack RP. Correction of alignment deformities during total knee arthroplasties: Staged soft-tissue releases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 1986;202:117–24.
Cameron HU, Welsh RP. Potential complications of total knee replacement following tibial osteotomy. Orthop Rev 1988;17:39–43.
Mann JW 3rd, Insall JN, Scuderi GR. Total knee arthroplasty in patients with associated extra articular angular deformity. Orthop Trans 1997;21:59.
Koenig JH, Maheshwari AV, Ranawat AS, Ranawat CS. Extra articular deformity is always correctable intraarticularly: In the affirmative. Orthopedics 2009;32:676.
Hungerford DS. Extra articular deformity is always correctable intraarticularly: To the contrary. Orthopedics 2009;32.
Ritter MA, Faris GW. Total knee replacement following extra articular deformities. Orthopedics 2003;26:969–70.
Mullaji A, Shetty GM. Computer-assisted total knee arthroplasty for arthritis with extra articular deformity. J Arthroplasty 2009;24:1164–9 e1.
Chou WY, Ko JY, Wang CJ, Wang FS, Wu RW, Wong T. Navigation-assisted total knee arthroplasty for a knee with malunion of the distal femur. J Arthroplasty 2008;23:1239.e13–9.
Kim KI, Ramteke AA, Bae DK. Navigation-assisted minimal invasive total knee arthroplasty in patients with extra articular femoral deformity. J Arthroplasty 2010;25:658.e17–22.
Lim HC, Bae JH, Neogi DS, Wang JH, Seok CW, Kim MK. Rotational alignment of femoral component and flexion gap balance in patients with distal femoral torsional deformity using navigation-assisted TKA. Orthopedics 2009;32:52–5.
Yau WP, Chiu KY, Tang WM, Ng TP. Coronal bowing of the femur and tibia in Chinese: Its incidence and effects on total knee arthroplasty planning. J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2007;15:32–6.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rajgopal, A., Vasdev, A., Dahiya, V. et al. Total knee arthroplasty in extra articular deformities: A series of 36 knees. IJOO 47, 35–39 (2013). https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106893
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5413.106893