Summary
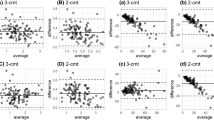
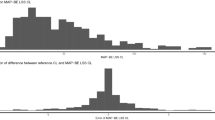
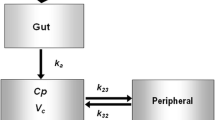
This study describes the methodology used to calculate the individual clearance (CL) and volume of distribution (Vd) of inulin using 1 or 2 blood samples taken during the disposition and elimination phase after a single intravenous perfusion, and the population parameters. The mean population parameters and their interindividual variability were obtained from an initial group of 90 patients including 38.5% who had diabetes, 49% who were obese, and 12.5% who were diabetic and obese. Among these patients, 44.5% had normal renal function (creatinine clearance ranging from 70 to 150 ml/min/1.73m2) and 20% showed renal insufficiency with a creatinine clearance ranging from 15 to 60 ml/min/1.73m2. A 2-compartment model was fitted to the population data using P-PHARM. The population parameter estimates of CL and Vd were 6.85 ± 1.04 L/h and 4.95 ± 0.84L, respectively. The interindividual variability of CL was explained by a linear dependency between serum creatinine and body area. The interindividual variability of Vd was explained by a linear dependency with body area. A test group of 25 additional patients was used to evaluate the predictive performance of the population parameters. Seven blood samples were collected from each individual in order to calculate individual parameter estimates using standard fitting procedures. These values were compared with those estimated by means of a Bayesian approach using population parameters and 1 or 2 samples selected from the individual observations. The results show that the bias of CL and Vd, estimated using either 1 or 2 samples, was not statistically different from zero, and that the precision of these parameters was excellent.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Levey A. Measurement of renal function in chronic renal disease. Kidney Int 1990; 38: 167–84
Bröchner-Mortensen J, Rödbro P. Selection of a routine method for determination of glomerular filtration rate in adult patients. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1976; 36: 35–43
O’Reilly PH, Brooman PJC, Martin PJ, et al. Accuracy and reproducibility of a new contrast clearance method for the determination of glomerular filtration rate. Br Med J 1986; 293: 234–6
Isaka Y, Fujiwara Y, Yamamoto S, et al. Modified plasma clearance technique using non-radioactive iothalamate for measuring GFR. Kidney Int 1992; 42: 1006–11
Boijsen M, Jacobsson L, Tylen U. Glomerular filtration rate estimated from a single plasma sample after contrast-enhanced radiological examinations. Clin Physiol 1988; 8: 309–16
Bianchi C, Donadio C, Tramonti G. Non-invasive methods for the measurement of total renal function. Nephron 1981; 28: 53–7
Prescott LF, Freestone S, McAuslane JAN. Reassessment of the single intravenous injection method with inulin for measurement of the glomerular filtration rate in man. Clin Sci 1991; 80: 167–76
Hall JE, Guyton AC, Far BM. A single-injection method for measuring glomerular filtration rate. Am J Physiol 1977; 232: F72–6
Tepe PG, Tauxe WN, Bagchi A, et al. Comparison of measurement of glomerular filtration rate by single sample, plasma disappearance slope/intercept and other methods. Eur J Nucl Med 1987; 13: 28–31
Astelig K, Hood B, Vikgren P. Beräkning av glomerulus-filtrationen med engans-injektion av inulin. Läkartidningen 1966; 63: 1554–9
Fisher M, Veall N. Glomerular filtration rate based on a single blood sample. BMJ 1975; 2: 542
Mertz DP. Observations on renal clearance and the volume of distribution of polyfructosan-S, a new inulin-like substance. Experientia 1963; 15: 248–9
Heyrovsky A. A new method for the determination of inulin in plasma and urine. Acta Clin Chem 1956; 1: 470–4
P-PHARM user’s guiue. 2nd ed. SIMED, Créteil, France 1994
Gomeni R, Pineau G, Mentré F. Population kinetics and conditional assessement of the optimal dosage regimen using the P-PHARM software package. Anticancer Res 1994; 14: 2321–6
Dempster AP, Laird NM, Rubin DB. Maximum likelihood from incomplete data via the EM algorithm. J Royal Statistical Society 1977; 39: 1–38
Sokal RR, Rohlf JRN. Biometry. San Francisco: W. H. Freeman and Company, 1969
Al-Banna MK, Kelman AW, Whiting B. Experimental design and efficient parameter estimation in population pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1990; 18: 347–60
Endrenyi L. Design of experiments for estimating enzyme and pharmacokinetic experiments. In: Endrenyi L, editor. Kinetic data analysis, design and analysis of enzyme and pharmacokinetic experiments. New York: Plenum Press, 1981: 137–67
Gomeni R. Estimate of the number and of the temporal sequence of measurements in a kinetic experiment. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 1990; 4(2 Suppl.): 117s–23s
Bressolle F, Ray P, Jacquet JM, et al. Bayesian estimation of doxorubicin pharmacokinetic parameters. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 1991; 29: 53–60
Fabre D, Bressolle F, Gomeni R, et al. Identification of patients with impaired hepatic drug metabolism using a limited sampling procedure for estimation of phenazone (antipyrine) pharmacokinetic parameters. Clin Pharmacokinet 1993; 24: 333–43
Westlake WJ. Symmetrical confidence intervals for bioequivalence trials. Biometrics 1976; 32: 741–4
Schuirmann DJ. A comparison of the two one-sided tests procedure and the power approach for assessing the equivalence of average bioavailability. J Pharmacokinet Biopharm 1987; 15: 657–80
Gomeni C, Gomeni R. SIPHAR: An integrated computer system for statistical and pharmacokinetic data analysis. In: Serio A, O’Moore R, Tardini A, et al., editors. Proceedings of the Seventh International Congress of Medical Informatics Europe 87; 1987 Sept 21-25; Rome: European Federation for Medical Informatics, 1987: 507–16
Childs WJ, Nicholls EJ, Horwich A. The optimisation of carboplatin dose in carboplatin, etoposide and bleomycin combination chemotherapy for good prognosis nonseminomatous germ cell tumours of the testis. Ann Oncol 1992; 3: 291–6
Brochner-Mortensen J. Current status on assessment and measurement of glomerular filtration rate. Clin Physiol 1985; 5: 1–17
Groth T, Tengstrom B. A simple method for estimation of glomerular filtration rate. Scan J Clin Lab Invest 1977; 37: 39–47
Beal SL, Sheiner LB. The NONMEM system. Am Statistician 1980; 34: 118–9
Mentré F, Gomeni R. A two-step iterative algorithm for estimation in nonlinear mixed effect models with an evaluation in population pharmacokinetics. J Biopharm Stat 1995; 5: In press
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kinowski, JM., Bressolle, F., Rodier, M. et al. A Limited Sampling Model with Bayesian Estimation to Determine Inulin Pharmacokinetics Using the Population Data Modelling Program P-PHARM. Clinical Drug Investigation 9, 260–269 (1995). https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199509050-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00044011-199509050-00003