Summary
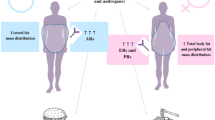
Obesity is common enough to constitute a serious medical and public health problem. Drug prescription for obese patients is difficult since dosages based on pharmacokinetic data obtained in normal-weight individuals could induce errors. In obese patients, physiopathological modifications are likely to affect drug tissue distribution and elimination. Body constitution is characterised by a higher percentage of fat and a lower percentage of lean tissue and water. Although the cardiac output and total blood volume are increased, the blood flow per gram of fat is less than in nonobese individuals. Histological hepatic alterations are commonly reported in morbidly obese individuals. A higher glomerular filtration rate is also observed.
Most of the pharmacokinetic information concerning obesity deals with distribution. Published data concerning molecules with moderate and weak lipophilicity are homogeneous. In obese compared with normal weight individuals, the total volume of distribution (Vd) is moderately increased (aminoglycosides, caffeine) or similar (H2-blockers, neuromuscular blockers), but the Vd corrected by kilogram of actual bodyweight is significantly smaller. These drugs distribute to a limited extent in excess bodyweight.
For highly lipophilic drugs, despite this common characteristic, discrepancies in distribution in obesity exist between drugs belonging to different pharmacological classes. Some drugs show a clear augmentation of Vd and elimination half-life (benzodiazepines, carbamazepine, trazodone, verapamil, sufentanil), indicating a marked distribution into adipose tissue. For others, Vd and Vd/kg are decreased (cyclosporin, propranolol), suggesting that factors others than lipid solubility intervene in tissue distribution.
As a general trend, the total clearance (CL) of drugs metabolised by oxidation, conjugation or reduction, and also of drugs with flow-dependent hepatic clearance, is not diminished in obesity. Usually CL is identical in obese and nonobese individuals, sometimes it is increased in obesity (enflurane, halothane, prednisolone, some benzodiazepines). With some drugs a significant reduction in CL is observed in obese individuals (methylprednisolone, propranolol). Renal clearance of aminoglycosides and cimetidine increases in obese individuals. Practical guidelines for dosage adjustment are proposed. For drugs with distribution restricted to lean tissues, the loading dose should be based on the ideal bodyweight of patients. For drugs markedly distributed into fat tissue the loading dose is based on total bodyweight. Adjustment of the maintenance dose depends on possible changes in CL. In some cases (atracurium, prednisolone) dosage adjustment does not follow these recommendations, owing to pharmacodynamic data.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ. Drug disposition in obese humans: An update. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 11: 199–231, 1986
Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Divoll M, Smith RB, Shader RT. The influence of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of oral alprazolam and triazolam. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 9: 177–183, 1984
Abernethy DR, Greenblatt DJ, Locniskar A, Ochs HR, Harmatz JS, et al. Obesity effects on nitrazepam disposition. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 551–557, 1986
Abernethy DR, Schwartz JB. Verapamil pharmacodynamics and disposition in obese hypertensive patients. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology 11: 209–215, 1988
Abernethy DR, Todd EL, Schwartz JB. Caffeine disposition in obesity. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 20: 61–66, 1985
Andersen T, Gluud C. Liver morphology in morbid obesity: a literature study. International Journal of Obesity 8: 97–106, 1984
Bauer LA, Drew Edwards WA, Patchen Dellinger E, Simonowitz DA. Influence of weight on aminoglycosides pharmacokinetics in normal weight and morbidly obese patients. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 24: 643–647, 1983
Bauer LA, Waring-Tran C, Drew Edwards WA, Raisys V, Ferreri L, et al. Cimetidine clearance in the obese. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 37: 425–430, 1985
Benedeck IH, Blouin A, McNarama PJ. Serum protein binding and the role of increased α1-acid glycoprotein in moderately obese male subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 941–946, 1984
Bentley JB, Vaughan RW, Gandolfi AJ, Cork R-C. Altered halothane metabolism: obese vs. nonobese subjects. Anesthesiology 55: A179, 1981
Bischoff KB, Dedrick RL. Thiopental pharmacokinetics. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 57: 1346–1351, 1968
Braillon A, Capron JP, Herve MA, Degott C, Quenum C. Liver in obesity. Gut 26: 133–139, 1985
Caraco Y, Zylbert-Katz E, Berry EM, Levy M. Obesity does not alter caffeine disposition. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 49: 177, 1991
Caraco Y, Zylber-Katz E, Berry EM, Levy M. Carbamazepine disposition in obesity. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 51: 133, 1992a
Caraco Y, Zylber-Katz E, Berry EM, Levy M. Significant weight reduction in obese subjects enhances carbamazepine elimination. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 51: 501–506, 1992b
Charland SL, Plezia PM, Bloom JW, Kramer K. The use of bioelectrical impedance to predict theophylline pharmacokinetics in obese subjects. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 45: 131, 1987
Cheymol G. Drug pharmacokinetics in the obese. Fundamental and Clinical Pharmacology 2: 239–256, 1988
Cheymol G, Poirier JM, Barre J, Pradalier A, Dry J. Comparative pharmacokinetics of intravenous propranolol in obese and normal volunteers. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 27: 874–879, 1987
Corcoran GB, Salazar DE, Schentag JJ. Excessive aminoglycoside nephrotoxicity in obese patients. American Journal of Medicine 85: 279, 1988
Cox J, Penn N, Masood M, Masood M, Hancock K, Parker D. Drug overdose - a hidden hazard of obesity. Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine 80: 708–709, 1987
Davis RL, Quenzer RW. Ranitidine pharmacokinetics in morbid obesity. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 47: 154, 1990
De Divitis O, Fazio S, Petitto M, Maddalena G, Contaldo F, et al. Obesity and cardiac function. Circulation 64: 477–482, 1981
Dunn TE, Ludwig EA, Slaughter RI, Carara DJ, Jusko WJ. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of methylprednisolone in obesity. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 49: 536–549, 1991
Editorial. New weight standards for men and women. Statistic Bulletin 40: 1–3, 1959
Epstein FH, Higgins M. Epidemiology of obesity. In Bjorntorp & Brodoff (Eds) Obesity, pp. 330–342, Lippincott Company, Philadelphia, 1992
Flechner SM, Kolbeinsson ME, Ta J, Lum B. The impact of body weight on cyclosporine pharmacokinetics in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 47: 806–810, 1989
Forbes GB, Welle SL. Lean body mass in obesity. International Journal of Obesity 7: 99–107, 1983
Gray DS, Bray GA, Bauer M, Kaplan K, Gemayel N, et al. Skin-fold thickness measurements in obese subjects. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 51: 571–577, 1990
Greenblatt DJ, Friedman H, Burstein ES, Scavone JM, Blyden GT, et al. Trazodone kinetics: effect of age gender, and obesity. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 42: 193–200, 1987
Le Jeunne C, Poirier J-M, Cheymol G, Ertzbischoff O, Engel F, et al. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous bisoprolol in obese and non-obese volunteers. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 41: 171–174, 1991
Lesse G, Deutsch S Measurement of adipose tissue blood flow and perfusion in man by uptake of 85 kr. Journal of Applied Physiology 23: 621–632, 1967
Lind MJ, Margison JM, Cerny T, Thatcher N, Wilkinson PM. Prolongation of ifosfamide elimination half-life in obese patients due to altered drug distribution. Cancer Chemotherapy Pharmacology 25: 139–142, 1989
Miller MS, Gandolfi AJ, Vaughan RW, Bentley JB. Disposition of enflurane in obese patients. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 215: 292–296, 1980
Milsap RL, Plaisance KI, Jusko WJ. Prednisolone disposition in obese men. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 36: 824–831, 1984
Poirier JM, Le Jeunne C, Cheymol G, Cohen A, Barre J, et al. Comparison of propranolol and sotalol pharmacokinetics in obese subjects. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 42: 344–348, 1990
Salazar DE, Corcoran GB. Predicting creatinine clearance and renal drug clearance in obese patients from estimated fat-free body mass. American Journal of Medicine 84: 1053–1060, 1988
Salazar DE, Schentag JJ, Corcoran GB. Obesity as a risk factor in drug-induced organ injury: V. Toxicokinetics of gentamycin in the obese overfed rat. Drug Metabolism and Disposition 20: 402–406, 1992
Schwartz AE, Matteo RS, Ornstein E, Halevy JD, Dia J. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of vecuronium in the obese surgical patient. Anesthesia and Analgesia 74: 515–518, 1992
Schwartz AE, Matteo RS, Ornstein E, Young WL, Myers KJ. Pharmacokinetics of sufentanil in obese patients. Anesthesia and Analgesia 73: 790–793, 1991
Stokholm KH, Brochner-Mortensen J, Hoilund-Carlsen PF. Increased glomerular filtration rate and adrenocortical function in obese women. International Journal of Obesity 4: 57–63, 1980
Varin F, Ducharme J, Theoret Y, Besner J-G, Bevan DR, et al. Influence of extreme obesity on the body disposition and neuromuscular blocking effect of atracurium. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 48: 12–25, 1990
Waters MR, Albano JDM, Scharman VL, Venkat Raman G. Pharmacokinetics of cyclosporin in man following a single oral dose: relationship to body fat content. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation 4: 71–74, 1989
Wilkes L, Danziger LH, Rodvold KA. Phenobarbital pharmacokinetics in obesity: A case report. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 22: 481–484, 1992
Yee GC, McGuire TR, Gmur DJ, Lennon TP, Deeg HJ. Blood cyclosporin pharmacokinetics in patients undergoing marrow transplantation influence of age, obesity and hematocrit. Transplantation 43: 399–402, 1988
Zuccaro P, Guandalini S, Pacifici R, Pichini S, Martino LD, et al. Fat body mass and pharmacokinetics of 6-mercaptopurine in children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 13: 37–41, 1991
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheymol, G. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of Drugs in Obesity. Clin-Pharmacokinet 25, 103–114 (1993). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325020-00003
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-199325020-00003