Summary
The use of salicylates in rheumatic diseases has been established for over 100 years. The more recent recognition of their modification of platelet and endothelial cell function has lead to their use in other areas of medicine.
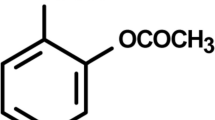
Aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) is still the most commonly used salicylate. After oral administration as an aqueous solution aspirin is rapidly absorbed at the low pH of the stomach millieu. Less rapid absorption is observed with other formulations due to the rate limiting step of tablet disintegration — this latter factor being maximal in alkaline pH. The rate of aspirin absorption is dependent not only on the formulation but also on the rate of gastric emptying.
Aspirin absorption follows first-order kinetics with an absorption half-life ranging from 5 to 16 minutes. Hydrolysis of aspirin to salicylic acid by nonspecific esterases occurs in the liver and, to a lesser extent, the stomach so that only 68% of the dose reaches the systemic circulation as aspirin. Both aspirin and salicylic acid are bound to serum albumin (aspirin being capable of irreversibly acetylating many proteins), and both are distributed in the synovial cavity, central nervous system, and saliva.
The serum half-life of aspirin is approximately 20 minutes. The fall in aspirin concentration is associated with a rapid rise in salicylic acid concentration. Salicylic acid is renally excreted in part unchanged and the rate of elimination is influenced by urinary pH, the presence of organic acids, and the urinary flow rate. Metabolism of salicylic acid occurs through glucuronide formation (to produce salicyl acyt glucuronide and salicyl phenolic glucuronide), conjugation with glycine (to produce salicyluric acid), and oxidation to gentisic acid. The rate of formation of salicyl phenolic glucuronide and salicyluric acid are easily saturated at low salicylic acid concentrations and their formation is described by Michaelis-Menten kinetics. The other metabolic products follow first-order kinetics. The serum half-life of salicylic acid is dose-dependent; thus, the larger the dose employed, the longer it will take to reach steady-state. There is also evidence that enzyme induction of salicyluric acid formation occurs.
No significant differences exist between the pharmacokinetics of the salicylates in the elderly or in children when compared with young adults. Apart from differences in free versus albumin-bound salicylate in various disease states and physiological conditions associated with low serum albumin, pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, chronic renal failure or liver disease are essentially the same. Pharmacokinetic interactions with various non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs do occur, but the clinical relevance of these is uncertain. Clinically important interactions may occur with heparin or oral anticoagulants, but these are due mainly to an effect on platelet function rather than on pharmacokinetic parameters.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali, M.A. and Routh, J.I.: Protein binding of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid. Clinical Chemistry 75: 1027–1038 (1969).
Anderson, J.: Disorders of metabolism; in Davies (Ed.) Textbook of Adverse Drug Reactions, pp.217–227 (Oxford University Press, London 1977).
Boardman, P.L. and Hart, F.D.: Clinical measurements of the anti-inflammatory effects of salicylates in rheumatoid arthritis. British Medical Journal 4: 264–268 (1967).
Bochner, F.; Graham, G.G.; Cham, B.E.; Imhoff, D.M. and Haavisto, T.M.: Salicylate metabolite kinetics after several salicylates. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 30: 266–275 (1981).
Boreham, D.R. and Martin, B.K.: The kinetics of elimination of salicylic acid and formation of gentisic acid. British Journal of Pharmacology 37: 294–297 (1969).
Borgå, O.; Odar-Cederlöf, I.; Ringberger, V. and Norlin, A.: Protein binding of salicylate in uremic and normal plasma. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 20: 464–475 (1976).
Brantmark, B.; Wahlin-Boll, E. and Melander, A.: Bioavailability of acetysalicylic acid and salicylic acid from rapid and slow release formulations, and in combination with dipyridamole. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 22: 309–314 (1982).
Brodie, B.B. Hurz, H. and Schanker, L.S.: The importance of dissolution constant and lipid solubility in influencing the passage of drugs into cercbrospinal fluid. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 130: 2025 (1960).
Brooks, P.M. and Khong, T.K.: Flurbiprofen-aspirin interactions: A double blind cross over study. Current Medical Research and Opinion 5: 53–57 (1977).
Brooks, P.M.; Roberts, M.S. and Patel, P.: Pharmacokinetics of sustained release aspirin. British Journal of Pharmacology 5: 337–339 (1978).
Brooks, P.M.; Walker, J.J.; Bell, M.A.; Buchanan, W.W. and Rhymer, A.R.: Indomethacin-aspirin interaction. A clinical appraisal. British Medical Journal 3: 69–71 (1975).
Buchanan. W.W.; Rooney, P.J. and Rennie. J.A.: Aspirin and the salicylates. Clinics in Rheumatic Diseases 5: 499–540 (1979).
Burch. J.W.; Shanford. N. and Majerus, P.W.: Inhibition of platelet prostaglandin synthesis by oral aspirin. Journal of Clinical Investigation 61: 314–319 (1978).
Calabro, J.T.; Burnstein, S.L. and Staley, H.L.: Correspondence Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 5: 251–252 (1976).
Canadian Co-operative Study Group: A randomised trial of aspirin and sulphinpyrazone in threatened stroke. New England Journal of Medicine 299: 53–59 (1978).
Castleden, C.M.; Volans, C.N. and Raymond, K.: The effect of aging on drug absorption from the gut. Age and Aging 6: 138–143 (1977).
Cham, B.E.; Bochner, F.; Imhoff. D.M.; Byrne, G. and Gunsberg, M.: In vitro and in vitro studies on the binding of salicylate to human plasma proteins. Evidence for one type of binding site. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 220: 648–653 (1982).
Cham, B.E.; Ross-Lee, L.; Bochner, F. and Imhoff, D.: Measurement of and pharmacokinetics of acetysalicylic acid by a novel high performance liquid chromatography assay. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 2: 365–372 (1980).
Chen, C.N.; Coleman, D.L.; Andrade, J.D. and Temple, A.R.: Pharmacokinetic model for salicylate in cerebrospinal fluid. Blood, organs and tissues. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 67: 38–45 (1978).
Cuny, G.; Royer, R.T.; Mur, J.M. et al.: Pharmacokinetics of salicylates in the elderly. Gerontology 25: 41–55 (1979).
Davison, C.: Salicylate metabolism in man. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 179: 249–268 (1971).
Dawson, I. and Pryse-Davies, J.: The distribution of certain enzyme systems in the normal human gastrointestinal tract. Gastroenterology 44: 745–760 (1963).
Day, R.O.; Dromgoole, S.H.: Furst, D.E.; Hignite, C. and Paulus, H.E.: Formation of methyl ester of salicyluric acid during quantitation of salicyluric acid in urine by high pressure liquid chromalography. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 70: 1090–1092 (1981).
Day, R.O.; Graham, G.G.; Reeve, R.; Smith, J.; Bieri. D.; Hounsell, J.: Hepworth, S. and Champion, G.D.: Relationship between unbound salicylate concentration and ototoxicity (Abstract 165). Australasian Society of Clinical and Experimental Pharmacologists Annual Meeting (1983b).
Day, R.O.; Pauli, P.D.; Champion, G.D. and Graham, G.G.: Evaluation of an enteric coated aspirin preparation. Australian and New Zealand Journal of Medicine 6: 45–50 (1976).
Day, R.O.; Shen, D.D. and Azamoff, D.L.: Induction of salicyluric acid formation in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with salicylates. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 8: 263–271 (1983a).
Done, A.K.: Salicylate pharmacokinetics and the pediatrician. Pediatrics 54: 670–672 (1974).
Dotevall, G. and Ekenved, G.: The absorption of acetylsalicylic acid from the stomach in relation to intragastric pH. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology 11: 801–805 (1976).
Findlay, J.W.; DcAngelis, R.L. Kearney, M.F.; Welch, R.M. and Findlay, J.M.: Analgesic drugs in breast milk and plasma. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 29: 625–633 (1981).
Furst, D.E.; Tozer, T.N. and Melmon, K.L.: Salicylate clearance, the resultant of protein binding and metabolism. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 26: 380–389 (1977).
Garretlson, K.K. Procknall, J.A. and Levy, G.: Fetal aquisition and neonatal elimination of a large amounl of salicylate. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 17: 98–103 (1975).
Genton, E.: Effect of acetylsalicylic acid in conditions associated with platelet aggregation or thrombosis in the systemic circulation: in Barnett et al. (Eds) Acetysalicylic Acid: New Uses for an Old Drug, pp.215–224 (Raven Press, New York 1982).
Gibaldi, M.: In Biopharmaccutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics. pp. 125–130 (Lea & Febiger, Philadelphia 1977).
Gibaldi, M.; Grundhofer, B. and Levy, G.: Effects of antacids on pH or urine. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 16: 520–525 (1974).
Goldberg, M.A.; Banlow, CF. and Roth, L.J.: The effects of carbon dioxide on the entry and accumulation of drugs in the central nervous system. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 131: 308–318 (1961).
Graham, G.G.; Champion, G.D.; Day, R.O. and Pauli, P.D.: Patterns of plasma concentrations and urinary excretion of salicylate in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 22: 410–420 (1977).
Graham, G.G. and Rowland, M.: Application of salivary salicylate data to biopharmaceutical studies of salicylates. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 1219–1222 (1972).
Grcnnan, D.R.; Ferry, D.G.; Ashworth, M.E.; Kenny, R.E. and MacKinnon, M.: The aspirin-ibuprofen interaction in rheumatoid arthritis. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 8: 497–503 (1979).
Gross, M. and Greenberg, L.A.: The Salicylates. A Critical Bibliographic Review (Hillhouse Press, New Haven 1948).
Gupta, J.P. and Gupta, V.: Serum aspirin esterase activity in women with habitual aspirin ingestion. Clinica Chimica Acta 81: 261–265 (1977).
Hansten, P.D.: Drug Interaclions. pp. 185–189 (Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia 1975).
Hansten, P.D. and Hayton, W.L.: Effect of antacid and ascorbic acid on scrum salicylate concentrations. Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 20: 326–331 (1980).
Harris, P.A. and Riegelman, S.: Acelylsalicylic acid hydrolysis in human blood and plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 56: 713–716 (1967).
Hawkins, D.; Pinckard, R.N. and Farr, R.S.: Acetylalion of human scrum albumin by acetylsalicylic acid. Science 160: 780–781 (1968).
Hogden, C.A.; Schanker, L.S.; Tocco, D.J. and Brodie, B.B.: Absorption of drugs from the stomach in the human. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 120: 540–545 (1957).
Hogden, C.A.M.; Tocco, D.J.; Brodie, B.B. et al.: On the mechanism of intestinal absorption of drugs. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 125: 275–281 (1959).
Jeremy, R. and Towson, J.: Interaction of aspirin and indomethacin in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Medical Journal of Australia 2: 127–129 (1970).
Lasagna, I.: Analecsic drugs. American Journal of Medical Sciences 242: 620–627 (1961).
Leonard, R.F. Knott, P.J.; Rankin, G.O.: Robinson, D.S. and Melnick, D.E.: Phenytoin-salicylatc interaction. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 29: 56–60 (1981).
Leonards, J.R.: Presence of acelylsalicylic acid in plasma following oral ingestion of aspirin. Proceedings of the Society for Experimental Biology and Medicine 110: 304–307 (1962).
Leonards, J.R.: The influence of solubility on the rate of gastrointestinal absorption of aspirin. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 4: 476–479 (1963).
Leonards, J.R. and Levy, G.: Absorption and metabolism of aspirin administered in enteric coated tablets. Journal of the American Medical Association 193: 93–98 (1965).
Levy, G.: Pharmacokinetics of salicylate elimination in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 54: 959–967 (1965).
Levy, G.: Drug biotransformation interactions in man. Non narcotic analgesics. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 71: 32–42 (1971).
Levy, G.: Clinical pharmacokinetics of aspirin. Pediatrics 62 (Suppl.): 867–872 (1978).
Levy, G.: Pharmacokinetics of salicylate in man. Drug Metabolism Reviews 9: 3–19 (1979).
Levy, G.: Clinical pharmacokinetics of salicylates: An assessment. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 10: 285S–290S (1981).
Levy, G. and Amsel, L.P.: Kinetics of competitive inhibition of salicylic acid conjugation with glycine in man. Biochemical Pharmacology 15: 1033–1038 (1966).
Levy, G. and Garrettson, L.K.: Kinetics of salicylate elimination by newborn infants of mothers who ingested aspirin before delivery. Pediatrics 53: 201 (1973).
Levy, G. and Giacomini, K.M.: Rational aspirin dosage regimens. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 23: 247–252 (1978).
Levy, G. and Hayes, B.A.: Physiochemical basis of the buffered acetylsalicylic acid controversy. New England Journal of Medicine 262: 1053 (1960).
Levy, G. and Hollister, L.E.: Dissolution rate limited absorption in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 54: 1121–1125 (1965).
Levy, G. and Leonards, J.R.: Absorption, metabolism and excretion of salicylates; in Smith and Smith (Eds) The Salicylates: A Critical Bibliographic Review, pp.5–48 (Inter Science Publishers, New York 1966).
Levy, G. and Leonards, J.R.: Urine pH and salicylate therapy. Journal of the American Medical Association 217: 81 (1971).
Levy, G. and Procknall, J.A.: Drug biotransformation interactions in man. I. Mutual inhibition in glucuronide formation of salicylic acid and salicylamide in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 57: 1330–1335 (1968).
Levy, G.; Procknall, J.A. and Garrettson, L.K.: Distribution of salicylate between neonatal and maternal serum at diffusion equilibrium. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 18: 210–214 (1975).
Levy, G.; Procknall, J.A.; Olufs, R. and Pachman, L.M.: Relationship between saliva salicylate concentration and free or total salicylate concentration in serum of children with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 27: 619–627 (1980).
Levy, G. and Sahli, B.A.: Comparison of the gastrointestinal absorption of aluminium acetylsalicylate and acetylsalicylate acid in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 58 (1962).
Levy, G. and Tsuchiya, T.: Salicylate accumulation kinetics in man. New England Journal of Medicine 287: 430–432 (1972).
Levy, G.; Tsuchiya, T. and Amsel, L.P.: Limited capacity of salicylphenolic glucuronide formation and its effects on the kinetics of salicylate elimination in man. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 13: 258–268 (1972).
Levy, G. and Yaffe, S.J.: Relationship between dose and apparent volume of distribution of salicylate in children. Pediatrics 54 713–717 (1974).
Liegler, D.G.; Henderson, E.S.; Hahn, M.A. and Oliverio, V.T.: The effect of organic acids on renal clearance of methotrexate in man. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 10: 849–857 (1969).
Lim, R.K.: Salicylate analgesia; in Smith and Smith (Eds) The Salicylates, p.155 (Inter Science Publishers, New York 1966).
Lorenzo, A.V. and Spector, R.: Transport of salicylic acid by the choroid plexus in vitro. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 184: 465–471 (1973).
Lowenthal, D.T.; Briggs, W.A. and Levy, G.: Kinetics of salicylate elimination by anephric patients. Journal of Clinical Investigation 54: 1221–1226 (1974).
McArthur, J.N.; Dawkins, P.D. and Smith, M.J.: The binding of indomethacin, salicylate and phenobarbitone to human whole blood in vitro. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 23: 32–36 (1971).
Mandel, M. A.: Synergistic effects of salicylic acid on methotrexate. Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery 57: 733–737 (1976).
Markiewicz, A. and Semenowiczk, A.: Time dependent changes in the pharmacokinetics of aspirin. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacology and Biopharmacy 17: 409–411 (1979).
Martin, B.K.: The formulation of aspirin; in Bean et al. (Eds) Advances in Pharmaceutical Sciences, vol. 3, pp. 107–171 (Academic Press, London 1971).
Mason, W.D. and Winer, N.: Kinetics of aspirin, salicylic acid and salicyluric acid following oral administration of aspirin as a tablet and two buffered solutions. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 70: 262–265 (1981).
Menguy, R.; Desbaillets, L.; Masters, Y.F. and Okabe, S.: Evidence for sex linked difference in aspirin metabolism. Nature 239: 102–103 (1972).
Milne, M.D.: The excretion of salicylate and its metabolites; in Dixon et al. (Eds). Salicylates: An International Symposium, pp.18–27 (J. & A. Churchill, London 1963).
Moncada, S. and Vane, J.R.: Pharmacology and endogenous roles of prostaglandin endoperoxides, thromboxane A2 and prostacyclin. Pharmacological Reviews 30: 293–331 (1979).
Mongan, E.; Kelly, P.; Nies, K.; Porter, W.W. and Paulus, H.E.: Tinnitus as an indication of therapeutic serum salicylate levels. Journal of the American Medical Association 226: 142–145 (1973).
Morgan, A.M. and Truitt, E.B.: Evaluation of acetysalicylic acid esterase in aspirin metabolism. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 54: 1640–1646 (1965).
Muller, F.O.; Hundt, H.K. and Dekock, A.C.: Decreased steady-state salicylic acid plasma levels associated with chronic aspirin ingestion. Current Medical Research and Opinion 3: 417–422 (1975).
Multz, C.V.; Bernhard, G.C.; Blechman, W.C.; Zane, S.; Restifo, R.A. and Varady, J.C.: A comparison of intermediate dose aspirin and placebo in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 15: 310–315 (1974).
Mustard, J.F.: The use of acetylsalicylic acid in the management of coronary artery disease; in Barnett et al. (Eds) Acetylsalicylic Acid: New Uses for an Old Drug, pp. 195–206 (Raven Press, New York 1982).
Orme, M.L’E.: Plasma concentrations and therapeutic effect of anti-inflammatory and antirheumatic drugs. Pharmacology and Therapeutics 16: 167–180 (1982).
Oyer, J.H.: Suppression of salicylate induced uricosurea by phenylbutazone. American Journal of Medical Sciences 251: 1 (1960).
Parrott, E.L.: Salicylate absorption from rectal suppositories. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 60: 867–872 (1971).
Pascale, L.R.: Inhibition of the uricosuric action of Benemid by salicylate. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine 45: 771 (1955).
Patrono, C.; Ciabuttoni, G.; Pugliese, F.; Pinca, E.; Castrucci, G.; De Salvo, A.; Satta, M.A. and Parachini, M.: Inhibition of platelet cyclo-oxygenase by aspirin like drugs: Methods for in vitro and in vim assessment. Agents and Actions (Suppl. 4): 138–144 (1979).
Pauli, P.; Day, R.; Graham, G. and Champion, D.: Single-dose evaluation of new enteric-coated aspirin preparation. Medical Journal of Australia 1: 617–619 (1976).
Paulus, H.E.; Siegel, M.; Mongan, E.; Okun, R. and Calabro, J.J.: Variations of scrum concentrations and half life of salicylate inpalienls with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 14: 527–532 (1971).
Peng, G.W.; Gadalla. M.A.; Smith. V.; Peng, A. and Chiou. W.L.: Simple and rapid high pressure liquid Chromatographie simultaneous determination of aspirin, salicylic acid and salicyluric acid in plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 67: 710–712 (1978).
Pinckard, R.N.; Hawkins, D. and Farr, R.S.: In vitro acetylation of plasma proteins, enzymes and DNA by aspirin. Nature 219: 68–69 (1968).
Prescott, L.F.: Pharmacokinctic drug interactions. Lancet 2: 1239–1243 (1969).
Rainsford, K.D.; Ford, N.L.V.; Brooks, P.M. and Watson, H.M.: Plasma aspirin esterases in normal individuals, patients with alcoholic liver disease and rheumatoid arthritis. Characterisation and the importance of enzymatic components. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 10: 413–420 (1980).
Rainsford, K.D.; Schweitzer, A. and Brune, K.: Distribution of acetyl compared to salicyl moiety of acetylsalicylic acid. Biochemical Pharmacology 32: 1307–1308 (1983).
Rciss, W.; Steirlin, H.; Degan, P.H.; Faigle, J.W.; Gérardin, A.; Moppert, J. Sallmann, A.: Schmid, K.; Schweizer, A.; Sule, M.; Theobald, W. and Wagner, J.: Pharmacokinetics and metabolism of the anti-inflammatory agent Voltaren. Scandinavian Journal of Rheumatology 22 (Suppl.): 17 (1978).
Reynolds, R.C. and Cluff, L.: Interaction of serum and sodium salicylate: Changes during acute infection and its influence on pharmacological activity. John Hopkins Hospital Bulletin 107: 278–290 (1960).
Roberts, M.S.; Rumble, R.H. and Brooks, P.M.: Salivary salicylate secretion and flow rate. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 6: 429 (1978).
Roberts, M.; Rumble, R.H.; Wanwimolruk, S.; Thomas, D. and Brooks; P.M.: Pharmacokinetics of aspirin and salicylate in elderly subjects and in patients with alcoholic liver disease. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 25: 253–261 (1983).
Rosenthal, R.K.; Bayles, T.B. and Fremont-Smith, K.: Simultaneous salicylate concentrations in synovial fluid and plasma in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis and Rheumatism 7: 103–109 (1964).
Ross-Lee, L.M.; Elms, M.J.; Cham, B.E.; Bochner, F.; Bunce, I.H. and Eadie, M.J.: Plasma levels of aspirin following effervescent and enteric coated tablets, and their effect on platelet function. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 23: 545–557 (1982).
Ross-Lee, L.M.; Eadie, M.J.; Heazlewood, V.; Bochner, F. and Tyrer, J.H.: Aspirin pharmacokinetics in migraine. The effect of mctroclopramide. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 24: 777–785 (1983).
Roth, G.J. and Chester, J.S.: Acelylation of the NH2-terminal serine of prostaglandin synlhetasc by aspirin. Journal of Biological Chemistry 253: 3782–3784 (1978).
Rowland, M. and Riegelman, S.: Determination of acetylsalicylic acid in plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 56: 717–720 (1967).
Rowland, M. and Riegelman, S.: Pharmacokinetics of acetylsalicylic acid and salicylic acid after intravenous administration in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 57: 1313–1319 (1968).
Rowland, M.; Riegelman, S.; Harris, P.A. and Sholkoff, S.D.: Absorption kinetics of aspirin in man following oral administration of an aqueous solution. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 379–385 (1972).
Rubin, A.; Rodda, B.E.; Warrick, P.; Gruber, Jr., C.M. and Ridolfo, A.S.: Interactions of aspirin with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in man. Arthritis and Rheumatism 16: 635–645 (1973).
Rumble, R.H.: Brooks, P.M. and Roberts, M.S.: Metabolism of salicylate during chronic aspirin therapy. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 9: 41–45 (1980).
Rumble, R.H.; Roberts, M.S. and Wanwimolruk, S.: Determination of aspirin and its major metabolites by high performance liquid chromalography with solvent extraction. Journal of Chromalography 225: 252–260 (1981).
Salem, S.A. and Stevenson, I.H.: Absorption kinetics of aspirin and quinine in elderly subjects. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 4: 397P (1977).
Schachler, D. and Manis, J.: Salicylate and salicyl conjugates: Flurometric estimation, biosynthesis and renal excretion in man. Journal of Clinical Investigation 37: 800–807 (1958).
Schanker, L.S.; Tocco, D.J.; Brodie, B.B. and Hogben, C.A.: Absorption of drugs from the rat small intestine. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 123: 81–88 (1958).
Schultz, P.; Perrier, C.V.; Ferber-Perrel, F.; Vanden Heuvel, W.J.A. and Steelman, S.L.: Diflunisal, a new acting analgesic and prostaglandin inhibition. Effect of concomitant acetylsalicylic acid therapy on ototoxicity and disposition of both drugs. Journal of International Medical Research 7: 61 (1976).
Serge, E.J.; Chaplin, M.; Forchielli, E.; Runkel, R. and Sevelius. H.: Naproxen-aspirin interactions in man. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 15: 374 (1974).
Siebert, D.J.; Bochner, F.; Imhoff, D.M.; Watts, S.; Lloyd, J.V.; Field, J. and Gabb, B.W.: Aspirin kinetics and platelets aggregation in man. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 33: 367–374 (1983).
Smith, J.B. and Willis, A.L.: Aspirin selectively inhibits prostaglandin production in human platelets. Nature 231: 235–237 (1971).
Smith, P.K.; Gleason, H.L. Stall, C.G. and Ogorzalck, S.: Studies on the pharmacology of salicylates. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 87: 237–255 (1946).
Smyth, C.J. and Bravo, J.F.: Antirheumatic drugs: Clinical, pharmacological and therapeutic aspects. Drugs 10: 394–425 (1975).
Soren, A.: Kinetics of salicylatcs in blood and joint fluid. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 16: 279–285 (1979).
Spector. R. and Lorenzo. A.U.: Transport and metabolism of salicylate in the CNS, in vivo studies. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 185: 276–286 (1973).
Taylor, J.R. and Halprin, K.M.: Effects of sodium salicylate and indomethacin on methotrexate-serum albumin binding. Archives of Dermatology 113: 588–591 (1977).
Thiessen, J.J.: Pharmacokinetics of salicylalcs; in Barnett et al. (Eds) Acetylsalicylic Acid: New Uses for an Old Drug, pp.49–61 (Raven Press, New York 1982).
Trinder, P.: Rapid determination of salicylatc in biological fluids. Biochemical Journal 57: 301–303 (1954).
Trnavska, Z. and Trnavska, K.: Characterisation of salicylate binding to synovial fluid and plasma protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 403–406 (1980).
Tsuchiya, T. and Levy, G.: Relationship between dose and plateau levels of drugs eliminated by parallel first order and capacity limited kinetics. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 541–544 (1972a).
Tsuchiya, T. and Levy, G.: Biotransformalion of salicylic acid and its acyl and phenolic giucuronides in man. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 61: 800–801 (1972b).
Tu, T.F.: Mutual suppression of the uricosuric effects of sulphinpyrazone and salicylate. A study in interactions between drugs. Journal of Clinical Investigation 42: 1330 (1963).
Vane, J.R.: Inhibition of prostaglandin-synthesis as a mechanism of action for aspirin-like drugs. Nature 231: 232–235 (1971).
Vesell, E.S.: Relationship between drug distribution and therapeutic effects in man. Annual Review of Pharmacology 14: 249–270 (1974).
Vivian, A.S. and Goldberg, I.B.: Recognising chronic salicylate intoxication in the elderly. Geriatrics 37: 91–97 (1982).
Volans, G.N.: Effects of food and exercise on the absorption of effervescent aspirin. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 1: 137–141 (1974).
Waller, L.J. Biggs, D.F. and Coutts, R.T.: Simultaneous GLC estimation of salicylic acid and aspirin in plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 63: 1754–1758 (1974).
Wanwimolruk, S.: Birkelt, D.J. and Brooks. P.M.: Protein binding of some non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Clinical Pharmacokinetics 7: 85–92 (1982).
Wanwimolruk, S.; Brooks, P.M. and Birkett, D.J.: Binding of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in plasma and synovial fluid of arthritis patients. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 15: 91–94 (1983).
Williams, R.L.; Upton, R.A.; Buskin, J.N. and Jones, R.M.: Ketoprofen-aspirin interactions. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 30: 226–231 (1981).
Willis, J.V.; Kendall, M.J. and Jack, D.B.: A study on the effect of aspirin on the pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous dielofenac sodium. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 18: 415 (1980).
Wilson, J.T.; Brown, R.D.; Bocchini, J.A. and Kearns, G.L.: Efficacy, disposition and pharmacodynamics of aspirin, acetaminophen and choline salicylatc in young febrile children. Therapeutic Drug Monitoring 4: 147–180 (1982).
Wilson, J.T.; Howell, R.L.; Holladay, M.W.; Brillis, G.M.; Chrastil, J.; Watson, J.T. and Taber, D.F.: Gentisuric acid: Metabolic formation in animals and identification as a metabolite of aspirin in man. Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics 23: 635–643 (1978).
Windorfer, A.; Kuenzer, W. and Urbanck, R.: The influence of age on the activity of acetylsalicylic acid estcrase and protein salicyle binding. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 7: 227–231 (1974).
Wolff, F.: Berg, R.; Bolte, A. and Putter, J.: Perinatal pharmacokinetics of acetylsalicylic acid. Archives of Gynccology 233: 15–22 (1982).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Needs, C.J., Brooks, P.M. Clinical Pharmacokinetics of the Salicylates. Clin Pharmacokinet 10, 164–177 (1985). https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198510020-00004
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2165/00003088-198510020-00004