Abstract
Background and Objectives
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a growing public health problem with an urgent need for new pharmacological agents. Cordyceps cicadae is widely used in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and has potential renoprotective benefits. The current study aimed to determine any scientific evidence to support its clinical use.
Methods
We analyzed the potential of two kinds of C. cicadae extract, total extract (TE) and acetic ether extract (AE), in treating kidney disease simulated by a subtotal nephrectomy (SNx) model. Sprague-Dawley rats were divided randomly into seven groups: sham-operated group, vehicle-treated SNx, Cozaar, 2 g/(kg·d) TE SNx, 1 g/(kg·d) TE SNx, 92 mg/(kg·d) AE SNx, and 46 mg/(kg·d) AE SNx. Renal injury was monitored using urine and serum analyses, and hematoxylin and eosin (HE) and periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) stainings were used to analyze the level of fibrosis. The expression of type IV collagen (Col IV), fibronectin (FN), transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1), and connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) was detected by immunohistochemistry.
Results
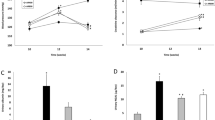
Renal injury, reflected in urine and serum analyses, and pathological changes induced by SNx were attenuated by TE and AE intervention. The depositions of Col IV and FN were also decreased by the treatments and were accompanied by reduced expression of TGF-β1 and CTGF. In some respects, 2 g/(kg·d) of TE produced better effects than Cozaar.
Conclusions
For the first time, we have shown that C. cicadae may inhibit renal fibrosis in vivo through the TGF-β1/CTGF pathway. Therefore, we conclude that the use of C. cicadae could provide a rational strategy for combating renal fibrosis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chen, X.M., Qi, W., Pollock, C.A., 2009. CTGF and chronic kidney fibrosis. Front. Biosci. (Schol. Ed.), 1(1):132–141. [doi:10.2741/e13]
Fan, J.M., Ng, Y.Y., Hill, P.A., Nikolic-Paterson, D.J., Mu, W., Atkins, R.C., Lan, H.Y., 1999. Transforming growth factor-β regulates tubular epithelial-myofibroblast transdifferentiation in vitro. Kidney Int., 56(4):1455–1467. [doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.1999.00656.x]
Gadola, L., Noboa, O., Marquez, M.N., Rodriguez, M.J., Nin, N., Boggia, J., Ferreiro, A., Garcia, S., Ortega, V., Musto, M.L., et al., 2004. Calcium citrate ameliorates the progression of chronic renal injury. Kidney Int., 65(4): 1224–1230. [doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00496.x]
Jin, Z.H., Chen, Y.P., 2006. Clinical observation on Cordyceps cicadae Shing Tang in preventing the progression of chronic renal failure. Chin. Arch. Tradit. Chin. Med., 24(8):1457–1459 (in Chinese).
Jin, Z.H., Chen, Y.P., Deng, Y.Y., 2005. The mechanism study of Cordyceps sobolifera mycelium preventing the progression of glomerulosclerosis. Chin. J. Integr. Tradit. West. Nephrol., 6(3):132–136 (in Chinese).
Kliem, V., Johnson, R.J., Alpers, C.E., Yoshimura, A., Couser, W.G., Koch, K.M., Floege, J., 1996. Mechanisms involved in the pathogenesis of tubulointerstitial fibrosis in 5/6-nephrectomized rats. Kidney Int., 49(3):666–678. [doi:10.1038/ki.1996.95]
Kuo, Y.C., Lin, C.Y., Tsai, W.J., Wu, C.L., Chen, C.F., Shiao, M.S., 1994. Growth inhibitors against tumor cells in Cordyceps sinensis other than cordycepin and polysaccharides. Cancer Invest., 12(6):611–615. [doi:10.3109/07357909409023046]
Kuo, Y.C., Tsai, W.J., Shiao, M.S., Chen, C.F., Lin, C.Y., 1996. Cordyceps sinensis as an immunomodulatory agent. Am. J. Chin. Med., 24(2):111–125. [doi:10.1142/S0192415X96000165]
Kuo, Y.C., Tsai, W.J., Wang, J.Y., Chang, S.C., Lin, C.Y., Shiao, M.S., 2001. Regulation of bronchoalveolar lavage fluids cell function by the immunomodulatory agents from Cordyceps sinensis. Life Sci., 68(9):1067–1082. [doi:10.1016/S0024-3205(00)01011-0]
Kuo, Y.C., Lin, L.C., Don, M.J., Liao, H.F., Tsai, Y.P., Lee, G.H., Chou, C.J., 2002. Cyclodesipeptide and dioxomorpholine derivatives isolated from the insect-body portion of the fungus Cordyceps cicadae. J. Chin. Med., 13(4):209–219.
Kuo, Y.C., Weng, S.C., Chou, C.J., Chang, T.T., Tsai, W.J., 2003. Activation and proliferation signals in primary human T lymphocytes inhibited by ergosterol peroxide isolated from Cordyceps cicadae. Br. J. Pharmacol., 140(5):895–906. [doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0705500]
Liu, Y., 2006. Renal fibrosis: new insights into the pathogenesis and therapeutics. Kidney Int., 69(2):213–217. [doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5000054]
Paterson, R.R., 2008. Cordyceps: a traditional Chinese medicine and another fungal therapeutic biofactory?. Phytochemistry, 69(7):1469–1495. [doi:10.1016/j.phytochem.2008.01.027]
Phanish, M.K., Winn, S.K., Dockrell, M.E., 2010. Connective tissue growth factor-(CTGF, CCN2)—a marker, mediator and therapeutic target for renal fibrosis. Nephron. Exp. Nephrol., 114(3):e83–e92. [doi:10.1159/000262316]
Qi, W., Chen, X., Poronnik, P., Pollock, C.A., 2008. Transforming growth factor-β/connective tissue growth factor axis in the kidney. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol., 40(1):9–13. [doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2007.01.006]
Shweke, N., Boulos, N., Jouanneau, C., Vandermeersch, S., Melino, G., Dussaule, J.C., Chatziantoniou, C., Ronco, P., Boffa, J.J., 2008. Tissue transglutaminase contributes to interstitial renal fibrosis by favoring accumulation of fibrillar collagen through TGF-β activation and cell infiltration. Am. J. Pathol., 173(3):631–642. [doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.080025]
Trivedi, H.S., Pang, M.M., Campbell, A., Saab, P., 2002. Slowing the progression of chronic renal failure: economic benefits and patients’ perspectives. Am. J. Kidney Dis., 39(4):721–729. [doi:10.1053/ajkd.2002.31990]
Wang, L., Chen, Y., 2006. Effect of artificial Cordyceps cicadae on proliferation and mesangial matrix production in human glomcrulus mesangial cell. Tradit. Chin. Med. Res., 19:9–11 (in Chinese).
Wang, Q., Liu, Z., 2004. Advances in studies on medicinal fungi Cordyceps cicadae. Chin. Tradit. Herbal Drugs, 35:469–471 (in Chinese).
Wojcikowski, K., Johnson, D.W., Gobe, G., 2004. Medicinal herbal extracts—renal friend or foe? Part Two: herbal extracts with potential renal benefits. Nephrology, 9(6): 400–405. [doi:10.1111/j.1440-1797.2004.00355.x]
Wojcikowski, K., Johnson, D.W., Gobe, G., 2006. Herbs or natural substances as complementary therapies for chronic kidney disease: ideas for future studies. J. Lab. Clin. Med., 147(4):160–166. [doi:10.1016/j.lab.2005.11.011]
Wu, Q.L., Liang, X.C., 2007. Survey of current experimental studies of effects of traditional Chinese compound recipe on diabetic peripheral neuropathy. China J. Chin. Mater. Med., 32(9):775–778.
Zhou, X., Gong, Z., Su, Y., Lin, J., Tang, K., 2009. Cordyceps fungi: natural products, pharmacological functions and developmental products. J. Pharm. Pharmacol., 61(3): 279–291. [doi:10.1211/jpp.61.03.0002]
Zuo, C., Xie, X.S., Qiu, H.Y., Deng, Y., Zhu, D., Fan, J.M., 2009. Astragalus mongholicus ameliorates renal fibrosis by modulating HGF and TGF-β in rats with unilateral ureteral obstruction. J. Zhejiang Univ.-Sci. B, 10(5): 380–390. [doi:10.1631/jzus.B0820230]
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Project supported by the Program of Shanghai Municipal Education Commission (No. 09jw25), the Xinglin Group Grant from the Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, and the Innovation Team of the College of the Shanghai Municipal Education Commission, China
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, R., Chen, Yp., Deng, Yy. et al. Cordyceps cicadae extracts ameliorate renal malfunction in a remnant kidney model. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 12, 1024–1033 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100034
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100034