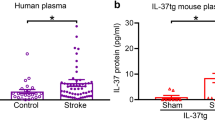
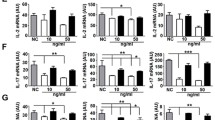
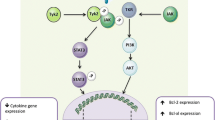
Abstract
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) has been implicated in neuroimmune responses and has pleiotropic actions in the brain. Compelling evidence has shown that IL-1 is a major mediator of inflammation and the progression of cell death in response to brain injury and cerebral ischemia. Its expression is strongly increased in these pathological conditions, and central administration of exogenous IL-1 significantly exacerbates ischemic brain damage. In contrast, inhibiting IL-1 actions (by intracerebroventricular [icv] injection of IL-1ra, neutralizing antibody to IL-1 or caspase-1 inhibitor) significantly reduces ischemic brain damage. IL-1 acts by binding to the IL-1 type-1 receptor (IL-1RI), which is to date, the only known functional receptor for IL-1. However, our recent investigations suggest that IL-1 can act independently of IL-1RI, raising the possibility that additional, as yet undiscovered, receptor(s) for IL-1 exist in the brain. The recent characterization of putative, new IL-1 ligands and new IL-1 receptor-related molecules leads to the hypothesis that there might be alternative IL-1 signaling pathway(s) in the central nervous system (CNS).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rothwell N. J. and Luheshi G. N. (2000) Interleukin 1 in the brain: biology, pathology and therapeutic target. Trends Neurosci. 23, 618–625.
Allan S. M. and Rothwell N. J. (2001) Cytokines and acute neurodegeneration. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2, 734–744.
Fisher M. and Garcia J. H. (1996) Evolving stroke and the ischemic penumbra. Neurology 47, 884–888.
Touzani O., Roussel S., and MacKenzie E. T. (2001) The ischaemic penumbra. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 14, 83–88.
Saito K., Suyama K., Nishida K., Sei Y., and Basile A. S. (1996) Early increases in TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1 beta levels following transient cerebral ischemia in gerbil brain. Neurosci. Lett. 206, 149–152.
Touzani O., Boutin H., Chuquet J., and Rothwell N. (1999) Potential mechanisms of interleukin-1 involvement in cerebral ischaemia. J. Neuroimmunol. 100, 203–215.
Schmidt J. A. (1984) Purification and partial biochemical characterization of normal human interleukin 1. J. Exp. Med. 160, 772–787.
Dinarello C. A. (1996) Biologic basis for interleukin-1 in disease. Blood 87, 2095–2147.
Sims J. E., Gayle M. A., Slack J. L., et al. (1993) Interleukin 1 signaling occurs exclusively via the type I receptor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 6155–6159.
Wesche H., Korherr C., Kracht M., Falk W., Resch K., and Martin M. U. (1997) The interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein (IL-1RAcP) is essential for IL-1-induced activation of interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase (IRAK) and stress-activated protein kinases (SAP kinases). J. Biol. Chem. 272, 7727–7731.
Lemaitre B., Nicolas E., Michaut L., Reichhart J. M., and Hoffmann J. A. (1996) The dorsoventral regulatory gene cassette spatzle/Toll/cactus controls the potent antifungal response in Drosophila adults. Cell 86, 973–983.
Eldon E., Kooyer S., D’Evelyn D., Duman M., Lawinger P., Botas J., and Bellen H. (1994) The Drosophila 18 wheeler is required for morphogenesis and has striking similarities to Toll. Development 120, 885–899.
O’Neill L. A. (2000) The interleukin-1 receptor/Toll-like receptor superfamily: signal transduction during inflammation and host defense. Sci. STKE. 2000, RE1.
McMahan C. J., Slack J. L., Mosley B., et al. (1991) A novel IL-1 receptor, cloned from B cells by mammalian expression, is expressed in many cell types. EMBO J. 10, 2821–2832.
Malinowsky D., Lundkvist J., Laye S., and Bartfai T. (1998) Interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein interacts with the type II interleukin-1 receptor. FEBS Lett. 429, 299–302.
Liu C., Hart R. P., Liu X. J., Clevenger W., Maki R. A., and De Souza E. B. (1996) Cloning and characterization of an alternatively processed human type II interleukin-1 receptor mRNA. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 20,965–20,972.
Jensen L. E., Muzio M., Mantovani A., and Whitehead A. S. (2000) IL-1 signaling cascade in liver cells and the involvement of a soluble form of the IL-1 receptor accessory protein. J. Immunol. 164, 5277–5286.
Wesche H., Henzel W. J., Shillinglaw W., Li S., and Cao Z. (1997) MyD88: an adapter that recruits IRAK to the IL-1 receptor complex. Immunity 7, 837–847.
Cao Z., Henzel W. J., and Gao X. (1996) IRAK: a kinase associated with the interleukin-1 receptor. Science 271, 1128–1131.
Muzio M., Ni J., Feng P., and Dixit V. M. (1997) IRAK (Pelle) family member IRAK-2 and MyD88 as proximal mediators of IL-1 signaling. Science 278, 1612–1615.
Cao Z., Xiong J., Takeuchi M., Kurama T., and Goeddel D. V. (1996) TRAF6 is a signal transducer for interleukin-1. Nature 383, 443–446.
O’Neill L. A. and Greene C. (1998) Signal transduction pathways activated by the IL-1 receptor family: ancient signaling machinery in mammals, insects, and plants. J. Leukoc. Biol. 63, 650–657.
Breder C. D., Dinarello C. A., and Saper C. B. (1988) Interleukin-1 immunoreactive innervation of the human hypothalamus. Science 240, 321–324.
Lue F. A., Bail M., Jephthah-Ochola J., Carayanniotis K., Gorczynski R., and Moldofsky H. (1988) Sleep and cerebrospinal fluid interleukin-1-like activity in the cat. Int. J. Neurosci. 42, 179–183.
Ban E., Milon G., Prudhomme N., Fillion G., and Haour F. (1991) Receptors for interleukin-1 (alpha and beta) in mouse brain: mapping and neuronal localization in hippocampus. Neuroscience 43, 21–30.
French R. A., VanHoy R. W., Chizzonite R., et al. (1999) Expression and localization of p80 and p68 interleukin-1 receptor proteins in the brain of adult mice. J. Neuroimmunol. 93, 194–202.
Liu C., Chalmers D., Maki R., and De Souza E. B. (1996) Rat homolog of mouse interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein: cloning, localization and modulation studies. J. Neuroimmunol. 66, 41–48.
Tomozawa Y., Inoue T., and Satoh M. (1995) Expression of type I interleukin-1 receptor mRNA and its regulation in cultured astrocytes. Neurosci. Lett. 195, 57–60.
Zetterstrom M., Lundkvist J., Malinowsky D., Eriksson G., and Bartfai T. (1998) Interleukin-1-mediated febrile responses in mice and interleukin-1 beta activation of NFkappaB in mouse primary astrocytes, involves the interleukin-1 receptor accessory protein. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 9, 131–138.
Pousset F., Cremona S., Dantzer R., Kelley K. W., and Parnet P. (2001) Dexamethasone upregulates type II IL-1 receptor in mouse primary activated astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 76, 901–909.
Brogi A., Strazza M., Melli M., and Costantino-Ceccarini E. (1997) Induction of intracellular ceramide by interleukin-1 beta in oligodendrocytes. J. Cell Biochem. 66, 532–541.
Blasi F., Riccio M., Brogi A., Strazza M., et al. (1999) Constitutive expression of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) in rat oligodendrocytes. Biol. Chem. 380, 259–264.
Buttini M., Sauter A., and Boddeke H. W. (1994) Induction of interleukin-1 beta mRNA after focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 23, 126–134.
Hillhouse E. W., Kida S., and Iannotti F. (1998) Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat causes a biphasic production of immunoreactive interleukin-1beta in the cerebral cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 249, 177–179.
Giulian D., Baker T. J., Shih L. C., and Lachman L. B. (1986) Interleukin 1 of the central nervous system is produced by ameboid microglia. J. Exp. Med. 164, 594–604.
Davies C. A., Loddick S. A., Toulmond S., Stroemer R. P., Hunt J., and Rothwell N. J. (1999) The progression and topographic distribution of interleukin-1beta expression after permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 19, 87–98.
Pearson V. L., Rothwell N. J., and Toulmond S. (1999) Excitotoxic brain damage in the rat induces interleukin-1beta protein in microglia and astrocytes: correlation with the progression of cell death. Glia 25, 311–323.
Sairanen T. R., Lindsberg P. J., Brenner M., and Siren A. L. (1997) Global forebrain ischemia results in differential cellular expression of interleukin-1beta (IL-1beta) and its receptor at mRNA and protein level. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17, 1107–1120.
Wang X., Barone F. C., Aiyar N. V., and Feuerstein G. Z. (1997) Interleukin-1 receptor and receptor antagonist gene expression after focal stroke in rats. Stroke 28, 155–161.
Touzani O., Boutin H., LeFeuvre R., Parker L., Miller A., Luheshi G., and Rothwell N. (2002) Interleukin-1 influences ischemic brain damage in the mouse independently of the interleukin-1 type I receptor. J. Neurosci. 22, 38–43.
Loddick S. A., MacKenzie A., and Rothwell N. J. (1996) An ICE inhibitor, z-VAD-DCB attenuates ischaemic brain damage in the rat. Neuroreport 7, 1465–1468.
Relton J. K. and Rothwell N. J. (1992) Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist inhibits ischaemic and excitotoxic neuronal damage in the rat. Brain Res. Bull. 29, 243–246.
Yamasaki Y., Matsuura N., Shozuhara H., Onodera H., Itoyama Y., and Kogure K. (1995) Interleukin-1 as a pathogenetic mediator of ischemic brain damage in rats. Stroke 26, 676–680.
Schielke G. P., Yang G. Y., Shivers B. D., and Betz A. L. (1998) Reduced ischemic brain injury in interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme-deficient mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 18, 180–185.
Friedlander R. M., Gagliardini V., Hara H., et al. (1997) Expression of a dominant negative mutant of interleukin-1 beta converting enzyme in transgenic mice prevents neuronal cell death induced by trophic factor withdrawal and ischemic brain injury. J. Exp. Med. 185, 933–940.
Boutin H., Lefeuvre R. A., Horai R., Asano M., Iwakura Y., and Rothwell N. J. (2001) Role of IL-1alpha and IL-1beta in ischemic brain damage. J. Neurosci. 21, 5528–5534.
Ushio S., Namba M., Okura T., et al. (1996) Cloning of the cDNA for human IFN-gamma-inducing factor, expression in Escherichia coli, and studies on the biologic activities of the protein. J. Immunol. 156, 4274–4279.
Parnet P., Garka K. E., Bonnert T. P., Dower S. K., and Sims J. E. (1996) IL-1Rrp is a novel receptor-like molecule similar to the type I interleukin-1 receptor and its homologues T1/ST2 and IL-1R AcP. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 3967–3970.
Torigoe K., Ushio S., Okura T., et al. (1997) Purification and characterization of the human interleukin-18 receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 25,737–25,742.
Born T. L., Thomassen E., Bird T. A., and Sims J. E. (1998) Cloning of a novel receptor subunit, AcPL, required for interleukin-18 signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 29,445–29,450.
Mulero J. J., Pace A. M., Nelken S. T., Loeb D. B., Correa T. R., Drmanac R., and Ford J. E. (1999) IL1HY1: A novel interleukin-1 receptor antagonist gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 263, 702–706.
Smith D. E., Renshaw B. R., Ketchem R. R., Kubin M., Garka K. E., and Sims J. E. (2000) Four new members expand the interleukin-1 superfamily. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 1169–1175.
Busfield S. J., Comrack C. A., Yu G., Chickering T. W., Smutko J. S., Zhou H., Leiby K. R., Holmgren L. M., Gearing D. P., and Pan Y. (2000) Identification and gene organization of three novel members of the IL-1 family on human chromosome 2. Genomics 66, 213–216.
Kumar S., McDonnell P. C., Lehr R., et al. (2000) Identification and initial characterization of four novel members of the interleukin-1 family. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 10,308–10,314.
Pan G., Risser P., Mao W., et al. (2001) IL-1H, an interleukin 1-related protein that binds IL-18 receptor/IL-1Rrp. Cytokine 13, 1–7.
Lin H., Ho A. S., Haley-Vicente D., et al. (2001) Cloning and characterization of IL-1HY2, a novel interleukin-1 family member. J. Biol. Chem. 276, 20,597–20,602.
Dunn E., Sims J. E., Nicklin M. J., and O’Neill L. A. (2001) Annotating genes with potential roles in the immune system: six new members of the IL-1 family. Trends Immunol. 22, 533–536.
Mitcham J. L., Parnet P., Bonnert T. P., et al. (1996) T1/ST2 signaling establishes it as a member of an expanding interleukin-1 receptor family. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 5777–5783.
Lovenberg T. W., Crowe P. D., Liu C., et al. (1996) Cloning of a cDNA encoding a novel interleukin-1 receptor related protein (IL 1R-rp2). J. Neuroimmunol. 70, 113–122.
Born T. L., Smith D. E., Garka K. E., Renshaw B. R., Bertles J. S., and Sims J. E. (2000) Identification and characterization of two members of a novel class of the interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) family. Delineation of a new class of IL-1R-related proteins based on signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 29,946–29,954.
Sana T. R., Debets R., Timans J. C., Bazan J. F., and Kastelein R. A. (2000) Computational identification, cloning, and characterization of IL-1R9, a novel interleukin-1 receptor-like gene encoded over an unusually large interval of human chromosome Xq22.2-q22.3. Genomics 69, 252–262.
Carrie A., Jun L., Bienvenu T., et al. (1999) A new member of the IL-1 receptor family highly expressed in hippocampus and involved in X-linked mental retardation. Nat. Genet. 23, 25–31.
Thomassen E., Renshaw B. R., and Sims J. E. (1999) Identification and characterization of SIGIRR, a molecule representing a novel subtype of the IL-1R superfamily. Cytokine 11, 389–399.
Debets R., Timans J. C., Homey B., et al. (2001) Two novel IL-1 family members, IL-1 delta and IL-1 epsilon, function as an antagonist and agonist of NF-kappa B activation through the orphan IL-1 receptor-related protein 2. J. Immunol. 167, 1440–1446.
Kumar S., Hanning C. R., Brigham-Burke M. R., et al. (2002) Interleukin-1F7b (IL-1H4/IL-1F7) is processed by caspase-1 and mature IL-1F7b binds to the IL-18 receptor but does not induce IFN-gamma production. Cytokine 18, 61–71.
Bufler P., Azam T., Gamboni-Robertson F., Reznikov L. L., Kumar S., Dinarello C. A., and Kim S. H. (2002) A complex of the IL-1 homologue IL-1F7b and IL-18-binding protein reduces IL-18 activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99, 13,723–13,728.
Wheeler R. D., Culhane A. C., Hall M. D., Pickering-Brown S., Rothwell N. J., and Luheshi G. N. (2000) Detection of the interleukin 18 family in rat brain by RT-PCR. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 77, 290–293.
Jander S., Schroeter M., and Stoll G. (2002) Interleukin-18 expression after focal ischemia of the rat brain: association with the late-stage inflammatory response. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 22, 62–70.
Jander S. and Stoll G. (1998) Differential induction of interleukin-12, interleukin-18, and interleukin-1beta converting enzyme mRNA in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis of the Lewis rat. J. Neuroimmunol. 91, 93–99.
Gatti S., Beck J., Fantuzzi G., Bartfai T., and Dinarello C. A. (2002) Effect of interleukin-18 on mouse core body temperature. Am. J. Physiol Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 282, R702-R709.
Conti B., Park L. C., Calingasan N. Y., Kim Y., Kim H., Bae Y., Gibson G. E., and Joh T. H. (1999) Cultures of astrocytes and microglia express interleukin 18. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 67, 46–52.
Loddick S. A., Liu C., Takao T., Hashimoto K., and De Souza E. B. (1998) Interleukin-1 receptors: cloning studies and role in central nervous system disorders. Brain Res. Brain Res. Rev. 26, 306–319.
Glaccum M. B., Stocking K. L., Charrier K., et al. (1997) Phenotypic and functional characterization of mice that lack the type I receptor for IL-1. J. Immunol. 159, 3364–3371.
Labow M., Shuster D., Zetterstrom M., et al. (1997) Absence of IL-1 signaling and reduced inflammatory response in IL-1 type I receptor-deficient mice. J. Immunol. 159, 2452–2461.
Luheshi G., Hopkins S. J., Lefeuvre R. A., Dascombe M. J., Ghiara P., and Rothwell N. J. (1993) Importance of brain IL-1 type II receptors in fever and thermogenesis in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 265, E585-E591.
Parker L. C., Luheshi G. N., Rothwell N. J., and Pinteaux E. (2002) IL-1beta signalling in glial cells in wildtype and IL-1RI deficient mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 136, 312–320.
Kumar S., Tzimas M. N., Griswold D. E., and Young P. R. (1997) Expression of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor homologue, is induced by proinflammatory stimuli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 235, 474–478.
Berglöf E., Andre R., Renshow B. R., et al. (2003) IL-1Rrp2 expression and IL-1F9 (IL-1H1) actions in brain cells. J. Immunol. 139, 36–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boutin, H., Kimber, I., Rothwell, N.J. et al. The expanding interleukin-1 family and its receptors. Mol Neurobiol 27, 239–248 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:27:3:239
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MN:27:3:239