Abstract
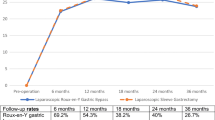
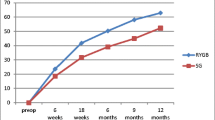
A body composition analysis is performed as part of pre-operative testing to establish a baseline for the patient. The purpose of this preliminary study is to track weight loss, percent body fat and percent lean tissue in post-operative bariatric patients. As this is accomplished, it is noted that the ratio between body fat and lean tissue changes and the basal metabolic rate decreases. It is interesting to note that lean tissue decreases along with body fat. Performing a body composition analysis every 3 months also assists in proper nutrition counseling for the patient. The method used to accomplish these readings is a bioelectrical impedance analysis. Using electrodes and a computer, the impedance reading is gathered from current weight, height and age of the subject. As weight is lost, basal metabolic rate slows and the body uses less calories for maintenance. Some depletion in lean tissue is noted with weight loss. If protein is decreased substantially from the diet, a great deal more lean tissue is lost. This preliminary study will track subjects over a 5-year period to document the long-term metabolic changes post-operatively and the effects reduced caloric intake has on the body.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gordon, M. Metabolic Changes after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass: A Preliminary Report. OBES SURG 3, 425–428 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1381/096089293765559151
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1381/096089293765559151