Abstract
Background
Colorectal cancer (CRC) oncogenesis was considered to be determined by interactions between genetic and environmental factors. Specific interacting factors that influence CRC morbidity have yet to be fully investigated.
Methods
A multi-institutional collaborative study with 1511 CRC patients and 2098 control subjects was used to compare the odds ratios for the occurrence of polymorphisms at 11 known single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). TaqMan PCR and questionnaires were used to evaluate the effects of environmental exposures.
Results
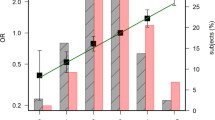
Variants of rs6983267 on 8q24 were the most significant markers of risk for CRC (odds ratio 1.16, 95% confidence interval 1.06–1.27, P = 0.0015). Non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (DM), a higher body mass index at age 20, and meat consumption were environmental risk factors, whereas a tuna-rich diet and vitamin intake were protective factors. The cohort of rs6983267 SNP major (T) allele at 8q24 and DM had a 1.66-fold higher risk ratio than the cohort of major allele patients without DM.
Conclusions
We confirmed that interactions between the genetic background and environmental factors are associated with increased risk for CRC. There is a robust risk of the minor G allele at the 8q24 rs6983267 SNP; however, a major T allele SNP could more clearly reveal a correlation with CRC specifically when DM is present.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zanke BW, Greenwood CM, Rangrej J, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on chromosome 8q24. Nat Genet. 2007;39:989–94.
Tomlinson IP, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L, et al. A genome-wide association study identifies colorectal cancer susceptibility loci on chromosomes 10p14 and 8q23.3. Nat Genet. 2008;40:623–30.
Tenesa A, Farrington SM, Prendergast JG, et al. Genome-wide association scan identifies a colorectal cancer susceptibility locus on 11q23 and replicates risk loci at 8q24 and 18q21. Nat Genet. 2008;40:631–7.
Wijnen JT, Brohet RM, van Eijk R, et al. Chromosome 8q23.3 and 11q23.1 variants modify colorectal cancer risk in Lynch syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:131–7.
Houlston RS, Webb E, Broderick P, et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies four new susceptibility loci for colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2008;40:1426–35.
Giovannucci E, Harlan DM, Archer MC, et al. Diabetes and cancer: a consensus report. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60:207–21.
Campbell PT, Deka A, Jacobs EJ, et al. Prospective study reveals associations between colorectal cancer and type 2 diabetes mellitus or insulin use in men. Gastroenterology. 139:1138–46.
Tuupanen S, Niittymaki I, Nousiainen K, et al. Allelic imbalance at rs6983267 suggests selection of the risk allele in somatic colorectal tumor evolution. Cancer Res. 2008;68:14–7.
Thompson CL, Plummer SJ, Acheson LS, Tucker TC, Casey G, Li L. Association of common genetic variants in SMAD7 and risk of colon cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:982–6.
Berndt SI, Potter JD, Hazra A, et al. Pooled analysis of genetic variation at chromosome 8q24 and colorectal neoplasia risk. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:2665–72.
Tomlinson I, Webb E, Carvajal-Carmona L, et al. A genome-wide association scan of tag SNPs identifies a susceptibility variant for colorectal cancer at 8q24.21. Nat Genet. 2007;39:984–8.
Tuupanen S, Turunen M, Lehtonen R, et al. The common colorectal cancer predisposition SNP rs6983267 at chromosome 8q24 confers potential to enhanced Wnt signaling. Nat Genet. 2009;41:885–90.
Koehne CH, Dubois RN. COX-2 inhibition and colorectal cancer. Semin Oncol. 2004;31:12–21.
North GL. Celecoxib as adjunctive therapy for treatment of colorectal cancer. Ann Pharmacother. 2001;35:1638–43.
Li L, Plummer SJ, Thompson CL, et al. A common 8q24 variant and the risk of colon cancer: a population-based case-control study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2008;17:339–42.
Curtin K, Lin WY, George R, et al. Meta association of colorectal cancer confirms risk alleles at 8q24 and 18q21. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2009;18:616–21.
Haiman CA, Le Marchand L, Yamamato J, et al. A common genetic risk factor for colorectal and prostate cancer. Nat Genet. 2007;39:954–6.
Pomerantz MM, Ahmadiyeh N, Jia L, et al. The 8q24 cancer risk variant rs6983267 shows long-range interaction with MYC in colorectal cancer. Nat Genet. 2009;41:882–4.
Yeager M, Xiao N, Hayes RB, et al. Comprehensive resequence analysis of a 136 kb region of human chromosome 8q24 associated with prostate and colon cancers. Hum Genet. 2008;124:161–70.
Acknowledgment
This work was supported in part by the following grants and foundations: CREST, Japan Science and Technology Agency (JST); Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research, grant numbers 20390360, 20591547, 20790960, 21591644, 21791295, 21791297, 215921014 and 21679006; and the Funding Program for Next Generation World-Leading Researchers (LS094); and NEDO (New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization) Technological Development for Chromosome Analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Shinya Ishimaru, Koshi Mimori and Ken Yamamoto contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishimaru, S., Mimori, K., Yamamoto, K. et al. Increased Risk for CRC in Diabetic Patients with the Nonrisk Allele of SNPs at 8q24. Ann Surg Oncol 19, 2853–2858 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2278-6
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-012-2278-6