Abstract
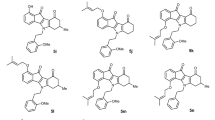
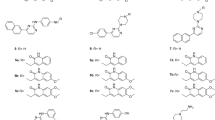
The review summarizes the most recent achievements in structure–activity relationship (SAR) studies of tariquidar and its analogs. Tariquidar is one of the most promising representatives of the third generation of multidrug resistance (MDR) modulators created so far. This fact determines the strong interest of different research groups in the development of tariquidar-like structures as selective inhibitors of MDR transporters in resistant human cancer cells. After the discovery of tariquidar, a number of analogs have been synthesized and pharmacologically tested, thus supplying good data for comprehensive analyses of their structure–activity relationships. In the review, the structural and pharmacological data of newly synthesized tariquidar-like compounds are first presented. Next, the main achievements in the SAR studies are described focusing on two main transport proteins: P-glycoprotein and breast cancer resistance protein. The reported results are discussed from the point of view of their significance and importance for future directions in the rational design of effective MDR modulators.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klein I, Sarkadi B, Varadi A. An inventory of the human ABC proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1461:237–62.
Fojo T, Bates S. Strategies for reversing drug resistance. Oncogene. 2003;22:7512–23.
Bodo A, Bakos E, Szeri F, Varadi A, Sarkadi B. The role of multidrug transporters in drug availability, metabolism and toxicity. Toxicol Lett. 2003;140:133–43.
Juliano RL, Ling V. A surface glycoprotein modulating drug permeability in Chinese hamster ovary cell mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976;455:152–62.
Gottesmann MM, Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427.
Ambudkar SV, Dey S, Hrycyna CA, Ramachandra M, Pastan I, Gottesman MM. Biochemical, cellular, and pharmacological aspects of the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1999;39:361–98.
Mirski SEL, Gerlach JH, Cole SPC. Multidrug resistance in a human small cell lung cancer cell line selected in adriamycin. Cancer Res. 1987;47:2594–8.
Boumendjel A, Baubichon-Cortay H, Trompier D, Perrotton T, Di Pietro A. Anticancer multidrug resistance mediated by MRP1: recent advances in the discovery of reversal agents. Med Res Rev. 2005;25:453–72.
Hipfner DR, Deeley RG, Cole SPC. Structural, mechanistic and clinical aspects of MRP1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1999;1461:359–76.
Leslie EM, Deeley RG, Cole SPC. Toxicological relevance of the multidrug resistance protein 1, MRP1 (ABCC1) and related transporters. Toxicology. 2001;167:3–23.
Kusuhara H, Sugiyama Y. ATP-binding cassette, subfamily G (ABCG family). Pflugers Arch. 2007;453:735–44.
Doyle LA, Yang WD, Abruzzo LV, et al. A multidrug resistance transporter from human MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95:15665–70.
Litman T, Brangi M, Hudson E, et al. The multidrug-resistant phenotype associated with overexpression of the new ABC half-transporter, MXR (ABCG2). J Cell Sci. 2000;113:2011–21.
Robey RW, Polgar O, Deeken J, To KW, Bates SE. ABCG2: determining its relevance in clinical drug resistance. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26:39–57.
Maliepaard M, van Gastelen MA, Tohgo A, et al. Circumvention of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP)-mediated resistance to camptothecins in vitro using non-substrate drugs or the BCRP inhibitor GF120918. Clin Cancer Res. 2001;7:935–41.
Abbott BL. ABCG2 (BCRP): a cytoprotectant in normal and malignant stem cells. Clin Adv Hematol Oncol. 2006;4:63–72.
Tsuruo T, Iida H, Tsukagoshi S, Sakurai Y. Enhancement of vincristine- and adriamycin-induced cytotoxicity by verapamil in P388 leukemia and its sublines resistant to vincristine and adriamycin. Biochem Pharmacol. 1982;31:3138–40.
Thomas H, Coley HM. Overcoming multidrug resistance in cancer: an update on the clinical strategy of inhibiting P-glycoprotein. Cancer Control. 2003;10:159–65.
Robert J, Jarry C. Multidrug resistance reversal agents. J Med Chem. 2003;46:4805–17.
Krishna R, Mayer LD. Multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer. Mechanisms, reversal using modulators of MDR and the role of MDR modulators in influencing the pharmacokinetics of anticancer drugs. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2000;11:265–83.
Ryder, H, Ashworth PA, Roe MJ, et al. Anthranilic acid derivatives as multi drug resistance modulators. WO98/17648, April 30, 1998.
Roe M, Folkes A, Ashworth P, et al. Reversal of P-glycoprotein mediated multidrug resistance by novel anthranilamide derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 1999;9:595–600.
Klinkhammer W. Design, Synthese und 3D-QSAR neuartiger P-gp-Modulatoren. [Ph D thesis]. Bonn: University of Bonn; 2006. URN: urn:nbn:de:hbz:5 N-08459. http://deposit.ddb.de/cgi-bin/dokserv?idn=981124488&dok_var=d1&dok_ext=pdf&filename=981124488.pdf.
Jekerle V, Klinkhammer W, Reilly RM, Piquette-Miller M, Wiese M. Novel tetrahydroisoquinolin–ethyl–phenylamine based multidrug resistance inhibitors with broad-spectrum modulating properties. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2007;59:61–9.
Jekerle V, Klinkhammer W, Scollard DA, Breitbach K, Reilly RM, Piquette-Miller M, et al.In vitro and in vivo evaluation of WK-X-34, a novel inhibitor of P-glycoprotein and BCRP, using radio imaging techniques. Int J Cancer. 2006;119:414–22.
Müller H, Klinkhammer W, Globisch C, Kassack MU, Pajeva IK, Wiese M. New functional assay of P-glycoprotein activity using Hoechst 33342. Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:7470–9.
Müller H, Pajeva IK, Globisch C, Wiese M. Functional assay and structure–activity relationships of new third-generation P-glycoprotein inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:2448–62.
Klinkhammer W, Müller H, Globisch C, Pajeva IK, Wiese M. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a small molecule library of 3rd generation multidrug resistance modulators. Bioorg Med Chem. 2009;17:2524–35.
Labrie P, Maddaford SP, Lacroix J, et al.In vitro activity of novel dual action MDR anthranilamide modulators with inhibitory activity at CYP-450. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:7972–87.
Labrie P, Maddaford SP, Lacroix J, et al.In vitro activity of novel dual action MDR anthranilamide modulators with inhibitory activity on CYP-450 (Part 2). Bioorg Med Chem. 2007;15:3854–68.
Egger M, Li X, Müller C, Bernhardt G, Buschauer A, König B. Tariquidar analogues: synthesis by CuI-catalysed N/O–aryl coupling and inhibitory activity against the ABCB1 transporter. Eur J Org Chem. 2007;2643–49.
Kühnle M, Egger M, Müller C, et al. Potent and selective inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2) derived from the P-glycoprotein (ABCB1) modulator tariquidar. J Med Chem. 2009;52:1190–7.
Mistry P, Stewart AJ, Dangerfield W, et al.In vitro and in vivo reversal of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance by a novel potent modulator, XR9576. Cancer Res. 2001;61:749–58.
Walker J, Martin C, Callaghan R. Inhibition of P-glycoprotein function by XR9576 in a solid tumour model can restore anticancer drug efficacy. Eur J Cancer. 2004;40:594–605.
Kohler S, Stein WD. Optimizing chemotherapy by measuring reversal of P-glycoprotein activity in plasma membrane vesicles. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2003;81:507–17.
Leyers S, Wiese M. Tariquidar at a concentration of 10 μM has no effect on MRP1 activity in 2008MRP1 cells. Unpublished results.
Robey RW, Steadman K, Polgar O, et al. Pheophorbide a is a specific probe for ABCG2 function and inhibition. Cancer Res. 2004;64:1242–6.
Fox E, Bates SE. Tariquidar (XR9576): a P-glycoprotein drug efflux pump inhibitor. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2007;7:447–59.
Globisch C, Pajeva IK, Wiese M. Structure–activity relationships of a series of tariquidar analogs as multidrug resistance modulators. Bioorg Med Chem. 2006;14:1588–98.
Pick A, Müller H, Wiese M. Structure–activity relationships of new inhibitors of breast cancer resistance protein (ABCG2). Bioorg Med Chem. 2008;16:8224–36.
Martin C, Berridge G, Mistry P, Higgins C, Charlton P, Callaghan R. The molecular interaction of the high affinity reversal agent XR9576 with P-glycoprotein. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;128:403–11.
Martin C, Berridge G, Higgins CF, Mistry P, Charlton P, Callaghan R. Communication between multiple drug binding sites on P-glycoprotein. Mol Pharmacol. 2000;58:624–32.
Shapiro B, Ling V. Positively cooperative sites for drug transport by P-glycoprotein with distinct drug specificities. Eur J Biochem. 1997;250:130–7.
Shapiro AB, Fox K, Lam P, Ling V. Stimulation of P-glycoprotein-mediated drug transport by prazosin and progesterone. Evidence for a third drug-binding site. Eur J Biochem. 1999;259:841–50.
Qu Q, Sharom F. Proximity of bound hoechst 33342 to the ATPase catalytic sites places the drug binding site of P-glycoprotein within the cytoplasmatic membrane leaflet. Biochemistry. 2002;41:4744–52.
Litman T, Skovsgaard T, Stein WDJ. Pumping of drugs by P-glycoprotein: a two-step process? Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;307:846–53.
Kondratov RV, Komarov PG, Becker Y, Ewenson A, Gudkov AV. Small molecules that dramatically alter multidrug resistance phenotype by modulating the substrate specificity of P-glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:14078–83.
Pajeva IK, Globisch C, Wiese M. Structure–function relationships of multidrug resistance P-glycoprotein. J Med Chem. 2004;47:2523–33.
Labrie P, Maddaford SP, Fortin S, et al. A comparative molecular field analysis (CoMFA) and comparative molecular similarity indices analysis (CoMSIA) of anthranilamide derivatives that are multidrug resistance modulators. J Med Chem. 2006;49:7646–60.
Müller, H. Funktionelle Untersuchungen des ABC-transporters P-glykoprotein. PhD thesis, University of Bonn, Bonn; 2007. urn:nbn:de:hbz:5N-12814. http://hss.ulb.uni-bonn.de/diss_online/math_nat_fak/2007/mueller_henrik.
Pajeva I, Globisch C, Fleischer R, Tsakovska I, Wiese M. Molecular modeling of P-glycoprotein and related drugs. Med Chem Res. 2005;14:106–17.
Pajeva IK, Wiese M. Molecular modeling of phenothiazines and related drugs as multidrug resistance modifiers: a comparative molecular field analysis study. J Med Chem. 1998;41:1815–26.
Acknowledgments
We thank our colleagues and especially Christoph Globisch, Werner Klinkammer, and Henrik Müller whose efforts contributed to our results and knowledge on the topic. The financial support from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation and Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft is also highly recognized.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest Editor: Marilyn E. Morris
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pajeva, I.K., Wiese, M. Structure–Activity Relationships of Tariquidar Analogs as Multidrug Resistance Modulators. AAPS J 11, 435–444 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-009-9118-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1208/s12248-009-9118-z