Abstract
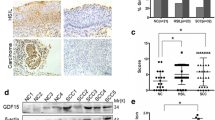
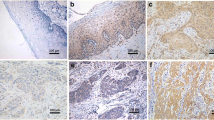
This study investigates the influence of fibroblast growth factor receptor type B (FGFRb) and fibroblast growth factor on cervical carcinogenesis associated with HPV16 E6/7 infection, using primary cancer cells isolated from Taiwanese patients with cervical cancer. Functional interaction between FGFRb in Cx cells and HPV16 E6/7 transfected Cx cells (CxWJ cells) following treatment with FGF-7, according to cell growth, invasive ability, and tumor growth in SCID mice. Our results indicate that the downregulation of FGFRb gene expression in CxWJ cells partially represses proliferation and the invasive ability provided by FGF-7 stimulation. In SCID mice, the FGF2 and FGFR1 gene expression ascend in CxWJ tumor nodule. These data provide evidence of a functional interaction between HPV16 E6/7 in FGFRb and FGF2, suggesting that cooperative stimulation of HPV E6/7 in inactivated FGFRb and the upregulation of FGF2 may be necessary to completely overcome the oncogenic function associated with the progression of cervical carcinogenesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hsu KF, Wu CL, Huang SC, et al. Conditionally replicating E1B-deleted adenovirus driven by the squamous cell carcinoma antigen 2 promoters for uterine cervical cancer therapy. Cancer Gene Ther. 2008;15(8):526–534.
Lang HC, Wu SL. Lifetime costs of the top five cancers in Taiwan. Eur J Health Econ. 2011 Mar 27. DOI: 10.1007/s10198-011-0307-1.
Chen CC, Lin JC, Jan JS, et al. Definitive intensity-modulated radiation therapy with concurrent chemotherapy for patients with locally advanced cervical cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 2011;122(1):9–13.
Suba EJ, Michelow PM, Raab SS. Human papillomavirus testing in the prevention of cervical cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2011; 103(19):368–383.
Mühlen S, Behren A, Iftner T, Simon C. Influence of HPV16 E2 and its localisation on the expression of matrix metalloproteinase-9. Int J Oncol. 2010;37(2):337–345.
No JH, Kim MK, Jeon YT, Kim YB, Song YS. Human papilloma-virus vaccine: widening the scope for cancer prevention. Mol Carcinog. 2011;50(4):244–253.
Zollner U, Schwarz TF. Diseases caused by human papilloma viruses. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2011;136(20):1067–1072.
Chen GJ, Forough R. Fibroblast growth factors, fibroblast growth factor receptors, diseases, and drugs. Recent Pat Cardiovasc Drug Discov. 2006;1(2):211–224.
Ucuzian AA, Brewster LP, East AT, Pang Y, Gassman AA, Greisler HP. Characterization of the chemotactic and mitogenic response of SMCs to PDGF-BB and FGF-2 in fibrin hydrogels. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;94(3):988–996.
Caverzasio J, Thouverey C. Activation of FGF receptors is a new mechanism by which strontium ranelate induces osteoblastic cell growth. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(3–4):243–250.
Schwertfeger KL. Fibroblast growth factors in development and cancer: insights from the mammary and prostate glands. Curr Drug Targets. 2009;10(7):632–644.
Manuvakhova M, Thottassery JV, Hays S, et al. Expression of the SNT-1/FRS2 phosphotyrosine binding domain inhibits activation of MAP kinase and PI3-kinase pathways and antiestrogen resistant growth induced by FGF-1 in human breast carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 2006;25(44):6003–6014.
Steele IA, Edmondson RJ, Bulmer JN, Bolger BS, Leung HY, Davies BR. Induction of FGF receptor 2-IIIb expression and response to its ligands in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20(41):5878–5887.
Cha JY, Lambert QT, Reuther GW, Der CJ. Involvement of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 isoform switching in mammary oncogenesis. Mol Cancer Res. 2008;6(3):435–445.
Oltean S, Sorg BS, Albrecht T, et al. Alternative inclusion of fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 exon IIIc in Dunning prostate tumors reveals unexpected epithelial mesenchymal plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(38):14116–14121.
Tsai SM, Wang WP. Expression and function of fibroblast growth factor (FGF) 7 during liver regeneration. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2011;27(6):641–652.
De Andrade JA, Thannickal VJ. Innovative approaches to the therapy of fibrosis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2009;21(6): 649–655.
Yanai M, Tatsumi N, Hasunuma N, Katsu K, Endo F, Yokouchi Y. FGF signaling segregates biliary cell-lineage from chick hepatoblasts cooperatively with BMP4 and ECM components in vitro. Dev Dyn. 2008;237(5):1268–1283.
Böhm F, Speicher T, Hellerbrand C, et al. FGF receptors 1 and 2 control chemically induced injury and compound detoxification in regenerating livers of mice. Gastroenterology. 2010;139(4): 1385–1396.
Halbert CL, Demers GW, Galloway DA. The E7 gene of human papillomavirus type 16 is sufficient for immortalization of human epithelial cells. J Virol. 1991;65(1):473–478.
Chou CY, Chen YH, Tzeng CC, Cheng YC, Chang CF, Chen TM. Establishment and characterization of a human-papillomavirus negative, p53-mutation negative human cervical cancer cell line. Cancer Lett. 1996;102(1–2):173–181.
Kim J, Kim PH, Yoo JY, et al. Double E1B 19 kDa- and E1B 55 kDa-deleted oncolytic adenovirus in combination with radiotherapy elicits an enhanced anti-tumor effect. Gene Ther. 2009;16(9): 1111–1121.
Chen MJ, Tang WY, Hsu CW, et al. Apoptosis induction in primary human colorectal cancer cell lines and retarded tumor growth in SCID mice by sulforaphane. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:415231.
Abu-Rustum NR, Sonoda Y. Fertility-sparing surgery in early-stage cervical cancer: indications and applications. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 2010;8(12):1435–1438.
Munagala R, Kausar H, Munjal C, Gupta RC. Withaferin A induces p53-dependent apoptosis by repression of HPV oncogenes and up-regulation of tumor suppressor proteins in human cervical cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2011:32(11): 1697–1705.
Ciotti M, Sesti F, Paba P, et al. Human papillomavirus (HPV) testing in the management of women with abnormal pap smears. Experience of a colposcopy referral clinic. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 2004;25(5):577–584.
Steele IA, Edmondson RJ, Bulmer JN, Bolger BS, Leung HY, Davies BR. Induction of FGF receptor 2-IIIb expression and response to its ligands in epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20(41):5878–5887.
Duchesne L, Tissot B, Rudd TR, Dell A, Fernig DG. N-glycosylation of fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 regulates ligand and heparan sulfate co-receptor binding. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(37):27178–27189.
Steele IA, Edmondson RJ, Leung HY, Davies BR. Ligands to FGF receptor 2-IIIb induce proliferation, motility, protection from cell death and cytoskeletal rearrangements in epithelial ovarian cancer cell lines. Growth Factors. 2006;24(1):45–53.
Li T, Jiang S. Effect of bFGF on invasion of ovarian cancer cells through the regulation of Ets-1 and urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Pharm Biol. 2010;48(2):161–165.
Kottakis F, Polytarchou C, Foltopoulou P, Sanidas I, Kampranis SC, Tsichlis PN. FGF-2 Regulates Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Angiogenesis through an NDY1/KDM2B-miR-101-EZH2 Pathway. Mol Cell. 2011;43(2):285–298.
Johansson A, Rudolfsson S, Hammarsten P, et al. Mast cells are novel independent prognostic markers in prostate cancer and represent a target for therapy. Am J Pathol. 2010;177(2): 1031–1041.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cheng, YM., Chou, CY., Hsu, YC. et al. Influence of HPV16 E6/7 on the Expression of FGF2 and FGFR Type B in Cervical Carcinogenesis. Reprod. Sci. 19, 580–586 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719111432874
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1933719111432874