Abstract
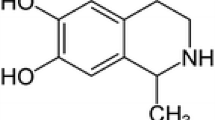
Salsolinol (1-methyl-6,7-dihydroxy-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinoline), the endogenous dopamine-derived catechol isoquinolines whose structure is similar with MPTP (1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine), may be a possible candidate of dopaminergic neurotoxins to elicit Parkinson’s disease (PD). Catechol isoquinolines can selectively target dopaminergic neurons, leading to dopaminergic neuronal death. However, the formation and nosogenesis of these toxins remains unclear. Salsolinol synthase is a novel enzyme which condensate dopamine and acetaldehyde to salsolinol. It is the first key enzyme in the metabolic pathway of catechol isoquinolines which directly affects salsolinol and its derivative metabolism in vivo. It is also one kind of Pictet-Spenglerase, which has been little studied and need more characterization. PC12 cells and rat brains were performed to illustrate the existence of salsolinol synthase in our study. The results indicate that salsolinol synthase is a low molecular weight protein, showing enhanced activity with increase in dopamine concentration. It is suggested that salsolinol synthase is sensitive to strong acid and stable to high-temperature. In this research, existence of salsolinol synthase was confirmed in vivo, and also provided some new evidences to elucidate the endogenous catechol isoquinoline neurotoxin substances involved in the pathogenesis of PD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhu, W., Wang, D., Zheng, J., et al., Clin. Chem., 2008, vol. 54, pp. 705–712.
Martinez-Alvarado, P., Dagnino-Subiabre, A., Paris, I., et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2001, vol. 283, pp. 1069–1076.
Nicklas, W.J., Youngster, S.K., Kindt, M.V., et al., Life Sci., 1987, vol. 8, no. 40, pp. 721–729.
Antkiewicz-Michaluk, L., Romanska, I., Papla, I., et al., Neuroscience, 2000, vol. 96, pp. 59–64.
Lorenc-Koci, E., Antkiewicz-Michaluk, L., Kaminska, A., et al., Neuroscience, 2008, vol. 156, pp. 973–986.
Deng, Y., Maruyama, W., Kawai, M., et al., Chromatogr., Ser. B, 1997, vol. 689, pp. 313–320.
Deng, Y., Maruyama, W., Dostert, P., et al., Chromatogr., Ser. B, 1995, vol. 670, pp. 47–54.
Musshoff, F., Schmidt, P., Dettmeyer, R., et al., Forensic. Sci. Int., 2000, vol. 113, pp. 359–366.
Song, Y., Xu, J., Hamme, A., et al., J. Chromatogr., Ser. A, 2006, vol. 1103, pp. 229–234.
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W, Dostert, P., et al., Neurosci. Lett., 1996, vol. 212, pp. 183–186.
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W., Yagi, K., et al., Neurobiology (Budapest), 2000, vol. 8, pp. 69–80.
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W., Zhang, J.H., et al., Life Sci., 1995, vol. 57, pp. 1061–1066.
Maruyama, W., Dostert, P., Matsubara, K., et al., Free Radic. Biol. Med., 1995, vol. 19, pp. 67–75.
Musshoff, F., Schmidt, P., Dettmeyer, R., et al., Forensic. Sci. Int., 1999, vol. 5, pp. 1–11.
Müller, T., Przuntek, H., Kuhn, W., et al., Mov. Disord., 1999, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 514–515.
Chen, X.C., Arshad, A., Qing, H., et al., Biologia, 2011, vol. 66, no. 6, pp. 1183–1188.
Chen, X.C., Arshad, A., Lin, X.Y., et al., IEEE/ICME International Conference on Complex Medical Engineering-CME1011.
Russo, G.L., De Nisco, E., Fiore, G., et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2003, vol. 308, no. 2, pp. 293–299.
De-Eknamkul, W., Ounaroon, A., Tanahashi, T., et al., Phytochemistry, 1997, vol. 45, pp. 477–484.
Paxinos, G. and Watson, C., New York: Elsevier, 2004.
Maruyama, W., Abe, T., Tohgi, H., et al., Ann. Neurol., 1996, vol. 40, pp. 119–122.
Bradford, M.M., Anal Biochem., 1976, vol. 72, pp. 248–254.
Ostrovskaya, R.U., Bull Exp. Biol. Med., 2012, vol. 153, no. 5, pp. 694–696.
Wang, R., Qing, H., Liu, X.Q., et al., Neurosci. Bull., 2008, vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 125–132.
Liu, Y., Roghani, A., and Edwards, R.H., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1992, vol. 89, pp. 9074–9078.
Takahashi, N., Miner, L.L., Sora, I., et al., Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 1997, vol. 94, pp. 9938–9943.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The article is published in the original.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X.C., Chen, Y., Wu, G.S. et al. Existence and characterization of Salsolinol synthase in neuronal cells and rat brain. Neurochem. J. 7, 192–197 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712413030045
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S1819712413030045