Abstract
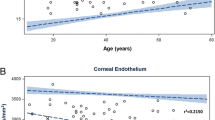
Senescence-associated alterations in the structure and function of the cornea make it more sensitive to such external agents as surgery, traumas, and disease, resulting in edema and vision impairment that can be corrected only by cornea transplantation. The role of aquaporins for cornea endothelium functioning, as well as age-related changes in their activity, is not entirely understood. We have studied age-related changes in the water permeability (Pf) of corneal endothelium plasma membranes and the mRNA expression levels of aquaporins aqp1 and aqp3 genes in Wistar and senescence-accelerated OXYS rats. At the age of 3 to 18 months, Pf increased in Wistar rats and decreased in OXYS rats, becoming two times lower than in the Wistar line. The expression of AQP1 mRNA (studied by real-time PCR) in the endothelium was the same in Wistar and OXYS rats at the age of 3 months. By the age of 18 months, it increased only in Wistar rats and became two times higher than in OXYS rats. The expression of aqp3 mRNA in the endothelium of 3-month-old OXYS rats was half that of Wistar rats and did not change with age, while it decreased in Wistar rats and at 18 months was four times lower than at 3 months. We propose that the increased water permeability of endothelial cells in Wistar rats is adaptive and compensates for the decrease in endothelial cell density with age, while the accelerated aging of OXYS rats eliminates this compensation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kolosova, N.G., Stefanova, N.A., Korbolina, E.E., Fursova, A.Zh., and Kozhevnikova, O.S., Senescenceaccelerated OXYS rats: a genetic model of premature aging and age-related diseases, Adv. Gerontol., 2014, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 294–298
Kolosova, N.G., Lebedev, P.A., Fursova, A.Zh., et al., Untimely aging OXYS rats as a model of senile cataracts, Usp. Gerontol., 2003, vol. 12, no. 12, pp. 143–148
Saprunova, V.B., Pilipenko, D.I., Alexeevsky, A.V., Fursova, A.Z., Kolosova, N.G., and Bakeeva, L.E., Lipofuscin granule dynamics during development of age-related macular degeneration, Biochemistry (Moscow), 2010, vol. 75, no. 2, pp. 130–138
Armitage, W.J., Preservation of human cornea, Transfus. Med. Hemother., 2011, vol. 38, pp. 143–147
Bonanno, J.A., Molecular mechanisms underlying the corneal endothelial pump, Exp. Eye Res., 2012, vol. 95, no. 1, pp. 2–7
Bourne, W.M. and McLaren, J.W., Clinical responses of the corneal endothelium, Exp. Eye Res., 2004, vol. 78, no. 3, pp. 561–572
Bryant, M.R. and McDonnell, P.J., A triphasic analysis of corneal swelling and hydration control, J. Biomech. Eng., 1998, vol. 120, pp. 370–381
Crane, J.M. and Verkman, A.S., Long-range nonanomalous diffusion of quantum dot-labeled aquaporin-1 water channels in the cell plasma membrane, Biophys. J., 2008, vol. 94, no. 2, pp. 702–713
Hamann, S., Zeuthen, T., La Cour, M., et al., Aquaporins in complex tissues: distribution of aquaporins 1–5 in human and rat eye, Am. J. Physiol., 1998, vol. 274, pp. C1332–C1345.
Ivanova, L.N., Babina, A.V., Baturina, G.S., and Katkova, L.E., Effect of vasopressin on the expression of genes for key enzymes of hyaluronan turn over in Wistar Albino Glaxo and Brattleboro rat kidneys, Exp. Physiol., 2013, vol. 98, no. 11, pp. 1608–1619
Kang, F., Kuang, K., Li, J., and Fischbarg, J., Cultured bovine corneal epithelial cells express a functional aquaporin water channel, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci., 1999, vol. 40, pp. 253–257
Kozhevnikova, O.S., Korbolina, E.E., Ershov, N.I., and Kolosova, N.G., Rat retinal transcriptome: effects of aging and AMD-like retinopathy, Cell Cycle, 2013, vol. 12, pp. 1745–1761
Kuang, K., Yiming, M., Wen, Q., et al., Fluid transport across cultured layers of corneal endothelium from aquaporin-1 null mice, Exp. Eye Res., 2004, vol. 78, no. 4, pp. 791–798
Li, J., Kuang, K., Nielsen, S., and Fischbarg, J., Molecular identification and immunolocalization of the water channel protein aquaporin 1 in CBCECs, Invest. Ophthalmol. Visual Sci., 1999, no. 40, pp. 1288–1292.
Maurice, D.M., The location of the fluid pump in the cornea, J. Physiol., 1972, vol. 221, pp. 43–54
Mergler, S. and Pleyer, U., The human corneal endothelium: New insights into electrophysiology and ion channels, Progr. Retinal Eye Res., 2007, vol. 26, pp. 359–378
Robben, J.H., Knoers, N.V., and Deen, P.M., Cell biological aspects of the vasopressin type-2 receptor and aquaporin 2 water channel in nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol., 2006, vol. 291, pp. F257–F270.
Shankardas, J., Patil, R.V., and Vishwanatha, J.K., Effect of down-regulation of aquaporins in human corneal endothelial and epithelial cell lines, Mol. Vision, 2010, vol. 16, pp. 1538–1548
Solenov, E., Watanabe, H., Manley, G.T., and Verkman, A.S., Sevenfold-reduced osmotic water permeability in primary astrocyte cultures from AQP-4-deficient mice, measured by a fluorescence quenching method, Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol., 2004, vol. 286, pp. 426–432
Thiagarajah, J.R. and Verkman, A.S., Aquaporin deletion in mice reduces corneal water permeability and delays restoration of transparency after swelling, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, vol. 277, vol. 21, pp. 19139–19144.
Verkman, A.S., Anderson, M.O., and Papadopoulos, M.C., Aquaporins: important but elusive drug targets, Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery, 2014, vol. 13, no. 4, pp. 259–277
Whitcher, J.P., Srinivasan, M., and Upadhyay, M.P., Corneal blindness: a global perspective, Bull. W.H.O., 2001, vol. 79, pp. 214–221
Yu, D., Thelin, W.R., Randell, S.H., and Boucher, R.C., Expression profiles of aquaporins in rat conjunctiva, cornea, lacrimal gland and Meibomian gland, Exp. Eye Res., 2012, vol. 103, pp. 22–32
Zarogiannis, S.G., Ilyaskin, A.V., Baturina, G.S., et al., Regulatory volume decrease of rat kidney principal cells after successive hypo-osmotic shocks, Math. Biosci., 2013, vol. 244, no. 2, pp. 176–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © G.S. Baturina, L.E. Katkova, N.G. Kolosova, E.I. Solenov, 2017, published in Uspekhi Gerontologii, 2017, Vol. 30, No. 5, pp. 659–664.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baturina, G.S., Katkova, L.E., Kolosova, N.G. et al. Age-Related Changes in Water Transport by Corneal Endothelial Cells in Rats. Adv Gerontol 8, 153–157 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057018020029
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S2079057018020029