Abstract
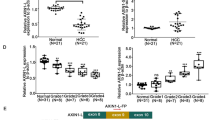
Colorectal cancer is one of the most common cancers in the world. Changes in AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 expression levels, whose diagnostic value was previously shown for several other cancer types, were studied in colorectal tumors. These genes encode aldose reductases, members of the aldo-keto reductase superfamily, which comprises enzymes capable to reduce a range of aromatic and aliphatic aldehydes and ketones. They are also involved in retinoid metabolism and carcinogenesis. AKR1B1 and AKR1B10 mRNA levels were compared in paired specimens of normal and colorectal tumor tissues using RT-PCR and quantitative real-time PCR. For the first time, the downregulation of these genes was demonstrated in colorectal carcinoma. AKR1B10 expression was decreased in most tumor specimens (88%, 65/74) even at the early stages, and in more than 60% of cases mRNA levels were decreased more than 10-fold. AKR1B1 mRNA levels were decreased in 10% of specimens. Therefore, these two structurally similar genes show quite different mRNA expression patterns in colorectal cancer, suggestive of their different functional roles in the intestine. Significant downregulation of AKR1B10 expression can be considered a potential diagnostic marker of colorectal cancer.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AKR:
-
aldo-keto redudase
- AKR1B1 and AKR1B10:
-
aldose redudases B1 and B10
- CRC:
-
colorectal cancer
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- RT-PCR:
-
reverse transcription with the subsequent PCR
- PCR-RT:
-
PCR in real time
References
Hyndman D., Bauman D.R., Heredia V.V., Penning T.M. 2003. The aldo-keto reductase superfamily homepage. Chem. Biol. Interact. 143/144, 621–631.
Jin Y., Penning T.M. 2007. Aldo-keto reductases and bioactivation/detoxication. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 47, 263–292.
Cao D., Fan S.T., Chung S.S. 1998. Identification and characterization of a novel human aldose reductase-like gene. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 11429–11435.
Yabe-Nishimura C. 1998. Aldose reductase in glucose toxicity: A potential target for the prevention of diabetic complications. Pharmacol. Rev. 50, 21–33.
Ko B., Ruepp B., Bohren K.M., Gabbay K.H., Chung S.S. 1997. Identification and characterization of multiple osmotic response sequences in the human aldose reductase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16431–16437.
Liu Z., Zhong L., Krishack P.A., Robbins S., Cao J.X., Zhao Yu., Chung S., Cao D. 2009. Structure and promoter characterization of aldo-keto reductase family 1 B10 gene. Gene. 437, 39–44.
Crosas B., Hyndman D.J., Gallego O., Martras S., Parés X., Flynn T.G., Farrés J. 2003. Human aldose reductase and human small intestine aldose reductase are efficient retinal reductases: Consequences for retinoid metabolism. Biochem. J. 373, 973–979.
Gallego O., Belyaeva O.V., Porté S., Ruiz F.X., Stetsenko A.V., Shabrova E.V., Kostereva N.V., Farrés J., Parés X., Kedishvili N.Y. 2006. Comparative functional analysis of human medium-chain dehydrogenases, short-chain dehydrogenases/reductases, and aldo-keto reductases with retinoids. Biochem. J. 399, 101–109.
Grimshaw C.E., Mathur E.J. 1989. Immunoquantitation of aldose reductase in human tissues. Anal. Biochem. 176, 66–71.
Hyndman D.J., Flynn T.G. 1998. Sequence and expression levels in human tissues of a new member of the aldo-keto reductase family. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1399, 198–202.
Penning T.M., Drury J.E. 2007. Human aldo-keto reductases: Functions, gene regulation, and single nucleotide polymorphisms. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 464, 241–250.
Fukumoto S., Yamauchi N., Moriguchi H., Hippo Y., Watanabe A., Shibahara J., Taniguchi H., Ishikawa S., Ito H., Yamamoto S., Iwanari H., Hironaka M., Ishikawa Y., Niki T., Sohara Y., Kodama T., Nishimura M., Fukayama M., Dosaka-Akita H., Aburatani H. 2005. Overexpression of the aldo-keto reductase family protein AKR1B10 is highly correlated with smokers’ nonsmall cell lung carcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 1776–1785.
Penning T.M. 2005. AKR1B10: A new diagnostic marker of non-small cell lung carcinoma in smokers. Clin. Cancer Res. 11, 1687–1690.
Ruiz F.X, Gallego O., Ardevol A., Moro A., Dominguez M., Alvarez S., Alvarez R., de Lera A.R., Rovira C., Fita I., Parés X., Farrés J. 2009. Aldo-keto reductases from the AKR1B subfamily: Retinoid specificity and control of cellular retinoic acid levels. Chem. Biol. Interact. 178, 171–177.
Mashkova T.D., Oparina N.I., Zinovyeva O.L., Kropotova E.S., Dubovaya V.I., Poltaraus A.V., Fridman M.V., Kopantsev E.P., Vinogradova T.M., Zinovyeva M.V., Laktionov K.K., Kasymova O.T., Zborovskaya I.V., Sverdlov E.D., Kisselev L.L. 2006. Transcription of TIMP3, DAPK1, and AKR1V10 in squamous-cell lung cancer. Mol. Biol. 40, 945–951.
Nagaraj N.S., Beckers S., Mensah J.K., Waigel S., Vigneswaran N., Zacharias W. 2006. Cigarette smoke condensate induces cytochromes P450 and aldo-keto reductases in oral cancer cells. Toxicol. Lett. 165, 182–194.
Scuric Z., Stain S.C., Anderson W.F., Hwang J.J. 1998. New member of aldose reductase family proteins over-expressed in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 27, 943–950.
Lee K.W., Ko B.C., Jiang Z., Cao D., Chung S.S. 2001. Overexpression of aldose reductase in liver cancers may contribute to drug resistance. Anticancer Drugs. 12, 129–132.
Yoshitake H., Takahashi M., Ishikawa H., Nojima M., Iwanari H., Watanabe A., Aburatani H., Yoshida K., Ishi K., Takamori K., Ogawa H., Hamakubo T., Kodama T., Araki Y. 2007. Aldo-keto reductase family 1, member B10 in uterine carcinomas: A potential risk factor of recurrence after surgical therapy in cervical cancer. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer. 17, 1300–1306.
Hyndman D., Flynn T.G. 1999. The aldo-keto reductases and their role in cancer. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 463, 427–434.
Jin J., Krishack P.A., Cao D. 2006. Role of aldo-keto reductases in development of prostate and breast cancer. Front Biosci. 11, 2767–2773.
Saraswat M., Mrudula T., Kumar P.U., Suneetha A., Rao T.S., Srinivasulu M., Reddy B. 2006. Overexpression of aldose reductase in human cancer tissues. Med. Sci. Monit. 12, CR525–CR529.
Jemal A., Siegel R., Ward E., Murray T., Xu J., Smigal C., Thun M.J. 2006. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 56, 36–30.
Manzeniuk O.Y., Malakho S.G., Pekhov V.M., Kosorukova I.S., Poltaraus A.V. 2006. Characterization of Russian universal kits for real-time PCR: Application to molecular oncodiagnosis. Mol. Biol. 40, 305–311.
Hackenberg M., Previti C., Luque-Escamilla P.L., Carpena P., Martinez-Aroza J., Oliver J.L. 2006. CpG-cluster: A distance-based algorithm for CpG-island detection. BMC Bioinform. 7, 446.
Lefrancois-Martinez A.M., Bertherat J., Val P., Tournaire C., Gallo-Payet N., Hyndman D., Veyssiere G., Bertagna X., Jean C., Martinez A. 2004. Decreased expression of cyclic adenosine monophosphate-regulated aldose reductase (AKR1B1) is associated with malignancy in human sporadic adrenocortical tumors. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 89, 3010–3019.
Camps J., Grade M., Nguyen O.T., Hormann P., Becker S., Hummon A.B., Rodriguez V., Chandrasekharappa S., Chen Y., Difilippantonio M.J., Becker H., Ghadimi B.M., Ried T. 2008. Chromosomal breakpoints in primary colon cancer at sites of structural variants in the genome. Cancer Res. 68, 1284–1295.
von Lintig J., Vogt K. 2000. Filling the gap in vitamin A research: Molecular identification of an enzyme cleaving beta-carotene to retinal. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 11915–11920.
Martin H.J., Maser E. 2009. Role of human aldo-keto-reductase AKR1B10 in the protection against toxic aldehydes. Chem. Biol. Interact. 178, 145–150.
Ames B.N. 1983. Dietary carcinogens and anticarcinogens. Oxygen radicals and degenerative diseases. Science. 221, 1256–1264.
Homann N., Tillonen J., Salaspuro M. 2000. Microbially produced acetaldehyde from ethanol may increase the risk of colon cancer via folate deficiency. Int. J. Cancer. 86, 169–173.
Zu X., Yan R., Robbins S., Krishack P.A., Liao D.F., Cao D. 2007. Reduced 293T cell susceptibility to acrolein due to aldose reductase-like-1 protein expression. Toxicol. Sci. 97, 562–528.
Yan R., Zu X., Ma J., Liu Z., Adeyanju M., Cao D. 2007. Aldo-keto reductase family 1B10 gene silencing results in growth inhibition of colorectal cancer cells: Implication for cancer intervention. Int. J. Cancer. 121, 2301–2306.
Kurtz A.J., Lloyd R.S. 2003. 1,N2-deoxyguanosine adducts of acrolein, crotonaldehyde, and trans-4-hydroxynonenal cross-link to peptides via Schiff base linkage. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5970–5976.
Hashimoto M., Sibata T., Wasada H., Toyokuni S., Uchida K. 2003. Structural basis of protein-bound endogenous aldehydes: Chemical and immunochemical characterizations of configurational isomers of a 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-histidine adduct. J. Biol. Chem. 278, 5044–5051.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Original Russian Text © E.S. Kropotova, R.A. Tychko, O.L. Zinov’eva, A.F. Zyryanova, S.L. Khankin, V.L. Cherkes, V.A. Aliev, S.F. Beresten, N.Yu. Oparina, T.D. Mashkova, 2010, published in Molekulyarnaya Biologiya, 2010, Vol. 44, No. 2, pp. 243–250.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kropotova, E.S., Tychko, R.A., Zinov’eva, O.L. et al. Downregulation of AKR1B10 expression in colorectal cancer. Mol Biol 44, 216–222 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893310020056
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0026893310020056