Abstract
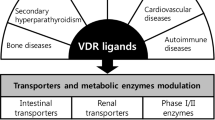
Experimental studies on the molecular regulation of human drug metabolism have revealed that vitamin D up-regulates transcription of several key enzymes, such as CYP3A4, through the vitamin D receptor pathway in intestinal and hepatic cells. Recent data suggest that this results in seasonal changes with higher clearance of orally administered drugs during periods with high UV-B radiation and vitamin D levels. Taken together, vitamin D status might contribute to inter- and intraindividual differences in drug metabolism, but the therapeutic impact of these findings remains to be established.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Hewison, Vitamin D and immune function: an overview, Proc. Nutr. Soc., 2012, 71, 50–61.
M. Zasloff, Fighting infections with vitamin D, Nat. Med., 2006, 12, 388–390.
J. H. O’Keefe, C. J. Lavie and M. F. Holick, Vitamin D supplementation for cardiovascular disease prevention, JAMA, J. Am. Med. Assoc., 2011, 306, 1546–1547; author reply 1547–1548.
C. Buttigliero, C. Monagheddu, P. Petroni, A. Saini, L. Dogliotti, G. Ciccone and A. Berruti, Prognostic role of vitamin D status and efficacy of vitamin D supplementation in cancer patients: a systematic review, Oncologist, 2011, 16, 1215–1227.
J. C. Fleet, M. DeSmet, R. Johnson and Y. Li, Vitamin D and cancer: a review of molecular mechanisms, Biochem. J., 2012, 441, 61–76.
L. Drocourt, J. C. Ourlin, J. M. Pascussi, P. Maurel and M. J. Vilarem, Expression of CYP3A4, CYP2B6, and CYP2C9 is regulated by the vitamin D receptor pathway in primary human hepatocytes, J. Biol. Chem., 2002, 277, 25125–25132.
J. Fan, S. Liu, Y. Du, J. Morrison, R. Shipman and K. S. Pang, Up-regulation of transporters and enzymes by the vitamin D receptor ligands, 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 and vitamin D analogs, in the Caco-2 cell monolayer, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 2009, 330, 389–402.
P. Schmiedlin-Ren, K. E. Thummel, J. M. Fisher, M. F. Paine, K. S. Lown and P. B. Watkins, Expression of enzymatically active CYP3A4 by Caco-2 cells grown on extracellular matrix-coated permeable supports in the presence of 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3, Mol. Pharmacol., 1997, 51, 741–754.
H. F. DeLuca, The vitamin D story: a collaborative effort of basic science and clinical medicine, FASEB J., 1988, 2, 224–236.
M. F. Holick, Vitamin D deficiency, N. Engl. J. Med., 2007, 357, 266–281.
R. Horst, S. Prapong, T. Reinhardt, N. Koszewski, J. Knutson and C. Bishop, Comparison of the relative effects of 1,24-dihydroxyvitamin D(2) [1,24-(OH)(2)D(2)], 1,24-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,24-(OH)(2)D(3)], and 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3) [1,25-(OH)(2)D(3)] on selected vitamin D-regulated events in the rat, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2000, 60, 701–708.
J. Ahn, K. Yu, R. Stolzenberg-Solomon, K. C. Simon, M. L. McCullough, L. Gallicchio, E. J. Jacobs, A. Ascherio, K. Helzlsouer, K. B. Jacobs, Q. Li, S. J. Weinstein, M. Purdue, J. Virtamo, R. Horst, W. Wheeler, S. Chanock, D. J. Hunter, R. B. Hayes, P. Kraft and D. Albanes, Genome-wide association study of circulating vitamin D levels, Hum. Mol. Genet., 2010, 19, 2739–2745.
J. B. Cheng, M. A. Levine, N. H. Bell, D. J. Mangelsdorf and D. W. Russell, Genetic evidence that the human CYP2R1 enzyme is a key vitamin D 25-hydroxylase, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2004, 101, 7711–7715.
D. E. Prosser and G. Jones, Enzymes involved in the activation and inactivation of vitamin D, Trends Biochem. Sci., 2004, 29, 664–673.
C. Carlberg, I. Bendik, A. Wyss, E. Meier, L. J. Sturzenbecker, J. F. Grippo and W. Hunziker, Two nuclear signalling pathways for vitamin D, Nature, 1993, 361, 657–660.
C. Carlberg and S. Seuter, A genomic perspective on vitamin D signaling, Anticancer Res., 2009, 29, 3485–3493.
T. T. Wang, L. E. Tavera-Mendoza, D. Laperriere, E. Libby, N. B. MacLeod, Y. Nagai, V. Bourdeau, A. Konstorum, B. Lallemant, R. Zhang, S. Mader and J. H. White, Large-scale in silico and microarray-based identification of direct 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 target genes, Mol. Endocrinol., 2005, 19, 2685–2695.
Z. Wang, Y. S. Lin, X. E. Zheng, T. Senn, T. Hashizume, M. Scian, L. J. Dickmann, S. D. Nelson, T. A. Baillie, M. F. Hebert, D. Blough, C. L. Davis and K. E. Thummel, An inducible cytochrome P450 3A4-dependent vitamin D catabolic pathway, Mol. Pharmacol., 2012, 81, 498–509.
T. Hashizume, Y. Xu, M. A. Mohutsky, J. Alberts, C. Hadden, T. F. Kalhorn, N. Isoherranen, M. C. Shuhart and K. E. Thummel, Identification of human UDP-glucuronosyltransferases catalyzing hepatic 1alpha,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 conjugation, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2008, 75, 1240–1250.
K. T. Kivisto, G. Bookjans, M. F. Fromm, E. U. Griese, P. Munzel and H. K. Kroemer, Expression of CYP3A4, CYP3A5 and CYP3A7 in human duodenal tissue, Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol., 1996, 42, 387–389.
J. C. Kolars, P. Schmiedlin-Ren, J. D. Schuetz, C. Fang and P. B. Watkins, Identification of rifampin-inducible P450IIIA4 (CYP3A4) in human small bowel enterocytes, J. Clin. Invest., 1992, 90, 1871–1878.
M. F. Paine, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, J. D. Perkins, C. L. Marsh, J. P. McVicar, D. M. Barr, B. S. Gillies and K. E. Thummel, First-pass metabolism of midazolam by the human intestine, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. (St. Louis), 1996, 60, 14–24.
A. K. Daly, Significance of the minor cytochrome P450 3A isoforms, Clin. Pharmacokinet., 2006, 45, 13–31.
M. F. Paine, M. Khalighi, J. M. Fisher, D. D. Shen, K. L. Kunze, C. L. Marsh, J. D. Perkins and K. E. Thummel, Characterization of interintestinal and intraintestinal variations in human CYP3A-dependent metabolism, J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther., 1997, 283, 1552–1562.
O. von Richter, O. Burk, M. F. Fromm, K. P. Thon, M. Eichelbaum and K. T. Kivisto, Cytochrome P450 3A4 and P-glycoprotein expression in human small intestinal enterocytes and hepatocytes: a comparative analysis in paired tissue specimens, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 2004, 75, 172–183.
K. E. Thummel, C. Brimer, K. Yasuda, J. Thottassery, T. Senn, Y. Lin, H. Ishizuka, E. Kharasch, J. Schuetz and E. Schuetz, Transcriptional control of intestinal cytochrome P-4503A by 1alpha,25-dihydroxy vitamin D3, Mol. Pharmacol., 2001, 60, 1399–1406.
P. Pavek, K. Pospechova, L. Svecova, Z. Syrova, L. Stejskalova, J. Blazkova, Z. Dvorak and J. Blahos, Intestinal cell-specific vitamin D receptor (VDR)-mediated transcriptional regulation of CYP3A4 gene, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2010, 79, 277–287.
P. D. Thompson, P. W. Jurutka, G. K. Whitfield, S. M. Myskowski, K. R. Eichhorst, C. E. Dominguez, C. A. Haussler and M. R. Haussler, Liganded VDR induces CYP3A4 in small intestinal and colon cancer cells via DR3 and ER6 vitamin D responsive elements, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun., 2002, 299, 730–738.
A. R. Webb, L. Kline and M. F. Holick, Influence of season and latitude on the cutaneous synthesis of vitamin D3: exposure to winter sunlight in Boston and Edmonton will not promote vitamin D3 synthesis in human skin, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab., 1988, 67, 373–378.
J. D. Lindh, M. L. Andersson, E. Eliasson, L. Bjorkhem-Bergman, Seasonal variation in blood drug concentrations and a potential relationship to vitamin D, Drug Metab. Dispos.: Biolog. Fate Chem., 2011, 39, 933–937.
J. K. Virtanen, T. Nurmi, S. Voutilainen, J. Mursu and T. P. Tuomainen, Association of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D with the risk of death in a general older population in Finland, Eur. J. Nutr., 2011, 50, 305–312.
R. K. Thirumaran, J. K. Lamba, R. B. Kim, B. L. Urquhart, J. C. Gregor, N. Chande, Y. Fan, A. Qi, C. Cheng, K. E. Thummel, S. D. Hall and E. G. Schuetz, Intestinal CYP3A4 and midazolam disposition in vivo associate with VDR polymorphisms and show seasonal variation, Biochem. Pharmacol., 2012, 84, 104–112.
T. Kantola, K. T. Kivisto and P. J. Neuvonen, Effect of itraconazole on the pharmacokinetics of atorvastatin, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 1998, 64, 58–65.
J. B. Schwartz, Effects of vitamin D supplementation in atorvastatin-treated patients: a new drug interaction with an unexpected consequence, Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 2009, 85, 198–203.
M. Karlgren, A. Vildhede, U. Norinder, J. R. Wisniewski, E. Kimoto, Y. Lai, U. Haglund and P. Artursson, Classification of inhibitors of hepatic organic anion transporting polypeptides (OATPs): influence of protein expression on drug–drug interactions, J. Med. Chem., 2012, 55, 4740–4763.
J. J. Eloranta, C. Hiller, M. Juttner, G. A. Kullak-Ublick, The SLCO1A2 gene, encoding the human organic anion transporting polypeptide 1A2 (OATP1A2), is transactivated by the vitamin D receptor (VDR), Mol. Pharmacol., 2012, 82, 37–46.
R. Persson, A. H. Garde, A. M. Hansen, K. Osterberg, B. Larsson, P. Orbaek and B. Karlson, Seasonal variation in human salivary cortisol concentration, Chronobiol. Int., 2008, 25, 923–937.
K. Bodin, U. Lindbom and U. Diczfalusy, Novel pathways of bile acid metabolism involving CYP3A4, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 2005, 1687, 84–93.
B. Berg, G. Helm, L. Petersohn and N. Tryding, Cholestasis of pregnancy. Clinical and laboratory studies, Acta Obstetr. Gynecol. Scand., 1986, 65, 107–113.
E. Wikstrom Shemer and H. U. Marschall, Decreased 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D levels in women with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy, Acta Obstetr. Gynecol. Scand., 2010, 89, 1420–1423.
M. K. DeGorter, C. Q. Xia, J. J. Yang and R. B. Kim, Drug transporters in drug efficacy and toxicity, Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol., 2012, 52, 249–273.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contribution to the Vitamin D Update collected papers.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lindh, J.D., Björkhem-Bergman, L. & Eliasson, E. Vitamin D and drug-metabolising enzymes. Photochem Photobiol Sci 11, 1797–1801 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1039/c2pp25194a
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/c2pp25194a