Abstract
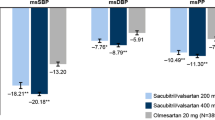
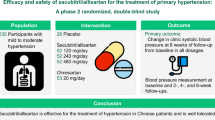
The therapeutic profile of olmesartan medoxomil, which is a recently developed angiotensin II (A II) receptor blocker, has been compared with four commonly used antihypertensive therapeutic drugs (atenolol, captopril, felodipine and losartan) in five separate multicentre, randomised, double-blind, parallel-group, phase III trials. The trials were designed to compare the efficacy of individually optimised dosages of olmesartan medoxomil and the comparator agent. The primary efficacy variable in all trials was the mean change from baseline to week 12 in trough mean sitting diastolic blood pressure (DBP). Olmesartan medoxomil (10–20 mg once daily (o.d.)) showed similar efficacy to atenolol (50–100 mg o.d.), both in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension and, when given together with hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) 25 mg o.d., in patients with moderate-to-severe hypertension. Olmesartan medoxomil (20–40 mg o.d.) was also similar in efficacy to felodipine (5–10 mg o.d.) in reducing BP in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. Compared with captopril (12.5–50 mg twice daily (b.i.d.)) and losartan (50–100 mg o.d.), in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension, olmesartan medoxomil (5–20 mg o.d. and 10–20 mg o.d., respectively) was significantly superior in terms of lowering DBP from baseline to week 12. In terms of the secondary efficacy variable, which was mean change from baseline to week 12 in trough mean sitting systolic BP, olmesartan showed significant superiority to atenolol, captopril and losartan in patients with mild-to-moderate hypertension. In the longer term, compared with losartan, a lower percentage of olmesartan-treated patients required concomitant HCTZ after 12 weeks of therapy. Olmesartan was well tolerated in all studies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Püchler K, Laeis P, Stumpe KO . Blood pressure response, but not adverse event incidence, correlates with dose of angiotensin II antagonist J Hypertens 2001 19 (Suppl 1): S41–S48
Thurman PA . Angiotensin II antagonism and the heart: valsartan in left ventricular hypertrophy Cardiology 1999 91 (Suppl 1): 3–7
Birkenhager WH, de Leeuw PW . Non-peptide angiotensin type I receptor antagonists in the treatment of hypertension J Hypertens 1999 17: 873–881
Gallagher M . Angiotensin II antagonists lead the way in hypertension management Inpharm 1998 1143: 13–15
De Leeuw PW . How do angiotensin II receptor antagonists affect blood pressure? Am J Cardiol 1999 84: 5K–6K
Mazzolai L, Burnier M . Comparative safety and tolerability of angiotensin II receptor antagonists Drug Safety 1999 21: 23–33
Brunner H . The new oral angiotensin II antagonist olmesartan medoxomil: a concise overview J Hum Hypertens 2002 16 (Suppl 2): S13–S16
Laeis P, Püchler K, Kirch W . The pharmacokinetic and metabolic profile of olmesartan medoxomil limits the risk of clinically relevant drug interactions J Hypertens 2001 19 (Suppl 1): S21–S32
Ball KJ, Williams PA, Stumpe KO . Relative efficacy of an angiotensin II antagonist compared with other antihypertensive agents. Olmesartan medoxomil versus antihypertensives J Hypertens 2001 19 (Suppl 1): S49–S56
Oparil S . Comparative antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan: comparison with other angiotensin II receptor antagonists J Hum Hypertens 2002 16 (Suppl 2): S17–S23
Oparil S et al. Comparative efficacy of olmesartan, losartan, valsartan, and irbesartan in the control of essential hypertension J Clin Hypertens 2001 3: 283–291
Flack JM et al. Blood pressure and mortality among men with prior myocardial infarction: Multiple Risk Factor Intervention Trial Research Group Circulation 1995 92: 2437–2445
Neutel JM . Safety and efficacy of angiotensin II receptor antagonists Am J Cardiol 1999 84: 13K–17K
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stumpe, K., Ludwig, M. Antihypertensive efficacy of olmesartan compared with other antihypertensive drugs. J Hum Hypertens 16 (Suppl 2), S24–S28 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001395
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001395
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Monotherapy and Dual Combination Therapies Based on Olmesartan: A Comprehensive Strategy to Improve Blood Pressure Control
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention (2017)
-
Management of Hypertension Using Olmesartan Alone or in Combination
Cardiology and Therapy (2017)
-
Olmesartan medoxomil: a guide to its use as monotherapy or in fixed-dose combinations with amlodipine and/or hydrochlorothiazide
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives (2016)
-
Patient Cases: 1. A Patient with Apparent Compliance
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention (2015)
-
Treatment of hypertension with olmesartan medoxomil, alone and in combination with a diuretic: an update
Journal of Human Hypertension (2007)