Abstract
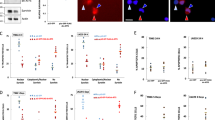
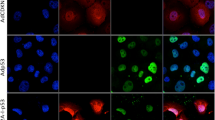
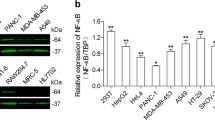
It has been demonstrated that survivin, a novel member of the inhibitor of apoptosis (IAP) protein family, is expressed in human cancers but is undetectable in normal differentiated tissues. We employed a recombinant adenoviral vector (reAdGL3BSurvivin) in which a tumor-specific survivin promoter and a luciferase reporter gene were inserted into the E1-deleted region of adenovirus vector. Luciferase activity was measured in both multiple tumor cell lines and two primary melanoma cells infected with reAdGL3BSurvivin. Human fibroblast and mammary epithelial cell lines were used as negative controls. A reAdGL3CMV, containing the CMV promoter and luciferase gene, was used as a positive control to normalize the luciferase activity generated by the survivin promoter. Our data revealed that the survivin promoter showed high activity in both established tumor cell lines and the primary melanoma cells. In contrast, the in vivo studies indicated that the activities of survivin promoter were extremely low in the major mouse organs. The survivin promoter appears to be a promising tumor-specific promoter exhibiting a “tumor on” and “liver off” profile, and therefore, it may prove to be a good candidate for transcriptional targeting of cancer gene therapy in a wide variety of tumors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bp:
-
base pairs
- CMV:
-
cytomegalovirus
- Cox-2:
-
cyclooxygenase 2
- MOI:
-
multiplicity of infection
- PFU:
-
plaque-forming units
- vp:
-
viral particles
- TSP:
-
tumor-specific promoter
References
Casado E, Nettelbeck DM, Gomez-Navarro J, et al. Transcriptional targeting for ovarian cancer gene therapy. Gynecol Oncol. 2001;82:229–237.
Nettelbeck DM, Jerome V, Muller R . Gene therapy: designer promoters for tumour targeting. Trends Genet. 2000;16:174–181.
Quan S, Pan G, Lu C, et al. Experimental studies in vitro on the alpha-fetoprotein-specific promoter mediated target gene therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao. 1999;21:111–117.
Easty DJ, Bennett DC . Protein tyrosine kinases in malignant melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2000;10:401–411.
Lee SE, Jin RJ, Lee SG, et al. Development of a new plasmid vector with PSA-promoter and enhancer expressing tissue-specificity in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Anticancer Res. 2000;20:417–422.
Yamamoto M, Alemany R, Adachi Y, et al. Characterization of the cyclooxygenase-2 promoter in an adenoviral vector and its application for the mitigation of toxicity in suicide gene therapy of gastrointestinal cancers. Mol Ther. 2001;3:385–394.
Adachi Y, Reynolds PN, Yamamoto M, et al. A midkine promoter-based conditionally replicative adenovirus for treatment of pediatric solid tumors and bone marrow tumor purging. Cancer Res. 2001;61:7882–7888.
Zhu ZB, Makhija SK, Lu B, et al. Transcriptionally targeted recombinant adenoviral vector expression in tumors through the CXCR4 tumor specific promoter. Gene Therapy. 2003; (in press).
Müller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al. Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis. Nature. 2001;410:50–56.
Loetscher M, Geiser T, O'Reilly T, et al. Cloning of a human seven-transmembrane domain receptor, LESTR, that is highly expressed in leukocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994;269:232–237.
Bleul CC, Farzan M, Choe H, et al. The lymphocyte chemoattractant SDF-1 is a ligand for LESTR/fusin and blocks HIV-1 entry. Nature. 1996;382:829–833.
D'Apuzzo M, Rolink A, Loetscher M, et al. The chemokine SDF-1, stromal cell-derived factor 1, attracts early stage B cell precursors via the chemokine receptor CXCR4. Eur J Immunol. 1997;27:1788–1793.
Ayehunie S, Garcia-Zepeda EA, Hoxie JA, et al. Human immunodeficiency virus-1 entry into purified blood dendritic cells through CC and CXC chemokine coreceptors. Blood. 1997;90:1379–1386.
Altieri DC . Xa receptor EPR-1. FASEB J. 1995;9:860–865.
Uren AG, Pakusch M, Hawkins CJ, et al. Cloning and expression of apoptosis inhibitory protein homologs that function to inhibit apoptosis and/or bind tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:4974–4978.
Takahashi R, Deveraux Q, Tamm I, et al. A single BIR domain of XIAP sufficient for inhibiting caspases. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:7787–7790.
Duckett CS, Nava VE, Gedrich RW, et al. A conserved family of cellular genes related to the baculovirus IAP gene and encoding apoptosis inhibitors. EMBO J. 1996;15:2685–2694.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Altieri DC . A novel anti-apoptosis gene, survivin, expressed in cancer and lymphoma. Nat Med. 1997;3:917–921.
Adida C, Crotty PL, McGrath J, et al. Developmentally regulated expression of the novel cancer anti-apoptosis gene survivin in human and mouse differentiation. Am J Pathol. 1998;152:43–49.
Bao R, Connolly DC, Murphy M, et al. Activation of cancer-specific gene expression by the survivin promoter. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2002;94:522–528.
Nasu S, Yagihashi A, Izawa A, et al. Survivin mRNA expression in patients with breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2002;22:1839–1843.
Sarela AI, Verbeke CS, Ramsdale J, et al. Expression of survivin, a novel inhibitor of apoptosis and cell cycle regulatory protein, in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;86:886–889.
Ikeguchi M, Kaibara N . survivin messenger RNA expression is a good prognostic biomarker for oesophageal carcinoma. Br J Cancer. 2002;87:883–887.
Das A, Tan WL, Teo J, Smith DR . Expression of survivin in primary glioblastomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2002;128:302–306.
Zaffaroni N, Pennati M, Colella G, et al. Expression of the anti-apoptotic gene survivin correlates with taxol resistance in human ovarian cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2002;59:1406–1412.
He TC, Zhou S, da Costa LT, et al. A simplified system for generating recombinant adenoviruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998;95:2509–2514.
Li F, Altieri DC . Transcriptional analysis of human survivin gene expression. Biochem J. 1999;344 Part 2:305–311.
Chakravarti A, Noll E, Black PM, et al. Quantitatively determined survivin expression levels are of prognostic value in human gliomas. J Clin Oncol. 2002;20:1063–1068.
Li F . Survivin study: what is the next wave. Journal of CellularPhysiology. 2003;197:8–29.
Asanuma K, Kobayashi D, Furuya D, et al. A role for survivin in radioresistance of pancreatic cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 2002;93:1057–1062.
Altieri DC . Validating survivin as a cancer therapeutic target. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:46–54.
Ambrosini G, Adida C, Sirugo G, et al. Induction of apoptosis and inhibition of cell proliferation by survivin gene targeting. J Biol Chem. 1998;273:11177–11182.
Tamm I, Wang Y, Sausville E, et al. IAP-family proteinsurvivin inhibits caspase activity and apoptosis induced by Fas (CD59), Bax, caspases, and anticancerdrugs. Cancer Res. 1998;58:5315–5320.
Yamamoto T, Manome Y, Nakamura M, et al. Downregulation of survivin expression by induction of the effector cell protease receptor-1 reduces tumor growth potential and results in an increased sensitivity to anticancer agents in human colon cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2002;38:2316–2324.
Andersen MH, Pedersen LO, Becker JC, et al. Identification of a cytotoxic T lymphocyte response to the apoptosis inhibitor protein survivin in cancer patients. Cancer Res. 2001;61:869–872.
van der Eb MM, Cramer SJ, Vergouwe Y, et al. Severe hepatic dysfunction after adenovirus-mediated transfer of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene and ganciclovir administration. Gene Ther. 1998;5:451–458.
Alvarez RD, Barnes MN, Gomez-Navarro J, et al. A cancer gene therapy approach utilizing an anti-erbB-2 single-chain antibody-encoding adenovirus (AD21): a phase I trial. Clin Cancer Res. 2000;6:3081–3087.
Nettelbeck DM, Rivera AA, Davydova RJ, et al. Cox2 promoter for tumor-specific targeting for adenovirual vector to melanoma. Melanoma Res. 2003;13:287–292.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by research grants from the National Institutes of Health: R01 CA83821, R01 HL67962, K12 HD01261-02 (WRHR) 5P50 CA83591 (Ovarian SPORE Developmental Grant.
We thank Dr Suresh Boppana for the control cell line, HFBC, and Dr D Dieckmann for two primary melanoma cells.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, Z., Makhija, S., Lu, B. et al. Transcriptional targeting of tumors with a novel tumor-specific survivin promoter. Cancer Gene Ther 11, 256–262 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700679
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cgt.7700679
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Engineering tumor-specific gene nanomedicine to recruit and activate T cells for enhanced immunotherapy
Nature Communications (2023)
-
Precise tumor immune rewiring via synthetic CRISPRa circuits gated by concurrent gain/loss of transcription factors
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Molecular Bio-Imaging Probe for Non-Invasive Differentiation Between Human Leiomyoma Versus Leiomyosarcoma
Reproductive Sciences (2020)
-
Survivin a radiogenetic promoter for glioblastoma viral gene therapy independently from CArG motifs
Clinical and Translational Medicine (2017)
-
Exploiting the Intron-splicing Mechanism of Insect Cells to Produce Viral Vectors Harboring Toxic Genes for Suicide Gene Therapy
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids (2012)