Abstract
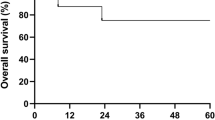
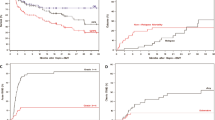
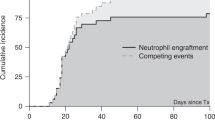
Multi-agent immunosuppressive therapy has produced improved survival for severe acquired aplastic anemia in children. Recently, some investigators have suggested that immunosuppressive therapy may replace bone marrow transplantation as first-line therapy for this disorder. To assess its validity, we compared the outcomes of bone marrow transplantation vsimmunosuppressive therapy in one institution from 1987 to 1997. We studied 46 consecutive patients less than 18 years of age who presented between January 1987 and April 1997. Inherited marrow failure syndromes and myelodysplastic syndromes were excluded. Patients received immunosuppressive therapy vs bone marrow transplantation based on availability of HLA-matched donors. The main outcome measures were survival, complete marrow and hematological remission, or partial remission but achieving independence from transfusional support. Twenty patients received multi-agent immunosuppressive therapy (cyclosporine, antithymocyte globulin and methylprednisolone); 11 attained complete remission and three partial remission for a transfusion-independent survival of 70%. Six patients died of infectious and hemorrhagic complications. Twenty-six patients were transplanted and 24 (93%) achieved complete remission; one achieved a PR, 25 remain transfusion independent with a median follow-up of 5.9 years or 70 months. One patient developed AML 34 months after successful transplant and one patient died due to graft failure and complications of transplant. There has been a striking improvement in survival for pediatric patients treated with multi-agent immunosuppression in the last decade. However, transplantation results have also improved and this remains the definitive first-line therapy for severe acquired aplastic anemia in this age group. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 26, 1149–1156.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
The International Agranulocytosis and Aplastic Anemia Study . Incidence of aplastic anemia: the relevance of diagnostic criteria Blood 1987 70: 1718–1721
Young NS, Alter BP . Definitive treatment of acquired aplastic anemia. In: Young NS, Alter BP (eds). Aplastic Anemia: Acquired and Inherited WB Saunders Co: Philadelphia 1993 pp 159–200
Thomas ED, Storb R, Fefer A et al. Aplastic anemia treated by bone marrow transplantation Lancet 1972 1: 284–289
Camitta BM, Thomas ED, Nathan DG et al. A prospective study of androgens and bone marrow transplantation for treatment of severe aplastic anemia Blood 1979 53: 504–514
Mathé G, Amiel JL, Schwarzenberg L et al. Bone marrow graft in man after conditioning by antilymphocytic serum Br Med J 1970 2: 131–136
Speck B, Gluckman E, Haak HL et al. Treatment of aplastic anemia by antithymocyte globulin with and without allogeneic bone marrow infusions Lancet 1977 2: 1145–1148
Speck B, Gratwohl A, Nissen C et al. Treatment of severe aplastic anemia Exp Hematol 1986 14: 126–132
Young N, Griffith P, Brittain E et al. A multicenter trial of antithymocyte globulin in aplastic anemia and related diseases Blood 1988 72: 1861–1868
Bayever E, Champlin R, Ho W et al. Comparison between bone marrow transplantation and antithymocyte globulin in treatment of young patients with aplastic anemia J Pediatr 1984 105: 920–925
Locasciulli A, van't Veer L, Bacigalupo A et al. Treatment with marrow transplantation or immunosuppression of childhood acquired severe aplastic anemia: a report from the EBMT SAA Working Party Bone Marrow Transplant 1990 6: 211–217
Halperin DS, Grisaru D, Freedman MH et al. Severe aplastic anemia in children: 11-year experience with bone marrow transplantation and immunosuppression therapy Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1989 11: 304–309
Lawlor ER, Anderson RA, Davis DH et al. Immunosuppressive therapy: a potential alternative to bone marrow transplantation as initial therapy for acquired severe aplastic anemia in childhood? J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1997 19: 115–123
Gillio A, Boulad F, Small T et al. Comparison of long-term outcome of children with severe aplastic anemia treated with immunosuppression versus bone marrow transplantation Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 1997 3: 18–24
Bacigalupo A, Broccia G, Corda W et al. Antilymphocyte globulin, cyclosporin, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with acquired severe aplastic anemia (SAA): a pilot study of the A+EBMT SAA working party Blood 1995 5: 1348–1353
Kaplan EL, Meier P . Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations J Am Stat Assoc 1958 53: 457–481
Peto R, Pike MC, Armitage P et al. Design and analysis of randomized clinical trials requiring prolonged observation of each patient, II: analysis and examples Br J Cancer 1977 35: 1–39
Mantel N, Haenszel W . Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease J Natl Cancer Inst 1959 22: 719–748
Kalbfleisch JD, Prentice RL . The Statistical Analysis of Failure Time Data Wiley: New York 1980 p 169
Gray RJ . A class of K-sample tests for comparing the cumulative incidence of a competing risk Ann Stat 1988 16: 1141–1154
Sanders JE, Whitehead J, Storb R et al. Bone marrow transplantation experience for children with aplastic anemia Pediatr 1986 77: 179–186
Gluckman E, Socie G, Devergie A et al. Bone marrow transplantation in 107 patients with severe aplastic anemia using cyclophosphamide and thoraco-abdominal irradiation for conditioning: long-term followup Blood 1991 78: 2451–2455
Bortin MM, Gale RP, Rimm AA . Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for 144 patients with severe aplastic anemia JAMA 1981 245: 1132–1139
Hows JM, Palmer S, Gordon-Smith EC . Use of cyclosporin A in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia Transplantation 1982 33: 382–386
Storb R, Doney KC, Thomas ED et al. Marrow transplantation with or without donor buffy coat cells for 65 transfused aplastic anemia patients Blood 1982 59: 236–246
Feig SA, Champlin R, Arensen E et al. Improved survival following bone marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia Br J Haematol 1983 54: 509–517
Ramsay WKC, Kim TH, Nesbit ME et al. Total lymphoid irradiation and cyclophosphamide as preparation of bone marrow transplantation in severe aplastic anemia Blood 1980 55: 344–346
Storb R, Deeg HJ, Farewell V et al. Marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: methotrexate alone compared with a combination of methotrexate and cyclosporin for prevention of acute graft versus host disease Blood 1986 69: 119–126
Gluckman E, Devergie A, Meletis J et al. Bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: report of 97 consecutive patients Bone Marrow Transplant 1987 2: 101–104
Anasetti C, Storb R, Longton G et al. Donor buffy coat cell infusion after marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia Blood 1988 72: 1099–1100
Storb R, Deeg HJ, Pepe M et al. Graft-versus-host disease prevention by methotrexate combined with cyclosporin compared to methotrexate alone in patients given marrow grafts for severe aplastic anemia: long-term followup of a controlled trial Br J Haematol 1989 72: 567–572
Bunin N, Leahey A, Kamani N et al. Bone marrow transplantation in pediatric patients with severe aplastic anemia: cyclophosphamide and antithymocyte globulin conditioning followed by recombinant human granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1996 18: 68–71
Storb R, Etzioni R, Anasetti C et al. Cyclophosphamide combined with antithymocyte globulin in preparation for allogeneic bone marrow transplants in patients with aplastic anemia Blood 1994 84: 941–949
May WS, Sensenbrenner LL, Burns WH et al. BMT for severe aplastic anemia using cyclosporin Bone Marrow Transplant 1993 11: 459–464
Bacipalupo A, Brand R, Oneto R et al. Treatment of acquired severe aplastic anemia: bone marrow transplantation compared with immunosuppressive therapy – the European group for blood and marrow transplantation experience Semin Hematol 2000 37: 69–80
McCann SR, Bacigalupo A, Gluckman E et al. Graft rejection and second bone marrow transplants for acquired aplastic anemia: a report form the aplastic anemia working party of the European Bone Marrow Transplant Group Bone Marrow Transplant 1994 13: 233–237
Gluckman E, Horowitz MM, Champlin RE et al. Bone marrow transplantation for severe aplastic anemia: influence of conditioning and graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis regimens on outcome Blood 1992 79: 269–275
Champlin RE, Horowitz MM, van Bekkum DW et al. Graft failure following bone marrow transplantation for severeaplastic anemia: risk factors and treatment results Blood 1989 73: 606–613
Sanders JE, Storb R, Anasetti C et al. Marrow transplant experience for children with severe aplastic anemia Am J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1994 16: 43–49
Horstmann M, Stockschlader M, Kabisch H et al. Cyclo-phosphamide/antithymocyte globulin conditioning of patients with severe aplastic anemia transplanted with bone marrow from HLA-identical related donors Ann Intern Med 1997 126: 116–122
Deeg HJ, Socie G, Shoch G et al. Malignancies after marrow transplantation for aplastic anemia and Fanconi anemia: a joint Seattle and Paris analysis of results in 700 patients Blood 1996 87: 386–392
Socie G, Henry-Amar M, Bacigalupo A et al. Malignant tumours occurring after treatment of aplastic anemia New Engl J Med 1993 329: 1152–1157
Hinterberger-Fischer M, Hocker P, Lechner K et al. Oral cyclosporin A is effective treatment for untreated and also for previously immunosuppressed patients with severe bone marrow failure Eur J Haematol 1989 43: 136–142
Leonard EM, Raefsky E, Griffith P et al. Cyclosporin therapy of aplastic anemia, congenital and acquired red cell aplasia Br J Haematol 1989 72: 278–284
Gluckman E, Esperou-Boudreau H, Baruchel A et al. Multicenter randomized study comparing cyclosporin A alone and antithymocyte globulin with prednisone for the treatment of severe aplastic anemia Blood 1992 79: 2540–2546
Frickhofen N, Kaltwasser JP, Schrezenmeier H et al. Treatment of aplastic anemia with antilymphocyte globulin and methylprednisolone with or without cyclosporine New Engl J Med 1991 324: 1297–1304
Schrezenmeier H, Marin P, Raghavachar A et al. Relapse of aplastic anemia after immunosuppressive treatment: a report from the European Bone Marrow Transplantation Group SAA Working Party Br J Haematol 1993 85: 371–377
Bacigalupo A, Hows J, Gluckman E et al. Bone marrow transplantation versus immunosuppression for the treatment of severe aplastic anaemia (SAA): a report of the EBMT SAA Working Party Br J Haematol 1988 70: 177–182
Doney K, Leisenring W, Storb R et al. Primary treatment of acquired aplastic anemia: outcomes with bone marrow transplantation and immunosuppressive therapy Ann Intern Med 1997 126: 107–115
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fouladi, M., Herman, R., Rolland-Grinton, M. et al. Improved survival in severe acquired aplastic anemia of childhood. Bone Marrow Transplant 26, 1149–1156 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702699
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702699
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Allo-HSCT compared with immunosuppressive therapy for acquired aplastic anemia: a system review and meta-analysis
BMC Immunology (2020)
-
Immunosuppressive Treatment of Acquired Aplastic Anemia and Immune-Mediated Bone Marrow Failure Syndromes
International Journal of Hematology (2002)