Abstract
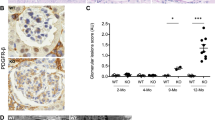
The autoimmune-prone BXSB/MpJ-Yaa mouse is a model of membranous proliferative glomerulonephritis (MPGN). Severe MPGN has been reported only in male BXSB/MpJ-Yaa mice because of the Y-linked autoimmune accelerator (Yaa) locus. However, we show that female BXSB/MpJ mice develop age-related MPGN without Yaa. Female BXSB/MpJ mice clearly developed MPGN characterized by increased mesangial cells, thickening of the glomerular basement membrane (GBM), double contouring and spike formation of GBM with T-cell infiltrations and podocyte injuries corresponding with increased autoantibody production and albuminuria. Analysis of the renal levels of the Fc gamma receptor (Fcgr) and interferon-activated gene 200 (Ifi200) family genes, which are MPGN candidate genes localized to the telomeric region of chromosome 1 (Chr.1), showed that Fcgr2b levels decreased, whereas Fcgr3 and Ifi202b levels increased in female BXSB/MpJ mice compared with healthy C57BL/6 mice. Furthermore, in isolated glomeruli, microarray analysis revealed that Fcgr3, Fcgr4 and Ifi202b expression was higher in male BXSB/MpJ-Yaa mice than in male BXSB/MpJ mice. These findings indicate that the BXSB/MpJ-type genome causes age-related MPGN with significant contribution from the telomeric region of Chr.1, and Yaa enhances the expression of genes localizing to this locus, thereby leading to severe MPGN in male mice.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $19.83 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Accession codes
References
Borchers AT, Leibushor N, Naguwa SM, Cheema GS, Shoenfeld Y, Gershwin ME . Lupus nephritis: a critical review. Autoimmun Rev 2012; 12: 174–194.
Henry T, Mohan C . Systemic lupus erythematosus—recent clues from congenic strains. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2005; 53: 207–212.
Nguyen C, Limaye N, Wakeland EK . Susceptibility genes in the pathogenesis of murine lupus. Arthritis Res 2002; 4: 255–263.
Ichii O, Konno A, Sasaki N, Endoh D, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y . Autoimmune glomerulonephritis induced in congenic mouse strain carrying telomeric region of chromosome 1 derived from MRL/MpJ. Histol Histopathol 2008; 23: 411–422.
Takai T . Fc receptors and their role in immune regulation and autoimmunity. J Clin Immunol 2005; 25: 1–18.
Reth M . Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature 1989; 338: 383–384.
Ravetch JV, Bolland S . IgG Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol 2001; 19: 275–290.
Ichii O, Konno A, Sasaki N, Endoh D, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y . Altered balance of inhibitory and active Fc gamma receptors in murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2008; 74: 339–347.
Choubey D . Interferon-inducible Ifi200-family genes as modifiers of lupus susceptibility. Immunol Lett 2012; 147: 10–17.
Zimmerman M, Yang D, Hu X, Liu F, Singh N, Browning D et al. IFN-γ upregulates survivin and Ifi202 expression to induce survival and proliferation of tumor-specific T cells. PLoS One 2010; 5: e14076.
Ludlow LE, Purton LE, Klarmann K, Gough DJ, Hii LL, Trapani JA et al. The role of p202 in regulating hematopoietic cell proliferation and differentiation. J Interferon Cytokine Res 2008; 28: 5–11.
Haywood ME, Rose SJ, Horswell S, Lees MJ, Fu G, Walport MJ et al. Overlapping BXSB congenic intervals, in combination with microarray gene expression, reveal novel lupus candidate genes. Genes Immun 2006; 7: 250–263.
Ichii O, Kamikawa A, Otsuka S, Hashimoto Y, Sasaki N, Endoh D et al. Overexpression of interferon-activated gene 202 (Ifi202) correlates with the progression of autoimmune glomerulonephritis associated with the MRL chromosome 1. Lupus 2010; 19: 897–905.
Merino R, Fossati L, Izui S . The lupus-prone BXSB strain: the Yaa gene model of systemic lupus erythematosus. Springer Semin Immunopathol 1992; 14: 141–157.
Kimura J, Ichii O, Otsuka S, Kanazawa T, Namiki Y, Hashimoto Y et al. Quantitative and qualitative urinary cellular patterns correlate with progression of murine glomerulonephritis. PLoS One 2011; 6: e16472.
Kimura J, Ichii O, Otsuka S, Sasaki H, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y . Close relations between podocyte injuries and membranous proliferative glomerulonephritis in autoimmune murine models. Am J Nephrol 2013; 38: 27–38.
Izui S, Higaki M, Morrow D, Merino R . The Y chromosome from autoimmune BXSB/MpJ mice induces a lupus-like syndrome in (NZW × C57BL/6)F1 male mice, but not in C57BL/6 male mice. Eur J Immunol 1988; 18: 911–915.
Oke V, Wahren-Herlenius M . Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: clinical aspects and molecular pathogenesis. J Intern Med 2013; 273: 544–554.
Kriz W, LeHir M . Pathways to nephron loss starting from glomerular diseases—insights from animal models. Kidney Int 2005; 67: 404–419.
Kawano S, Lin Q, Amano H, Kaneko T, Nishikawa K, Tsurui H et al. Phenotype conversion from rheumatoid arthritis to systemic lupus erythematosus by introduction of Yaa mutation into FcγRIIB-deficient C57BL/6 mice. Eur J Immunol 2013; 43: 770–778.
Bouman A, Heineman MJ, Faas MM . Sex hormones and the immune response in humans. Hum Reprod Update 2005; 11: 411–423.
Ichii O, Konno A, Sasaki N, Endoh D, Hashimoto Y, Kon Y . Onset of autoimmune glomerulonephritis derived from the telomeric region of MRL-chromosome 1 is associated with the male sex hormone in mice. Lupus 2009; 18: 491–500.
Zhou XJ, Lv JC, Bu DF, Yu L, Yang YR, Zhao J et al. Copy number variation of FCGR3A rather than FCGR3B and FCGR2B is associated with susceptibility to anti-GBM disease. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 45–51.
Fujii T, Hamano Y, Ueda S, Akikusa B, Yamasaki S, Ogawa M et al. Predominant role of FcgammaRIII in the induction of accelerated nephrotoxic glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int 2003; 64: 1406–1416.
Floege J, Radeke HR, Johnson RJ . Glomerular cells in vitro versus the glomerulus in vivo. Kidney Int 1994; 45: 360–368.
Radeke HH, Janssen-Graalfs I, Sowa EN, Chouchakova N, Skokowa J, Löscher F et al. Opposite regulation of type II and III receptors for immunoglobulin G in mouse glomerular mesangial cells and in the induction of anti-glomerular basement membrane (GBM) nephritis. J Biol Chem 2002; 277: 27535–27544.
Jiang Y, Hirose S, Sanokawa-Akakura R, Abe M, Mi X, Li N et al. Genetically determined aberrant down-regulation of FcgammaRIIB1 in germinal center B cells associated with hyper-IgG and IgG autoantibodies in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Int Immunol 1999; 11: 1685–1691.
Xiu Y, Nakamura K, Abe M, Li N, Wen XS, Jiang Y et al. Transcriptional regulation of Fcgr2b gene by polymorphic promoter region and its contribution to humoral immune responses. J Immunol 2002; 169: 4340–4346.
Pritchard NR, Cutler AJ, Uribe S, Chadban SJ, Morley BJ, Smith KG . Autoimmune-prone mice share a promoter haplotype associated with reduced expression and function of the Fc receptor FcgammaRII. Curr Biol 2000; 10: 227–230.
Xin H, Pramanik R, Choubey D . Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein upregulates expression of the Ifi202 gene encoding an interferon-inducible negative regulator of cell growth. Oncogene 2003; 22: 4775–4785.
Chen J, Panchanathan R, Choubey D . Stimulation of T cells up-regulates expression of Ifi202, an interferon-inducible lupus susceptibility gene, through activation of JNK/c-Jun pathway. Immunol Lett 2008; 118: 13–20.
Subramanian S, Tus K, Li QZ, Wang A, Tian XH, Zhou J et al. A Tlr7 translocation accelerates systemic autoimmunity in murine lupus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 9970–9975.
Espeli M, Bokers S, Giannico G, Dickinson HA, Bardsley V, Fogo AB et al. Local renal autoantibody production in lupus nephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol 2011; 22: 296–305.
Bekar KW, Owen T, Dunn R, Ichikawa T, Wang W, Wang R et al. Prolonged effects of short-term anti-CD20 B cell depletion therapy in murine systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 2443–2457.
Ramanujam M, Bethunaickan R, Huang W, Tao H, Madaio MP, Davidson A . Selective blockade of BAFF for the prevention and treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus nephritis in NZM2410 mice. Arthritis Rheum 2010; 62: 1457–1468.
Chan OT, Hannum LG, Haberman AM . A novel mouse with B cells but lacking serum antibody reveals an antibody independent role for B cells in murine lupus. J Exp Med 1999; 189: 1639–1648.
Fillatreau S . Cytokine-producing B cells as regulators of pathogenic and protective immune responses. Ann Rheum Dis 2013; 72: 80–84.
Fujimoto M . Regulatory B cells in skin and connective tissue diseases. J Dermatol Sci 2010; 60: 1–7.
Harris DP, Goodrich S, Gerth AJ, Peng SL, Lund FE . Regulation of IFN-gamma production by B effector 1 cells: essential roles for T-bet and the IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol 2005; 174: 6781–6790.
Seeling M, Hillenhoff U, David JP, Schett G, Tuckermann J, Lux A et al. Inflammatory monocytes and Fcγ receptor IV on osteoclasts are critical for bone destruction during inflammatory arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2013; 110: 10729–10734.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Graduate School of Veterinary Medicine, Hokkaido University, a Grant-in-Aid for JSPS Fellows (No. 25000961), a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientist (No. 24688033) and a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research B (No. 24380156) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on Genes and Immunity website
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kimura, J., Ichii, O., Nakamura, T. et al. BXSB-type genome causes murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis: pathological correlation between telomeric region of chromosome 1 and Yaa. Genes Immun 15, 182–189 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2014.4
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
BXSB/MpJ-Yaa mouse model of systemic autoimmune disease shows increased apoptotic germ cells in stage XII of the seminiferous epithelial cycle
Cell and Tissue Research (2020)
-
Modified scanning electron microscopy reveals pathological crosstalk between endothelial cells and podocytes in a murine model of membranoproliferative glomerulonephritis
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Local CD34-positive capillaries decrease in mouse models of kidney disease associating with the severity of glomerular and tubulointerstitial lesions
BMC Nephrology (2017)
-
Congenic mice demonstrate the presence of QTLs conferring obesity and hypercholesterolemia on chromosome 1 in the TALLYHO mouse
Mammalian Genome (2017)
-
Overexpression of Toll-like receptor 8 correlates with the progression of podocyte injury in murine autoimmune glomerulonephritis
Scientific Reports (2014)