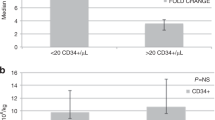
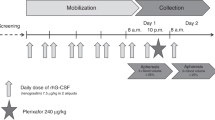
Abstract
Some reports have suggested that rituximab administration before PBSC mobilization may adversely affect PBSC yield. We conducted a prospective randomized trial of PBSC mobilization using etoposide and G-CSF with or without rituximab to determine whether its addition would adversely affect CD34+ cell yield in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Twenty seven patients were mobilized with etoposide and G-CSF and 28 with etoposide, G-CSF and rituximab. There were no adverse consequences of rituximab on CD34+ cell yield, or hematopoietic recovery or immunoglobulin levels after transplantation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benekli M, Hahn T, Shafi F, Qureshi A, Alam AR, Czuczman MS et al. Effect of rituximab on peripheral blood stem cell mobilization and engraftment kinetics in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma patients. Bone Marrow Transplant 2003; 32: 139–143.
Hoerr A, Gao F, Hidalgo J, Tiwari D, Blum K, Vikram M et al. Effects of pretransplantation treatment with rituximab on outcomes of autologous stem-cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 4561–4566.
Buckstein R, Imrie K, Spaner D, Potichnyi A, Robinson JB, Nanji S et al. Stem cell function and engraftment is not affected by ‘in vivo purging’ with rituximab for autologous stem cell treatment for patients with low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Semin Oncol 1999; 26 (5 Suppl 14): 115–122.
Hosing C, Saliba RM, Korbling M, Acholonu S, McMannis J, Anderlini P et al. High-dose rituximab does not negatively affect peripheral blood stem cell mobilization kinetics in patients with intermediate-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2006; 47: 1290–1294.
de Latour RP, Chaoui D, Bourhis JH, Belhocine R, Park S, Legrand O et al. Mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells after DHAP regimen with or without Rituximab: a large multicenter comparative study in patients with malignant lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 2007; 48: 897–904.
Kamezaki K, Kikushige Y, Numata T, Miyamoto T, Takase K, Henzan H et al. Rituximab does not compromise the mobilization and engraftment of autologous peripheral blood stem cells in diffuse-large B-cell lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 39: 523–527.
Copelan EA, Ceselski SK, Ezzone SA, Lasky LC, Penza SL, Bechtel TP et al. Mobilization of peripheral blood progenitor cells with high dose etoposide and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with breast cancer, non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, and Hodgkin's disease. J Clin Oncol 1997; 15: 759–765.
Avery RK, Pohlman BL, Mossad SB, Goormastic M, Longworth DL, Kalaycio ME et al. The efficacy of prophylactic outpatient antibiotics for the prevention of neutropenic fever associated with high-dose etoposide (VP-16) for stem cell mobilization. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 30: 311–314.
Copelan EA, Penza SL, Pohlman B, Avalos BR, Goormastic M, Andresen SW et al. Autotransplantation following busulfan, etoposide, and cyclophosphamide in patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2005; 25: 1243–1248.
Sharp JG, Kessinger A, Mann S, Crouse DA, Armitage JO, Bierman P et al. Outcome of high-dose therapy and autologous transplantation in non-Hodgkin's lymphoma based on the presence of tumour in the marrow or infused hematopoietic harvest. J Clin Oncol 1996; 14: 214–219.
Jacobsen E, Freedman A . B-cell purging in autologous stem-cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Lancet Oncol 2004; 5: 711–717.
Van Heeckeren WJ, Vollweiler J, Fu P, Cooper BW, Meyerson H, Lazarus HM et al. Randomised comparison of two B-cell purging protocols for patients with B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma: in vivo purging with rituximab versus ex vivo purging with CliniMACS CD34+ cell enrichment device. Br J Haematol 2005; 132: 42–55.
Ladetto M, Zallio F, Vallet S, Ricca I, Cuttica A, Caracciolo D et al. Concurrent administration of high-dose chemotherapy and rituximab is feasible and effective chemo/immunotherapy for patients with high-risk non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Leukemia 2001; 15: 1941–1949.
Koc ON, Gerson SL, Cooper BW, Laughlin M, Meyerson H, Kutteh L et al. Randomized cross-over trial of progenitor-cell mobilization: high dose cyclophosphamide plus granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) versus granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor plus G-CSF. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 1824–1830.
Boeve S, Strupeck J, Creech S, Stiff PJ . Analysis of remobilization success in patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplants who fail an initial mobilization: risk factors, cytokine use and cost. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 997–1003.
Chabannon C, Le Corroller AG, Viret F, Eillen C, Faucher C, Moatti JP et al. Cost-effectiveness of repeated aphereses in poor mobilizers undergoing high-dose chemotherapy and autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Leukemia 2003; 17: 811–813.
Tomblyn M, Burns LJ, Blazar B, Wagner J, Lee C, Rogers T et al. Difficult stem cell mobilization despite adequate CD34+ cell dose predicts shortened progression free and overall survival after autologous HSCT for lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 111–118.
Flinn I, O'Donnell P, Vogelsang G, Abrams R, Noga S, Marcellus D et al. Immunotherapy with rituximab during peripheral blood stem cell transplantation for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2000; 6: 628–632.
Goldberg S, Pecora A, Alter R, Kroll M, Rowley S, Waintraub S et al. Unusual viral infections (progressive multi-focal leukoencephalopathy and cytomegalovirus disease) after high-dose chemotherapy with autologous blood stem cell rescue and peritransplantation rituximab. Blood 2002; 99: 1486–1488.
Lemieux B, Tartas S, Traulle C, Espinouse D, Thieblemont C, Bouafia F et al. Rituximab-related late-onset neutropenia after autologous stem cell transplantation for aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 2004; 33: 921–923.
Goldschmidt H, Hegenbart U, Wallmeier M, Hohaus S, Haas R . Factors influencing collection of peripheral blood progenitor cells following high-dose cyclophosphamide and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in patients with multiple myeloma. Br J Haematol 1997; 98: 736–744.
Fermand JP, Ravaud P, Chevret S, Divine M, Leblond V, Macro M et al. High-dose therapy and autologous peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in multiple myeloma: up-front or rescue treatment? Results of a multicenter sequential randomized clinical trial. Blood 1998; 92: 3131–3136.
Tarella C, Caracciolo D, Gavarotti P, Bondesan P, Cherasco C, Omede P et al. Circulating progenitors following high-dose sequential (HDS) chemotherapy with Interverals between drug courses severely impair progenitor mobilization. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 223–228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Copelan, E., Pohlman, B., Rybicki, L. et al. A randomized trial of etoposide and G-CSF with or without rituximab for PBSC mobilization in B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transplant 43, 101–105 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.306
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.306
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Efficacy of hematopoietic stem cell mobilization regimens in patients with hematological malignancies: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Stem Cell Research & Therapy (2022)
-
A single center’s experience using four different front line mobilization strategies in lymphoma patients planned to undergo autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2017)
-
Autologous haematopoietic stem cell mobilisation in multiple myeloma and lymphoma patients: a position statement from the European Group for Blood and Marrow Transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2014)
-
Effectiveness of etoposide chemomobilization in lymphoma patients undergoing auto-SCT
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2013)
-
Clinical review: Serious adverse events associated with the use of rituximab - a critical care perspective
Critical Care (2012)