Abstract
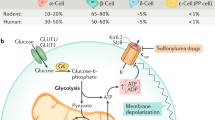
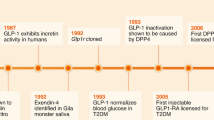
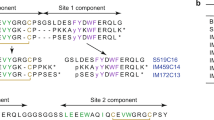
In mammalian tissues the C-terminal amide structure has been found to occur only in neuroactive or hormonally-active peptides1. About half known neuropeptide and peptide hormones have this unique chemical feature. Using a chemical detection method2, a search for previously unknown peptides that possess the C-terminal amide structure in extracts of brain and intestine was carried out3 and a number of novel neuropeptides and hormonal peptides4, designated neuropeptide Y5,6, PHI7, peptide YY8, galanin9 and neuropeptide K10 were isolated. We recently performed a similar search in porcine pancreas and found a high concentration of a peptide having a glycine amide at its C-terminus. Here we report the isolation, primary structure and biological activity of this novel peptide. The 49-residue peptide strongly inhibits glucose-induced insulin release from the isolated perfused pancreas and was therefore named pancreastatin. It may be important in the regulation of insulin secretion and in the pathogenesis and treatment of diabetes mellitus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narita, K., Matsuo, H. & Nakajima, T. in Protein Sequence Determination (ed. Needleman, S. B.) 30–130 (Springer, Berlin, 1975).
Tatemoto, K. & Mutt, V. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 75, 4115–4119 (1978).
Tatemoto, K. & Mutt, V. Nature 285, 417–418 (1980).
Tatemoto, K. Biomed. Res. 4, Suppl. 1, 1–6 (1983).
Tatemoto, K., Carlquist, M. & Mutt, V. Nature 296, 659–660 (1982).
Tatemoto, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 5485–5489 (1982).
Tatemoto, K. & Mutt, V. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 6603–6607 (1981).
Tatemoto, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 79, 2514–2518 (1982).
Tatemoto, K., Rokaeus, A., Jornvall, H., McDonald, T. J. & Mutt, V. FEBS Lett. 164, 124–128 (1983).
Tatemoto, K., Lundberg, J. M., Jornvall, H. & Mutt, V. Biochem. biophys. Res. Commun. 128, 947–953 (1985).
Jorpes, J. E. & Mutt, V. US patent 3,013,944 (1961).
Gregory, H., Hardy, P. M., Jones, D. S., Kenner, G. W. & Sheppard, R. C. Nature 204, 931–933 (1964).
du Vigneaud, V., Lawler, H. C. & Popenoe, A. J. Am. chem. Soc. 4880–4881 (1953).
Merrifield, R. B. J. Am. chem. Soc. 85, 2149–2154 (1963).
Loubatières, A., Mariani, M. M., Ribes, G., de Malbose, H. & Chapel, J. Diabetologia 5, 1–10 (1969).
Efendić, S., Luft, R. & Wajngot, A. Endocrine Rev. 5, 395–410 (1984).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tatemoto, K., Efendić, S., Mutt, V. et al. Pancreastatin, a novel pancreatic peptide that inhibits insulin secretion. Nature 324, 476–478 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/324476a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/324476a0
This article is cited by
-
Chromogranin A-derived peptides pancreastatin and catestatin: emerging therapeutic target for diabetes
Amino Acids (2023)
-
Chromogranin A and its derived peptides: potential regulators of cholesterol homeostasis
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2023)
-
Cerebrospinal fluid proteomics implicates the granin family in Parkinson’s disease
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Comparative iTRAQ Proteomics Reveals Multiple Effects of Selenium Yeast on Dairy Cows in Parturition
Biological Trace Element Research (2020)
-
The zinc transporter Zip14 (SLC39a14) affects Beta-cell Function: Proteomics, Gene expression, and Insulin secretion studies in INS-1E cells
Scientific Reports (2019)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.