Abstract
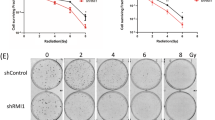
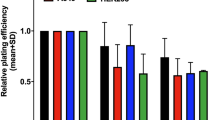
Mammalian Hus1 plays an important role in maintaining genomic integrity. Cells lacking mouse Hus1 are hypersensitive to DNA damage inducers including UV and camptothecin (CPT). By using clonogenic assay, we show here that Hus1 deficient mouse cells are hypersensitive to ionizing radiation (IR) compared with their Hus1-positive counterparts. However, these cells show similar induction levels and similar rejoining rates of DNA double strand breaks (DSBs) following IR, indicating that the effect of Hus1 on cell radiosensitivity is independent of nonhomologous end-joining (NHEJ). By combining an I-SceI-induced-DNA DSBs system and a siRNA approach, we also show that knocking down Hus1 decreases the efficiency of homologous recombination repair (HRR), which is associated with the cellular sensitivity to IR-induced killing. Together, these results indicate that the role of Hus1 affecting the sensitivity of cells to IR-induced killing is independent of NHEJ but might be linked to HRR.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
21 February 2008
An Erratum to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.1
References
Chen M-J, Lin Y-T, Lieberman HB, Chen G, Lee EY-HP . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 16580–16586.
Couedel C, Mills KD, Barchi M, Shen L, Olshen A, Johnson RD et al. (2004). Genes Dev 18: 1293–1304.
Golding SE, Rosenberg E, Khalil A, McEwen A, Holmes M, Neill S, Povirk LF, Valerie K . (2004). J Biol Chem 279: 15402–15410.
Hang H, Lieberman HB . (2000). Genomics 65: 24–33.
Hopkins KM, Auerbach W, Wang XY, Hande MP, Hang H, Wolgemuth DJ et al. (2004). Mol Cell Biol 24: 7235–7248.
Hu B, Wang H, Wang X, Lu H-R, Huang C, Powell SN et al. (2005). Cancer Res 65: 8613–8616.
Hu B, Zhou XY, Wang X, Zeng ZC, Iliakis G, Wang Y . (2001). J Biol Chem 276: 17693–17698.
Lindsey-Boltz LA, Bermudez VP, Hurwitz J, Sancar A . (2001). Proc Natl Am Soc 98: 11236–11241.
Mills KD, Ferguson DO, Essers J, Eckersdorff M, Kanaar R, Alt FW . (2004). Genes Dev 18: 1283–1292.
Nickoloff JA, Brenneman MA . (2004). Methods Mol Biol 262: 35–52.
Pierce AJ, Johnson RD, Thompson LH, Jasin M . (1999). Genes Dev 13: 2633–2638.
Rauen M, Burtelow MA, Dufault VM, Karnitz LM . (2000). J Biol Chem 275: 29767–29771.
Roos-Mattjus P, Hopkins KM, Oestreich AJ, Vroman BT, Johnson KL, Naylor S et al. (2003). J Biol Chem 278: 24428–24437.
Wang HY, Wang HC, Powell SN, Iliakis G, Wang Y . (2004a). Cancer Res 64: 7139–7143.
Wang X, Guan J, Hu B, Weiss RS, Iliakis G, Wang Y . (2004b). Nucl Acids Res 32: 767–775.
Weiss RS, Enoch T, Leder P . (2000). Genes Dev 14: 1886–1898.
Weiss RS, Leder P, Vaziri C . (2003). Mol Cell Biol 23: 791–803.
Weiss RS, Matsuoka S, Elledge SJ, Leder P . (2002). Current Biol 12: 73–77.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs M Jasin and JA Nickoloff for reagents and Nancy Mott for help in the preparation of the manuscript. This work is supported by a grant from NASA NAG2-1628 (to YW) and by grant NIH RO1 CA108773 (to RSW).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Hu, B., Weiss, R. et al. The effect of Hus1 on ionizing radiation sensitivity is associated with homologous recombination repair but is independent of nonhomologous end-joining. Oncogene 25, 1980–1983 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209212
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.onc.1209212
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Targeted deletion of mouse Rad1 leads to deficient cellular DNA damage responses
Protein & Cell (2011)
-
Mouse Rad1 deletion enhances susceptibility for skin tumor development
Molecular Cancer (2010)