Summary:
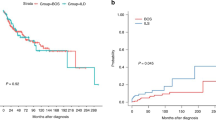
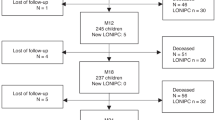
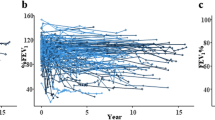
We evaluated the incidence, the risk factors, and the outcome of late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications (LONIPCs) among 50 patients who underwent allogeneic stem cell transplantation from unrelated donors. Of the 39 patients surviving at least 3 months, 10 (26%) fulfilled the diagnostic criteria of LONIPCs and were further subclassified as having bronchiolitis obliterans (four patients), bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia (four patients), and interstitial pneumonia (two patients). Two patients had a durable partial remission after treatment with prednisone and cyclosporine; the remaining eight patients did not respond to treatment and five of them died of respiratory failure. Advanced stage of disease at transplant and chronic extensive graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) were significantly associated with the development of LONIPCs. Pulmonary function test (PFT) results before transplantation were similar in all patients, but patients with LONIPCs had a significant decrease in PFT indexes at the third month after BMT compared with controls. Moreover, the rate of cyclosporine taper during the fourth and fifth months after BMT was significantly more rapid in patients with LONIPCs than in controls, suggesting that the risk of LONIPCs may be influenced by a faster reduction of GVHD prophylaxis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Soubani AO, Miller KB, Hassoun, PM . Pulmonary complications of bone marrow transplantation. Chest 1996; 109: 1066–1077.
Ralph DD, Springmeyer SC, Sullivan KM et al. Rapidly progressive air-flow-obstruction in marrow transplant recipients. Possible association between obliterative bronchiolitis and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Am Rev Respir Dis 1984; 129: 641–644.
Holland HK, Wingard JR, Beschorner WE et al. Bronchiolitis obliterans in bone marrow transplantation and its relationship to chronic graft-versus-host-disease and low serum IgG. Blood 1988; 72: 621–628.
Palmas A, Tefferi A, Myers JL et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Br J Haematol 1998; 100: 680–687.
Duncker C, Dohr D, von Harsdorf S et al. Non-infectious lung complications are closely associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease: a single center study of incidence, risk factors and outcome. Bone Marrow Transplant 2000; 25: 1263–1268.
Schultz KR, Green GJ, Wensley D et al. Obstructive lung disease in children after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Blood 1994; 9: 3212–3220.
Wolff D, Reichenberger F, Steiner B et al. Progressive interstitial fibrosis of the lung in sclerodermoid chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 2002; 29: 357–360.
Cutler C, Giri S, Jeyapalan S et al. Acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral-blood stem-cell and bone marrow transplantation: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 3685–3691.
Arai S, Vogelsang GB . Management of graft-versus-host disease. Blood Rev 2000; 14: 190–204.
Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A et al. Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HLA-matched sibling donors. Transplantation 1974; 18: 295–304.
Shulman HM, Sullivan KM, Weiden PL et al. Chronic graft-versus host syndrome in man: a long term clinicopathologic study of 20 Seattle patients. Am J Med 1980; 69: 204–217.
ATS . statement – Snowbird workshop on standardization of spirometry. Am Rev Respir Dis 1979; 119: 831–838.
Clark JG, Crawford SW, Madtes DK, Sullivan KM . Obstructive lung disease after allogeneic marrow transplantation. Clinical presentation and course. Ann Intern Med 1989; 111: 368–376.
Colby TV, Myers JL . Clinical and histologic spectrum of bronchiolitis obliterans, including bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia. Semin Respir Med 1992; 13: 119–133.
Sakaida E, Nakaseko C, Hariam A et al. Late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic bone marrow transplantationare significantly associated with chronic graft-versus-host disease and graft-versus-leukaemia effect. Blood 2003; 101: 4236–4242.
Curtis DJ, Smale A, Thien F et al. Chronic airflow obstruction in long-term survivors of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 16: 169–173.
Socie G, Mary JY, Esperou H et al. Health and functional status of adult recipient 1 year after allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Br J Haematol 2001; 113: 194–201.
Cerveri I, Fulgoni P, Giorgiani G et al. Lung function abnormalities after bone marrow transplantation in children: has the trend recently changed? Chest 2001; 120: 1900–1906.
Gore EM, Lawton CA, Ash RC et al. Pulmonary function changes in long-term survivors of bone marrow transplantation. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 1996; 36: 67–75.
Beinert T, Dull T, Wolf K et al. Late pulmonary impairment following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Eur J Med Res 1996; 1: 343–348.
Crawford SW, Pepe M, Lin D et al. Abnormalities of pulmonary function tests after bone marrow transplantation predict nonrelapse mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1995; 152: 690–695.
Thomas O, Mahe M, Campion L et al. Long-term complications of total body irradiation in adults. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2001; 1: 125–131.
Lund MB, Kongerund J, Brinch L et al. Decreased lung function in one year survivors of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation conditioned with high-dose busulphan and cyclophosphamide. Eur Respir J 1995; 8: 1269–1274.
Sociè G, Clift RA, Blaise D et al. Busulfan plus cyclophosphamide compared with total-body irradiation plus cyclophosphamide before marrow transplantation for myeloid leukaemia: long-term follow-up of 4 randomized studies. Blood 2001; 98: 3569–3574.
Poletti V, Salvucci M, Zanchini R et al. The lung as target organ in patients with hematologic disorders. Haematologica 2000; 85: 855–864.
Sociè G, Stone JV, Wingard JR et al. Long-term survival and late deaths after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med 1999; 341: 14–21.
Weiden PL, Flournoy N, Thomas ED et al. Antileukemic effect of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of allogeneic-marrow graft. N Engl J Med 1979; 300: 1068–1073.
Sullivan KM, Weiden PL, Storb R et al. Influence of acute and chronic graft-versus-host disease on relapse and survival after bone marrow transplantation from HLA-identical sibling as treatment of acute and chronic leukaemia. Blood 1989; 73: 1720–1728.
Zaucha JM, Gooley T, Bensinger WI et al. CD34 cell dose in granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood mononuclear cell grafts affects engraftment kinetics and development of extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease after human leukocyte antigen-identical sibling transplantation. Blood 2001; 98: 3221–3227.
Mohty M, Bilger K, Jourdan E et al. Higher doses of CD34+ peripheral blood stem cells are associated with increased mortality from chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Leukemia 2003; 17: 869–875.
Lonnqvist B, Aschan J, Ljungman P, Ringden O . Long-term cyclosporine therapy may decrease the risk of chronic graft-versus-host disease. Br J Haematol 1990; 74: 547–548.
Bacigalupo A, Majolino A, Van Lint MT et al. Cyclosporine A and chronic graft-versus-host disease. Bone Marrow Transplant 1990; 6: 341–344.
Mengarelli A, Iori AP, Romano A et al. One-year cyclosporine prophylaxis reduces the risk of developing extensive chronic graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell transplantation. Heamatologica 2003; 88: 315–323.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Patriarca, F., Skert, C., Sperotto, A. et al. Incidence, outcome, and risk factors of late-onset noninfectious pulmonary complications after unrelated donor stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 33, 751–758 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704426
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1704426
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Clinical characteristics of late-onset interstitial pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2023)
-
Selection bias in follow-up studies of stem cell transplantation survivors: an experience within the Maastricht Observational study of late effects after Stem cell trAnsplantation (MOSA)
Annals of Hematology (2023)
-
Risk factors and prognosis of non-infectious pulmonary complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2022)
-
Risk factors and clinical features for post-transplant thoracic air-leak syndrome in adult patients receiving allogeneic haematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Patterns of onset and outcome of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
International Journal of Hematology (2019)