Abstract
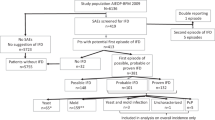
Invasive fungal infections (IFI) with substantial mortality constitute an increasing problem among BMT patients. From 1986 to 1996 148 children underwent BMT, and are included in a retrospective analysis of the incidence, risk factors and outcome of IFI. By histopathology or culture-proven IFI (Candida, 10; Aspergillus, 8) was documented in 12/73 (16%) allogeneic and in 6/75 (8%) autologous BMT patients. Of these 18 patients, 15 subsequently died, and in 12 (66%) IFI was regarded as the main cause of death. In addition to the patients with documented IFI, 48 had suspected and 82 no fungal infection. Invasive candidal infections were more frequent in patients with semiquantitatively estimated abundant candidal colonization as compared with those with no colonization (18% vs 3%, P = 0.015). In the allogeneic group, 50% of those with severe (grades III–IV) aGVHD had IFI as opposed to 8% of those with no or mild aGVHD (P < 0.001). Regarding cGVHD, 57% of those with extensive cGVHD vs 5% of those with absent or limited cGVHD had IFI (P < 0.001). The dose of steroids was associated with IFI: 77% of those who received high-dose steroids (methylprednisolone 0.25–1 g/day for 5 days) vs 5% of those with conventional-dose (prednisone 2 mg/kg/day) had IFI (P < 0.001). Particularly for BMT patients at risk, new, quicker and better diagnostic tests and more effective anti-fungal agents, both for prophylaxis and treatment, are needed. Bone Marrow Transplantation (2000) 26, 999–1004.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Goodrich JM, Reed EC, Mori M et al. Clinical features and analysis of risk factors for invasive candidal infection after marrow transplantation J Infect Dis 1991 164: 731–740
Wald A, Leisenring W, van Burik JA, Bowden RA . Epidemiology of Aspergillus infections in a large cohort of patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation J Infect Dis 1997 175: 1459–1466
Anttila VJ, Elonen E, Nordling S et al. Hepatosplenic candidiasis in patients with acute leukemia: incidence and prognostic implications Clin Infect Dis 1997 24: 375–380
Verfaillie C, Weisdorf D, Haake R et al. Candida infections in bone marrow transplant recipients Bone Marrow Transplant 1991 8: 177–184
Jantunen E, Ruutu P, Niskanen L et al. Incidence and risk factors for invasive fungal infections in allogeneic BMT recipients Bone Marrow Transplant 1997 19: 801–808
Morrison VA, Haake RJ, Weisdorf DJ . Non-Candida fungal infections after bone marrow transplantation: risk factors and outcome Am J Med 1994 96: 497–503
Chandrasekar PH, Weinmann A, Shearer C . Autopsy-identified infections among bone marrow transplant recipients: a clinico-pathologic study of 56 patients Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 16: 675–681
Benhamou E, Hartmann O, Nogues C et al. Does ketokonazole prevent fungal infection in children treated with high dose chemotherapy and bone marrow transplantation? Results of a randomized placebo-controlled trial Bone Marrow Transplant 1991 7: 127–131
Klingspor L, Stintzing G, Fasth A, Tollemar J . Deep Candida infection in children receiving allogeneic bone marrow transplants: incidence, risk factors and diagnosis Bone Marrow Transplant 1996 17: 1043–1049
Mäkipernaa A, Saarinen UM, Siimes MA . Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in children: single institution experience from 1974 to 1992 Acta Paediatr 1995 84: 683–688
Hovi L, Lindqvist C, Donner U, Saarinen UM . Opportunistic osteomyelitis in the jaws of children on immunosuppressive chemotherapy J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 1996 18: 90–94
Sulahian A, Tabouret M, Ribaud P et al. Comparison of an enzyme immunoassay and latex agglutination test for detection of galactomannan in the diagnosis of invasive aspergillosis Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1996 15: 139–145
Einsele H, Hebart H, Roller G et al. Detection and identification of fungal pathogens in blood by using molecular probes J Clin Microbiol 1997 35: 1353–1360
Chanock SJ, Walsh TJ . Molecular diagnosis of Candida infection in the compromised host: current status and future prospects Int J Infect Dis 1997 1: 20–24
Ribaud P, Chastang C, Latge JP et al. Survival and prognostic factors of invasive aspergillosis after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation Clin Infect Dis 1999 28: 322–330
Riley DK, Pavia AT, Beatty PG et al. Surveillance cultures in bone marrow transplant recipients: worthwhile or wasteful? Bone Marrow Transplant 1995 15: 469–473
Hoppe JE, Klausner M, Klingebiel T, Niethammer D . Retrospective analysis of yeast colonization and infections in paediatric bone marrow transplant recipients Mycoses 1997 40: 47–54
Gotzshe PC, Johansen HK . Routine antifungal therapy in cancer patients. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. The Cochrane Library: Copenhagen, vol 3, 1998
Bowden RA . Fungal infections after hematopoietic cell transplantation. In: Thomas ED, Blume KG, Forman SJ (eds) Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation Blackwell Science: Malden, MA pp 550–559
Guiot HF, Fibbe WE, van ’t Wout JW . Risk factors for fungal infection in patients with malignant hematologic disorders: implications for empirical therapy and prophylaxis Clin Infect Dis 1994 18: 525–532
Martino P, Girmenia C, Micozzi A et al. Prospective study of Candida colonization, use of empiric amphotericin B and development of invasive mycosis in neutropenic patients Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 1994 13: 797–804
O'Donnell MR, Schmidt GM, Tegtmeier BR et al. Prediction of systemic fungal infection in allogeneic marrow recipients: impact of amphotericin prophylaxis in high-risk patients J Clin Oncol 1994 12: 827–834
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant from the Nona and Kullervo Väre Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hovi, L., Saarinen-Pihkala, U., Vettenranta, K. et al. Invasive fungal infections in pediatric bone marrow transplant recipients: single center experience of 10 years. Bone Marrow Transplant 26, 999–1004 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702654
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bmt.1702654
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Impact of antifungal stewardship interventions on the susceptibility of colonized Candida species in pediatric patients with malignancy
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A phase I dose finding study of intravenous voriconazole in pediatric patients undergoing hematopoietic cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2020)
-
Changing face of Candida colonization pattern in pediatric patients with hematological malignancy during repeated hospitalizations, results of a prospective observational study (2016–2017) in shiraz, Iran
BMC Infectious Diseases (2019)
-
Genotyping bacterial and fungal pathogens using sequence variation in the gene for the CCA-adding enzyme
BMC Microbiology (2016)
-
Cerebral Fungal Infection in Pediatric Cancer Patients
Current Fungal Infection Reports (2015)