Abstract
Background/objectives
Nutritional risk screening (NRS) score has been reported as a predictor of postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing abdominal surgery, although the correlation between NRS and anastomotic leakage (AL) after rectal cancer surgery is uncertain. This study aimed to evaluate the association between NRS score and AL following rectal cancer surgery.
Subject/methods
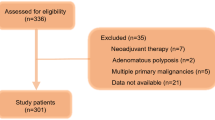
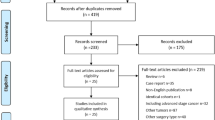
We retrospectively reviewed data of rectal cancer patients from a tertiary referral center in South Korea, and included 1063 patients with primary rectal cancer who underwent sphincter-preserving surgery between January 2011 and December 2015. We utilized the Chonnam National University Hwasun Hospital-Nutritional Risk Screening Tool (CNUHH-NRST), which was developed and cross-validated on the basis of the NRS 2002 and MST, as a screening tool of nutritional risk. Patients with NRS scores ≥4 were compared with those with NRS scores <4, and the risk factors for AL were analyzed.
Results
One-hundred-nineteen (11.2%) patients had high nutritional risk (NRS score ≥4). The patients with a nutritional risk had more advanced tumor stages than those without nutritional risk. AL occurred in 69 (6.5%) patients. The multivariate logistic regression analysis showed high American Society of Anesthesiologists score (odds ratio (OR) = 2.435, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.085–5.469), long operative time (OR = 1.975, 95% CI = 1.177–3.313), and high NRS score (OR = 2.044, 95% CI = 1.085–3.851) as independent risk factors of AL.
Conclusions
The NRS score was an independent predictive factor of AL after rectal cancer surgery. Patients with nutritional risks who require rectal cancer surgery should be carefully managed.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDermott FD, Heeney A, Kelly ME, Steele RJ, Carlson GL, Winter DC. Systematic review of preoperative, intraoperative and postoperative risk factors for colorectal anastomotic leaks. Br J Surg. 2015;102:462–79.
Qu H, Liu Y, Bi DS. Clinical risk factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic anterior resection for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Surg Endosc. 2015;29:3608–17.
Park JS, Choi GS, Kim SH, Kim HR, Kim NK, Lee KY, et al. Multicenter analysis of risk factors for anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic rectal cancer excision: the Korean laparoscopic colorectal surgery study group. Ann Surg. 2013;257:665–71.
Frasson M, Flor-Lorente B, Rodriguez JL, Granero-Castro P, Hervas D, Alvarez Rico MA, et al. Risk factors for anastomotic leak after colon resection for cancer: multivariate analysis and nomogram from a multicentric, prospective, national study with 3193 patients. Ann Surg. 2015;262:321–30.
Rencuzogullari A, Benlice C, Valente M, Abbas MA, Remzi FH, Gorgun E. Predictors of anastomotic leak in elderly patients after colectomy: nomogram-based assessment from the American College of Surgeons National Surgical Quality Program Procedure-Targeted Cohort. Dis Colon Rectum. 2017;60:527–36.
Bosaeus I. Nutritional support in multimodal therapy for cancer cachexia. Support Care Cancer. 2008;16:447–51.
Jung MR, Park YK, Kim EY, Jang SJ. Validation of an electronic nutritional risk screening tool for hospital cancer patients. Surg Metab Nutr. 2012;3:16–22.
Mazaki T, Ebisawa K. Enteral versus parenteral nutrition after gastrointestinal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials in the English literature. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008;12:739–55.
Bauer J, Capra S, Ferguson M. Use of the scored Patient-Generated Subjective Global Assessment (PG-SGA) as a nutrition assessment tool in patients with cancer. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2002;56:779–85.
Detsky AS, McLaughlin JR, Baker JP, Johnston N, Whittaker S, Mendelson RA, et al. What is subjective global assessment of nutritional status? J Parenter Enter Nutr. 1987;11:8–13.
Ferguson ML, Bauer J, Gallagher B, Capra S, Christie DR, Mason BR. Validation of a malnutrition screening tool for patients receiving radiotherapy. Australas Radiol. 1999;43:325–7.
Kondrup J, Rasmussen HH, Hamberg O, Stanga Z. Nutritional risk screening (NRS 2002): a new method based on an analysis of controlled clinical trials. Clin Nutr. 2003;22:321–36.
Sungurtekin H, Sungurtekin U, Balci C, Zencir M, Erdem E. The influence of nutritional status on complications after major intraabdominal surgery. J Am Coll Nutr. 2004;23:227–32.
Schiesser M, Muller S, Kirchhoff P, Breitenstein S, Schafer M, Clavien PA. Assessment of a novel screening score for nutritional risk in predicting complications in gastrointestinal surgery. Clin Nutr. 2008;27:565–70.
Guo W, Ou G, Li X, Huang J, Liu J, Wei H. Screening of the nutritional risk of patients with gastric carcinoma before operation by NRS 2002 and its relationship with postoperative results. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;25:800–3.
Schwegler I, von Holzen A, Gutzwiller JP, Schlumpf R, Muhlebach S, Stanga Z. Nutritional risk is a clinical predictor of postoperative mortality and morbidity in surgery for colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 2010;97:92–97.
Poziomyck AK, Weston AC, Lameu EB, Cassol OS, Coelho LJ, Moreira LF. Preoperative nutritional assessment and prognosis in patients with foregut tumors. Nutr Cancer. 2012;64:1174–81.
Zhou W, Xu X, Yan J, Mou Y. Nutritional risk is still a clinical predictor of postoperative outcomes in laparoscopic abdominal surgery. Surg Endosc. 2013;27:2569–74.
Kwag SJ, Kim JG, Kang WK, Lee JK, Oh ST. The nutritional risk is a independent factor for postoperative morbidity in surgery for colorectal cancer. Ann Surg Treat Res. 2014;86:206–11.
Ho JW, Wu AH, Lee MW, Lau SY, Lam PS, Lau WS, et al. Malnutrition risk predicts surgical outcomes in patients undergoing gastrointestinal operations: results of a prospective study. Clin Nutr. 2015;34:679–84.
Sun Z, Kong XJ, Jing X, Deng RJ, Tian ZB. Nutritional risk screening 2002 as a predictor of postoperative outcomes in patients undergoing abdominal surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE. 2015;10:e0132857.
Correia MI, Waitzberg DL. The impact of malnutrition on morbidity, mortality, length of hospital stay and costs evaluated through a multivariate model analysis. Clin Nutr. 2003;22:235–9.
Kruizenga H, van Keeken S, Weijs P, Bastiaanse L, Beijer S, Huisman-de Waal G, et al. Undernutrition screening survey in 564,063 patients: patients with a positive undernutrition screening score stay in hospital 1.4 d longer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;103:1026–32.
Thomas MN, Kufeldt J, Kisser U, Hornung HM, Hoffmann J, Andraschko M, et al. Effects of malnutrition on complication rates, length of hospital stay, and revenue in elective surgical patients in the G-DRG-system. Nutrition. 2016;32:249–54.
Veyrie N, Ata T, Muscari F, Couchard AC, Msika S, Hay JM, et al. Anastomotic leakage after elective right versus left colectomy for cancer: prevalence and independent risk factors. J Am Coll Surg. 2007;205:785–93.
Kang CY, Halabi WJ, Chaudhry OO, Nguyen V, Pigazzi A, Carmichael JC, et al. Risk factors for anastomotic leakage after anterior resection for rectal cancer. JAMA Surg. 2013;148:65–71.
Turrentine FE, Denlinger CE, Simpson VB, Garwood RA, Guerlain S, Agrawal A, et al. Morbidity, mortality, cost, and survival estimates of gastrointestinal anastomotic leaks. J Am Coll Surg. 2015;220:195–206.
Rahbari NN, Weitz J, Hohenberger W, Heald RJ, Moran B, Ulrich A, et al. Definition and grading of anastomotic leakage following anterior resection of the rectum: a proposal by the International Study Group of Rectal Cancer. Surgery. 2010;147:339–51.
Lee SY, Kim CH, Kim YJ, Kim HR. Impact of anal decompression on anastomotic leakage after low anterior resection for rectal cancer: a propensity score matching analysis. Lange Arch Surg. 2015;400:791–6.
Schneider SM, Veyres P, Pivot X, Soummer AM, Jambou P, Filippi J, et al. Malnutrition is an independent factor associated with nosocomial infections. Br J Nutr. 2004;92:105–11.
Salvino RM, Dechicco RS, Seidner DL. Perioperative nutrition support: who and how. Cleve Clin J Med. 2004;71:345–51.
Zhu QL, Feng B, Lu AG, Wang ML, Hu WG, Li JW, et al. Laparoscopic low anterior resection for rectal carcinoma: complications and management in 132 consecutive patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2010;16:4605–10.
Weimann A, Braga M, Carli F, Higashiguchi T, Hubner M, Klek S, et al. ESPEN guideline: clinical nutrition in surgery. Clin Nutr. 2017;36:623–50.
Bozzetti F, Gavazzi C, Miceli R, Rossi N, Mariani L, Cozzaglio L, et al. Perioperative total parenteral nutrition in malnourished, gastrointestinal cancer patients: a randomized, clinical trial. J Parenter Enter Nutr. 2000;24:7–14.
Wu GH, Liu ZH, Wu ZH, Wu ZG. Perioperative artificial nutrition in malnourished gastrointestinal cancer patients. World J Gastroenterol. 2006;12:2441–4.
Benoist S, Brouquet A. Nutritional assessment and screening for malnutrition. J Visc Surg. 2015;152:S3–7.
Chen Y, Liu BL, Shang B, Chen AS, Liu SQ, Sun W, et al. Nutrition support in surgical patients with colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2011;17:1779–86.
Kim CH, Lee SY, Kim HR, Kim YJ. Nomogram prediction of anastomotic leakage and determination of an effective surgical strategy for reducing anastomotic leakage after laparoscopic rectal cancer surgery. Gastroenterol Res Pract. 2017;2017:4510561.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S.Y., Jung, M.R., Kim, C.H. et al. Nutritional risk screening score is an independent predictive factor of anastomotic leakage after rectal cancer surgery. Eur J Clin Nutr 72, 489–495 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0112-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41430-018-0112-3
This article is cited by
-
A preoperative prediction model based on Lymphocyte-C-reactive protein ratio predicts postoperative anastomotic leakage in patients with colorectal carcinoma: a retrospective study
BMC Surgery (2022)
-
Long-term oncological outcomes of low anterior resection for rectal cancer with and without preservation of the left colic artery: a retrospective cohort study
BMC Cancer (2021)
-
Role of Nutrition in the Elderly Surgical Patient – Review of the Literature and Current Recommendations
Current Geriatrics Reports (2021)
-
Effect of preoperative immunonutrition on outcomes of colon cancer surgery: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial
Trials (2020)
-
Is abdominal vascular calcification score valuable in predicting the occurrence of colorectal anastomotic leakage? A meta-analysis
International Journal of Colorectal Disease (2020)