Abstract
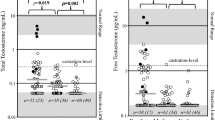
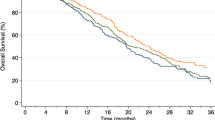
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the relationship of baseline body mass index (BMI) and serum testosterone level with prostate cancer outcomes in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer (CRPC). BMI and testosterone levels were evaluated for their ability to predict overall survival (OS) and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) declines in the TAX327 clinical trial, an international phase III randomized trial of one of the two schedules of docetaxel and prednisone compared with mitoxantrone and prednisone. In this study of 1006 men with CRPC, the median serum testosterone level was 14.5 ng per 100 ml (range 0–270), the median BMI was 27 kg m−2 (range 15.7–46.5), and 26% of men were obese or morbidly obese (BMI⩾30). Obesity was associated with younger age, lower PSA and alkaline phosphatase levels, and higher performance status, primary Gleason sum, testosterone and hemoglobin compared to absence of obesity. In multivariate analysis, neither BMI, presence of obesity, nor baseline testosterone was significantly associated with OS or PSA declines. Higher testosterone levels among obese men suggest incomplete gonadal suppression with current therapies, but these differences may not be clinically relevant in men with CRPC. There was evidence of potential hemodilution of PSA and alkaline phosphatase levels in obese men.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Murray T et al. Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 2008; 58: 71–96.
Armstrong AJ, Garrett-Mayer E, Ou Yang YC, Carducci MA, Tannock I, de WR et al. Prostate-specific antigen and pain surrogacy analysis in metastatic hormone-refractory prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 3965–3970.
Armstrong AJ, Garrett-Mayer ES, Yang YC, de WR, Tannock IF and Eisneberger M . A contemporary prognostic nomogram for men with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer: a TAX327 study analysis. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 6396–6403.
Halabi S, Small EJ, Kantoff PW, Kattan MW, Kaplan EB, Dawson NA et al. Prognostic model for predicting survival in men with hormone-refractory metastatic prostate cancer. J Clin Oncol 2003; 21: 1232–1237.
Smaletz O, Scher HI, Small EJ, Verbel DA, McMillan A, Regan K et al. Nomogram for overall survival of patients with progressive metastatic prostate cancer after castration. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 3972–3982.
Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, McDowell MA, Tabak CJ and Flegal KM . Prevalence of overweight and obesity in the United States, 1999–2004. JAMA 2006; 295: 1549–1555.
Andersson SO, Wolk A, Bergstrom R, Adami HO, Engholm G, Englund A et al. Body size and prostate cancer: a 20-year follow-up study among 135006 Swedish construction workers. J Natl Cancer Inst 1997; 89: 385–389.
Rodriguez C, Patel AV, Calle EE, Jacobs EJ, Chao A, Thun MJ et al. Body mass index, height, and prostate cancer mortality in two large cohorts of adult men in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2001; 10: 345–353.
Rodriguez C, Freedland SJ, Deka A, Jacobs EJ, McCullough ML, Patel AV et al. Body mass index, weight change, and risk of prostate cancer in the Cancer Prevention Study II Nutrition Cohort. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev 2007; 16: 63–69.
Efstathiou JA, Bae K, Shipley WU, Hanks GE, Pilepich MV, Sandler HM et al. Obesity and mortality in men with locally advanced prostate cancer: analysis of RTOG 85-31. Cancer 2007; 110: 2691–2699.
Freedland SJ, Aronson WJ, Kane CJ, Presti JC. Jr., Amling CL, Elashoff D et al. Impact of obesity on biochemical control after radical prostatectomy for clinically localized prostate cancer: a report by the Shared Equal Access Regional Cancer Hospital database study group. J Clin Oncol 2004; 22: 446–453.
Gong Z, Agalliu I, Lin DW, Stanford JL, Kristal AR et al. Obesity is associated with increased risks of prostate cancer metastasis and death after initial cancer diagnosis in middle-aged men. Cancer 2007; 109: 1192–1202.
Buschemeyer III WC, Freedland SJ . Obesity and prostate cancer: epidemiology and clinical implications. Eur Urol 2007; 52: 331–343.
Banez LL, Hamilton RJ, Partin AW, Vollmer RT, Sun L, Rodriguez C et al. Obesity-related plasma hemodilution and PSA concentration among men with prostate cancer. JAMA 2007; 298: 2275–2280.
Renehan AG, Zwahlen M, Minder C, O'Dwyer ST, Shalet SM, Egger M et al. Insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I, IGF binding protein-3, and cancer risk: systematic review and meta-regression analysis. Lancet 2004; 363: 1346–1353.
Shaneyfelt T, Husein R, Bubley G, Mantzoros CS . Hormonal predictors of prostate cancer: a meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol 2000; 18: 847–853.
Baker SD, Scher HI, Li J, Beekman KW, Stewart J, Collins C et al. Effect of androgen-ablation and hormonal cycling on docetaxel (D) clearance in patients with metastatic prostate cancer (MPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2005; 23: 4608.
Rudek MA, Sparreboom A, Garrett-Mayer ES, Armstrong DK, Wolff AC, Verweij J and Baker SD et al. Factors affecting pharmacokinetic variability following doxorubicin and docetaxel-based therapy. Eur J Cancer 2004; 40: 1170–1178.
Attard G, Yap TA, Reid AH, Parker C, Barrett SM, Raynaud F et al. Phase I study of continuous oral dosing of an irreversible CYP17 inhibitor, abiraterone (A), in castration refractory prostate cancer (CRPC) patients (p) incorporating the evaluation of androgens and steroid metabolites in plasma and tumor. J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007; 25: 5063.
Chen CD, Welsbie DS, Tran C, Baek SH, Chen R, Vessella R et al. Molecular determinants of resistance to antiandrogen therapy. Nat Med 2004; 10: 33–39.
Febbo PG, Richie JP, George DJ, Loda M, Manola J, Shankar S et al. Neoadjuvant docetaxel before radical prostatectomy in patients with high-risk localized prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 5233–5240.
Ryan CJ, Rosenberg J, Lin A, Valiente J, Kim J and Small EJ . Phase I evaluation of abiraterone acetate (CB7630), a 17 alpha hydroxylase C17,20-Lyase inhibitor in androgen-independent prostate cancer (AiPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007; 25: 5064.
Tannock IF, de WR, Berry WR, Horti J, Pluzanska A, Chi KN et al. Docetaxel plus prednisone or mitoxantrone plus prednisone for advanced prostate cancer. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 1502–1512.
Smith MR . Obesity and sex steroids during gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist treatment for prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 241–245.
Halabi S, Ou SS, Vogelzang NJ and Small EJ . Inverse correlation between body mass index and clinical outcomes in men with advanced castration-recurrent prostate cancer. Cancer 2007; 110: 1478–1484.
Halabi S, Ou SS, Vogelzang NJ, Scher H and Small EJ . A novel intermediate endpoint for predicting overall survival in men with metastatic castration-recurrent prostate cancer (CRPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007; 25: 5113.
Montgomery RB, Goldman B, Tangen CM, Hussain M, Petrylak DP, Page S et al. Association of body mass index with response and survival in men with metastatic prostate cancer: Southwest Oncology GroupTtrials 8894 and 9916. J Urol 2007; 178: 1946–1951.
Ryan CJ, Rosenberg J, Lin A, Valiente J, Kim J and Small EJ . Phase I evaluation of abiraterone acetate (CB7630), a 17 alpha hydroxylase C17,20-lyase inhibitor in androgen-independent prostate cancer (AiPC). J Clin Oncol (Meeting Abstracts) 2007; 25: 5064.
Acknowledgements
We thank the many patients who volunteered to participate in the TAX327 study and the investigators who recruited them and managed their care, listed below.
MA Rosenthal from Australia; D Campos (Argentina); H Gurney and M Stockler (Australia); M Rauchenwald (Austria); T Gil, Y Humblet and A van Oosterom (Belgium); D Herchenhorn (Brazil); S Ernst, L Lacombe, M Moore, F Saad, D Soulieres, P Venner and E Winquist (Canada); M Urban (Czech Republic); P Kellokumpu-Lehtinen (Finland); G Deplanque, B Duclos, I Krakowski and L Mignot, S Oudard and C Theodore (France); J Breul and R Paul (Germany); I Bodrogi (Hungary); S Bracarda (Italy); G Chahine (Lebanon); JL Bruins and JA Witjes (the Netherlands); T Demkow and K Bar (Poland); O Kariakine and M Matveev (Russia); I Andrasina (Slovak Republic); D Vorobiof (South Africa); J Bellmunt and J-R Germa (Spain); I Turesson and A Widmark (Sweden); A Horwich, T Roberts, ND James and J Wylie (United Kingdom); and L Baez, W Dugan and N Tirumali (United States).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Armstrong, A., Halabi, S., de Wit, R. et al. The relationship of body mass index and serum testosterone with disease outcomes in men with castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 12, 88–93 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.36
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/pcan.2008.36
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
The obesity paradox in metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2022)
-
Blood platelet volume predicts treatment-specific outcomes of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2020)
-
Prognostic value of testosterone for the castration-resistant prostate cancer patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2020)
-
Body mass index and mortality in prostate cancer patients: a dose–response meta-analysis
Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases (2016)
-
Optimal Pharmacotherapeutic Management of Hormone-Sensitive Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Drugs (2013)