Abstract
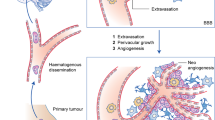
Over the past 10 years, improving the outcome of breast cancer patients with brain metastases has become an important challenge. The suboptimal results of whole-brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in these patients have led to the development of irradiation modalities with new technical and biological approaches. By ensuring better sparing of critical organs such as the hippocampus, highly conformal irradiation therapy may partially preserve long-term neurocognitive functions. An additional radiation boost to the tumor bed improves local control. Radiosensitizing agents and radioprotectors that modify response to radiation have also been designed to improve the efficacy of treatment or prevent neurological toxicity. This Review outlines the current strategies and novel developments in WBRT, with a particular focus on new irradiation modalities and experiences of radiosensitization.
Key Points
-
Whole-brain radiation therapy remains the standard treatment for breast cancer patients with four or more brain metastases
-
Age, number of brain metastases, controlled primary tumor, and performance status are important prognostic factors; molecular features should also be considered for predicting prognosis in patients with breast cancer
-
Delivering a radiation boost to the tumor bed could improve local control in selected patients, but improvements in overall survival have not been established
-
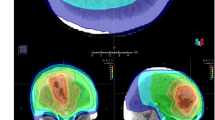
Intensity-modulated radiation therapy allows sparing of critical organs, such as the hippocampus, but its benefits have not yet been validated
-
Undifferentiated chemoradiation approaches have shown no conclusive benefit, but innovative strategies that target specific molecular subsets are encouraged
-
Radioprotectors designed to prevent neurological toxicity, such as amifostine, have not yet demonstrated clinical benefit
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
19 July 2010
In the version of this article initially published online, there was a mistake in section two in Box 1, and the order of some of the references cited in the text, box, tables and reference list was incorrect. The errors have been corrected in all electronic versions of the text.
References
Weil, R. J., Palmieri, D. C., Bronder, J. L., Stark, A. M. & Steeg, P. S. Breast cancer metastasis to the central nervous system. Am. J. Pathol. 167, 913–920 (2005).
Bendell, J. C. et al. Central nervous system metastases in women who receive trastuzumab-based therapy for metastatic breast carcinoma. Cancer 97, 2972–2977 (2003).
Borgelt, B. et al. The palliation of brain metastases: final results of the first two studies by the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 6, 1–9 (1980).
Tsao, M. N. et al. Radiotherapeutic management of brain metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Treat. Rev. 31, 256–273 (2005).
Wadasadawala, T., Gupta, S., Bagul, V. & Patil, N. Brain metastases from breast cancer: management approach. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 3, 157–165 (2007).
Patchell, R. A. The management of brain metastases. Cancer Treat. Rev. 29, 533–540 (2003).
Patchell, R. A. et al. A randomized trial of surgery in the treatment of single metastases to the brain. N. Engl. J. Med. 322, 494–500 (1990).
Noordijk, E. M. et al. The choice of treatment of single brain metastasis should be based on extracranial tumor activity and age. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 29, 711–717 (1994).
Mintz, A. H. et al. A randomized trial to assess the efficacy of surgery in addition to radiotherapy in patients with a single cerebral metastasis. Cancer 78, 1470–1476 (1996).
Patchell, R. A. et al. Postoperative radiotherapy in the treatment of single metastases to the brain: a randomized trial. JAMA 280, 1485–1489 (1998).
Suh, J. H. Stereotactic radiosurgery for the management of brain metastases. N. Engl. J. Med. 362, 1119–1127 (2010).
Kased, N. et al. Gamma Knife radiosurgery for brain metastases from primary breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 75, 1132–1140 (2009).
Amendola, B. E., Wolf, A. L., Coy, S. R., Amendola, M. & Bloch, L. Gamma knife radiosurgery in the treatment of patients with single and multiple brain metastases from carcinoma of the breast. Cancer J. 6, 88–92 (2000).
Muacevic, A., Kreth, F. W., Tonn, J. C. & Wowra, B. Stereotactic radiosurgery for multiple brain metastases from breast carcinoma. Cancer 100, 1705–1711 (2004).
Chougule, P. B. et al. Randomized treatment of brain metastasis with gamma knife radiosurgery, whole brain radiotherapy or both [abstract]. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 48, 114 (2000)
Aoyama, H. et al. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole-brain radiation therapy vs stereotactic radiosurgery alone for treatment of brain metastases: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 295, 2483–2491 (2006).
Mueller, R. P. et al. Adjuvant whole-brain radiotherapy versus observation after radiosurgery or surgical resection of 1–3 cerebral metastases: Results of the EORTC 22952-26001 study [abstract]. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 2008 (2009).
Chang, E. L. et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10, 1037–1044 (2009).
Patel, A. J. et al. Factors influencing the risk of local recurrence after resection of a single brain metastasis. J. Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2009.11.JNS09659.
Tsao, M. N. et al. Clinical practice guideline on the optimal radiotherapeutic management of brain metastases. BMC Cancer 5, 34 (2005).
Wong, W. W., Schild, S. E., Sawyer, T. E. & Shaw, E. G. Analysis of outcome in patients reirradiated for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 34, 585–590 (1996).
Shaw, E. et al. Single dose radiosurgical treatment of recurrent previously irradiated primary brain tumours and brain metastases: final report of RTOG protocol 90-05 Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 47, 291–298 (2000).
Patel, R. R. & Mehta, M. P. Targeted therapy for brain metastases: improving the therapeutic ratio. Clin. Cancer Res. 13, 1675–1683 (2007).
DeAngelis, L. M. et al. The role of postoperative radiotherapy after resection of single brain metastases. Neurosurgery 24, 798–805 (1989).
Ricard, D., Taillia, H. & Renard, J. L. Brain damage from anticancer treatments in adults. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 21, 559–565 (2009).
De Angelis, L. M., Delattre, J. Y. & Posner, J. B. Radiation-induced dementia in patients cured of brain metastases. Neurology 39, 789–796 (1989).
Rades, D., Lohynska, R., Veninga, T., Stalpers, L. J. & Schild, S. E. Evaluation of 2 whole-brain radiotherapy schedules and prognostic factors for brain metastases in breast cancer patients. Cancer 110, 2587–2592 (2007).
Gaspar, L. et al. Recursive partitioning analysis (RPA) of prognostic factors in three Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) brain metastases trials. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 37, 745–751 (1997).
Weltman, E. et al. Radiosurgery for brain metastases: a score index for predicting prognosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 46, 1155–1161 (2000).
Nieder, C., Marienhagen, K., Astner, S. T. & Molls, M. Prognostic scores in brain metastases from breast cancer. BMC Cancer 9, 105 (2009).
Le Scodan, R. et al. Brain metastases from breast carcinoma: validation of the radiation therapy oncology group recursive partitioning analysis classification and proposition of a new prognostic score. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 69, 839–845 (2007).
Pestalozzi, B. C. et al. Identifying breast cancer patients at risk for Central Nervous System (CNS) metastases in trials of the International Breast Cancer Study Group (IBCSG). Ann. Oncol. 17, 935–944 (2006).
Eichler, A. F. et al. Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer: the importance of HER-2 status. Cancer 112, 2359–2367 (2008).
Wolstenholme, V., Hawkins, M., Ashley, S., Tait, D. & Ross, G. HER2 significance and treatment outcomes after radiotherapy for brain metastases in breast cancer patients. Breast 17, 661–665 (2008).
Niwinska, A., Murawska, M. & Pogada, K. Breast cancer brain metastases: differences in survival depending on biological subtype, RPA RTOG prognostic class and systemic treatment after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT). Ann. Oncol. 21, 942–948 (2010).
Hines, S. L. et al. Clinical outcomes after a diagnosis of brain metastases in patients with estrogen- and/or human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive versus triple-negative breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 19, 1561–1565 (2008).
Lee, S. S. et al. Brain metastases in breast cancer: prognostic factors and management. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 111, 523–530 (2008).
Rades, D., Pluemer, A., Veninga, T., Dunst, J. & Schild, S. E. A boost in addition to whole-brain radiotherapy improves patient outcome after resection of 1 or 2 brain metastases in recursive partitioning analysis class 1 and 2 patients. Cancer 110, 1551–1559 (2007).
Hoskin, P. J., Crow, J. & Ford, H. T. The influence of extent and local management on the outcome of radiotherapy for brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 19, 111–115 (1990).
Kondziolka, D., Patel, A., Lunsford, L. D., Kassam, A. & Flickinger, J. C. Stereotactic radiosurgery plus whole brain radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for patients with multiple brain metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 45, 427–434 (1999).
Andrews, D. W. et al. Whole brain radiation therapy with or without stereotactic radiosurgery boost for patients with one to three brain metastases: phase III results of the RTOG 9508 randomised trial. Lancet 363, 1665–1672 (2004).
Bhatnagar, A. K., Flickinger, J. C., Kondziolka, D. & Lunsford, L. D. Stereotactic radiosurgery for four or more intracranial metastases. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 64, 898–903 (2006).
Tomita, N. et al. Helical tomotherapy for brain metastases: dosimetric evaluation of treatment plans and early clinical results. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 7, 417–424 (2008).
Gupta, T. et al. Planning and delivery of whole brain radiation therapy with simultaneous integrated boost to brain metastases and synchronous limited-field thoracic radiotherapy using helical tomotherapy: a preliminary experience. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 8, 15–22 (2009).
Sterzing, F. et al. Reirradiation of multiple brain metastases with helical tomotherapy. A multifocal simultaneous integrated boost for eight or more lesions. Strahlenther. Onkol. 185, 89–93 (2009).
Hsu, F. et al. Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneous integrated boost for 1–3 brain metastases: a feasibility study using volumetric modulated arc therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 76, 1480–1485 (2010).
Langer, C. J. & Mehta, M. P. Current management of brain metastases, with a focus on systemic options. J. Clin. Oncol. 23, 6207–6219 (2005).
Murray, K. J. et al. A randomized phase III study of accelerated hyperfractionation versus standard in patients with unresected brain metastases: a report of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) 9104. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 39, 571–574 (1997).
Monje, M. L., Mizumatsu, S., Fike, J. R. & Palmer, T. D. Irradiation induces neural precursor-cell dysfunction. Nat. Med. 8, 955–962 (2002).
Gutiérrez, A. N. et al. Whole brain radiotherapy with hippocampal avoidance and simultaneously integrated brain metastases boost: a planning study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 69, 589–597 (2007).
Ghia, A. et al. Distribution of brain metastases in relation to the hippocampus: implications for neurocognitive functional preservation. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 68, 971–977 (2007).
Soussain, C. et al. CNS complications of radiotherapy and chemotherapy. Lancet 374, 1639–1651 (2009).
Bauman, G. et al. Simultaneous infield boost with helical tomotherapy for patients with 1 to 3 brain metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 30, 38–44 (2007).
Welsh, J. S. et al. Helical tomotherapy as a means of delivering scalp-sparing whole brain radiation therapy. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 4, 661–662 (2005).
Correa, D. D. & Ahles, T. A. Neurocognitive changes in cancer survivors. Cancer J. 14, 396–400 (2008).
Kreukels, B. P., van Dam, F. S., Ridderinkhof, K. R., Boogerd, W. & Schagen, S. B. Persistent neurocognitive problems after adjuvant chemotherapy for breast cancer. Clin. Breast Cancer 8, 80–87 (2008).
Rugo, H. S. & Ahles, T. The impact of adjuvant therapy for breast cancer on cognitive function: current evidence and directions for research. Semin. Oncol. 30, 749–762 (2003).
Viani, G. A. et al. Whole brain radiotherapy with radiosensitizer for brain metastases. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 28, 1 (2009).
Xu, S. et al. Effects of Motexafin gadolinium on tumor metabolism and radiation sensitivity. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 49, 1381–1390 (2001).
Mehta, M. P. et al. Survival and neurologic outcomes in a randomized trial of motexafin gadolinium and whole-brain radiation therapy in brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 2529–2536 (2003).
Amorino, G. P. et al. Enhancement of tumor oxygenation and radiation response by the allosteric effector of hemoglobin, RSR13. Radiat. Res. 156, 294–300 (2001).
Shaw, E. et al. RSR13 plus cranial radiation therapy in patients with brain metastases: comparison with the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group Recursive Partitioning Analysis Brain Metastases Database. J. Clin. Oncol. 21, 2364–2371 (2003).
Suh, J. H. et al. Phase III study of efaproxiral as an adjunct to whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 24, 106–114 (2006).
Scott, C., Suh, J., Stea, B., Nabid, A. & Hackman, J. Improved survival, quality of life, and quality-adjusted survival in breast cancer patients treated with efaproxiral (Efaproxyn) plus whole-brain radiation therapy for brain metastases. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 30, 580–587 (2007).
Suh, J. H. et al. Results of the phase III ENRICH (RT-016) study of efaproxiral administered concurrently with whole brain radiation therapy (WBRT) in women with brain metastases from breast cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 72, S50–S51 (2008).
Knisely, J. P. et al. A phase III study of conventional radiation therapy plus thalidomide versus conventional radiation therapy for multiple brain metastases (RTOG 0118). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 71, 79–86 (2008).
Eyre, H. J. et al. Randomized trial of radiotherapy versus radiotherapy plus metronidazole for the treatment of metastatic cancer to brain. J. Neurooncol. 2, 325–330 (1984).
Komarnicky, L. T. et al. A randomized phase III protocol for the evaluation of misonidazole combined with radiation in the treatment of patients with brain metastases (RTOG-7916). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 20, 53–58 (1991).
Phillips, T. L., Scott, C. B., Leibel, S. A., Rotman, M. & Weigensberg, I. J. Results of a randomized comparison of radiotherapy and bromodeoxyuridine with radiotherapy alone for brain metastases: report of RTOG trial 89-05. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 33, 339–348 (1995).
Corn, B. W. et al. Prospective evaluation of quality of life and neurocognitive effects in patients with multiple brain metastases receiving whole-brain radiotherapy with or without thalidomide on Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) trial 0118. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 71, 71–78 (2008).
Cerchietti, L. C. et al. Phase I/II study of selective cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor celecoxib as a radiation sensitizer in patients with unresectable brain metastases. J. Neurooncol. 71, 73–81 (2005).
Cassier, P. A. et al. A phase 2 trial of whole-brain radiotherapy combined with intravenous chemotherapy in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer. Cancer 113, 2532–2538 (2008).
Hedde, J. P. et al. A phase I/II trial of topotecan and radiation therapy for brain metastases in patients with solid tumors. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 68, 839–844 (2007).
Addeo, R. et al. Phase 2 trial of temozolomide using protracted low-dose and whole-brain radiotherapy for nonsmall cell lung cancer and breast cancer patients with brain metastases. Cancer 113, 2524–2531 (2008).
Addeo, R. et al. Concomitant treatment of brain metastasis with whole brain radiotherapy [WBRT] and temozolomide [TMZ] is active and improves quality of life. BMC Cancer 7, 18 (2007).
Verger, E. et al. Temozolomide and concomitant whole brain radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases: a phase II randomized trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 61, 185–191 (2005).
Antonadou, D. et al. Phase II randomized trial of temozolomide and concurrent radiotherapy in patients with brain metastases. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 3644–3650 (2002).
Park, Y. H. et al. Trastuzumab treatment improves brain metastasis outcomes through control and durable prolongation of systemic extracranial disease in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer patients. Br. J. Cancer 100, 894–900 (2009).
Stemmler, H. J. et al. Ratio of trastuzumab levels in serum and cerebrospinal fluid is altered in HER2-positive breast cancer patients with brain metastases and impairment of blood-brain barrier. Anticancer Drugs 18, 23–28 (2007).
Liang, K. et al. Sensitization of breast cancer cells to radiation by trastuzumab. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2, 1113–1120 (2003).
Lin, N. U. et al. Multicenter phase II study of lapatinib in patients with brain metastases from HER2-positive breast cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 1452–1459 (2009).
Shah, N., Groom, N., Jackson, S., Sibtain, A. & Hoskin, P. A pilot study to assess the feasibility of prior scalp cooling with palliative whole brain radiotherapy. Br. J. Radiol. 73, 514–516 (2000).
Cuscela, D. et al. Protection from radiation-induced alopecia with topical application of nitroxides: fractionated studies. Cancer J. Sci. Am. 2, 273–278 (1996).
Metz, J. M. et al. A phase I study of topical Tempol for the prevention of alopecia induced by whole brain radiotherapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 10, 6411–6417 (2004).
Brizel, D. M. et al. Phase III randomized trial of amifostine as a radioprotector in head and neck cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 18, 3339–3345 (2000).
Nieder, C., Andratschke, N. H., Wiedenmann, N. & Molls, M. Prevention of radiation-induced central nervous system toxicity: a role for amifostine? Anticancer Res. 24, 3803–3809 (2004).
Lamproglou, I. et al. Radiation-induced cognitive dysfunction: the protective effect of ethyol in young rats. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 57, 1109–1115 (2003).
Magné, N. et al. The efficacy and toxicity of EGFR in the settings of radiotherapy: Focus on published clinical trials. Eur. J. Cancer 44, 2133–2143 (2008).
Magné, N., Chargari, C., Soria, J. C. & Deutsch, E. Concomitant chemo-radiotherapy in clinical trials: to promote step by step rational development. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 70, 206–215 (2009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
C. Chargari and Y. M. Kirova prepared the outline for the manuscript and wrote the content. All authors contributed to discussion of content for the article, researched data to include in the manuscript, reviewed and edited the manuscript before submission, and revised the manuscript in response to the peer-reviewers' comments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chargari, C., Campana, F., Pierga, JY. et al. Whole-brain radiation therapy in breast cancer patients with brain metastases. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 7, 632–640 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.119
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2010.119
This article is cited by
-
A phase I trial of sorafenib with whole brain radiotherapy (WBRT) in breast cancer patients with brain metastases and a correlative study of FLT-PET brain imaging
Breast Cancer Research and Treatment (2021)
-
Distribution of metastasis in the brain in relation to the hippocampus: a retrospective single-center analysis of 565 metastases in 116 patients
Cancer Imaging (2019)
-
The breast graded prognostic assessment is associated with the survival outcomes in breast cancer patients receiving whole brain re-irradiation
Journal of Neuro-Oncology (2018)
-
Clinical implication of Time To Brain Metastasis (TTBM) according to breast cancer subtypes
SpringerPlus (2013)
-
Breast cancer—what about radiosurgery for brain metastasis?
Nature Reviews Clinical Oncology (2011)