Abstract
Aberrant folding of proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum activates the bifunctional transmembrane kinase/endoribonuclease Ire1. Ire1 excises an intron from HAC1 messenger RNA in yeasts and Xbp1 messenger RNA in metozoans encoding homologous transcription factors. This non-conventional mRNA splicing event initiates the unfolded protein response, a transcriptional program that relieves the endoplasmic reticulum stress. Here we show that oligomerization is central to Ire1 function and is an intrinsic attribute of its cytosolic domains. We obtained the 3.2-Å crystal structure of the oligomer of the Ire1 cytosolic domains in complex with a kinase inhibitor that acts as a potent activator of the Ire1 RNase. The structure reveals a rod-shaped assembly that has no known precedence among kinases. This assembly positions the kinase domain for trans-autophosphorylation, orders the RNase domain, and creates an interaction surface for binding of the mRNA substrate. Activation of Ire1 through oligomerization expands the mechanistic repertoire of kinase-based signalling receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Main
Approximately one-third of all proteins in eukaryotes enter the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for processing and folding. The quality of protein folding is monitored by the ER-membrane-resident kinase/RNase Ire1, which is activated by misfolded proteins. On activation, Ire1 initiates a non-spliceosomal mRNA splicing reaction. Translation of the spliced mRNA yields an unfolded protein response (UPR)-specific transcription factor, termed Hac1 (ref. 1) in yeasts and Xbp1 (ref. 2) in metazoans, that induces a comprehensive transcriptional program to adjust the protein-folding capacity of the ER according to need. The UPR is activated in cancers3,4, viral infections5, protein-folding diseases6,7 and other cellular anomalies8,9.
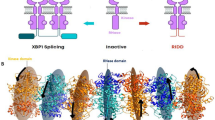
Under ER stress conditions, the ER-lumenal domain of Ire1 acts as a sensor of unfolded proteins10 (Fig. 1a). It crystallizes as a polymer that has two distinct crystallographic interfaces important for function10. This feature can explain an early observation of oligomerization of Ire1 during the UPR11 and provide a structural rationalization of Ire1 organization into UPR-induced clusters (foci) that can be observed by live cell imaging12,13. Oligomerization of the ER-lumenal domain of Ire1 has been proposed to promote dimerization and activation of the kinase/RNase domains10,14 analogous to other cell-surface signalling receptors15. Additionally, trans-autophosphorylation and binding of ADP are thought to contribute to activation of the Ire1 RNase16,17.
a, A general scheme of Ire1 activation during the UPR summarizing the key events. The kinase domain of Ire1 is coloured light brown; the RNase domain is coloured purple. TM, transmembrane. b, Schematic representation of RNA substrates used in this work. Triangles mark sites of specific cleavage by Ire1. c, Ire1 constructs used for cleavage assays and structure determination. d, Cooperative activation profiles for Ire1KR, Ire1KR24 and Ire1KR32 obtained using 5′-32P-HP21, with (filled circles) and without (open circles) cofactor. E, enzyme. Asterisks are used for reference in Fig. 2. Assay details are provided in Methods.
A recent crystal structure of the kinase/RNase domain of Ire1 reveals a two-fold symmetric dimer with a back-to-back arrangement of the kinase domains, compactly attached to an RNase dimer proposed to have two independent active sites14. The back-to-back arrangement of the kinases in the dimer is unexpected because it positions the phosphorylation sites in the activation loops more than 40 ångström (Å) away from the active site of the partnering molecule in the dimer. This arrangement does not seem to be productive for the trans-autophosphorylation of Ire1 observed in vivo11. We propose that a different Ire1 dimer enables the trans-autophosphorylation reaction (below). Dimerization of the RNase domains has been proposed to match functionally the conserved pair of splice sites in HAC1/Xbp1 mRNA14 (Fig. 1b). Our results indicate an alternative explanation because we observe fully reactive RNA substrates that contain only a single splice site, as well as poorly reactive RNA substrates that contain dual splice sites. In this work, we combine several approaches to show that the cytosolic region of Ire1 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae undergoes spontaneous oligomerization that activates Ire1 for signalling in the UPR.
Activation of the Ire1 RNase by oligomerization
We prepared variants of the cytosolic portion of Ire1 that contain the kinase and the RNase domains (Ire1KR), as well as the kinase and the RNase domains extended by 24 (Ire1KR24), 32 (Ire1KR32) or 120 (Ire1KR120, ref. 18) amino acids towards the amino terminus. These extensions are part of a ∼120-amino-acid-long linker domain that tethers the kinase/RNase domains to the transmembrane region (Fig. 1a, c and Supplementary Fig. 1a). Ire1KR120 showed an RNase activity indistinguishable from that of Ire1KR32 but proved unsuitable for crystallization and was not pursued further. All Ire1 constructs site-specifically cleaved 5′-32P-labelled stem-loop oligoribonucleotide17 (HP21) derived from the Xbp1 mRNA (Fig. 1b and Supplementary Fig. 1b; Methods). The observed rate constant exhibited a non-Michaelis dependence on the enzyme concentration and increased cooperatively with a Hill coefficient n = 2 for Ire1KR and Ire1KR24 and, surprisingly, a Hill coefficient n = 3.5–8 for Ire1KR32 (Fig. 1d). This observation indicates that the RNase activity of Ire1 arises from self-association with the formation of predominantly dimers for Ire1KR and Ire1KR24, and oligomers for Ire1KR32.
At protein concentrations above 10 µM, reactions with Ire1KR32 appeared as a heterogeneous suspension, indicating self-association of Ire1KR32 (Fig. 2a). The presence of several oligomeric species was apparent on analytical ultracentrifugation of the sample (Fig. 2b). The oligomerization could be readily reversed and RNase activity suppressed by addition of salt to the solution (Fig. 2a, c). The visible aggregation seemed to be specific because it was strongly induced by cofactors. In contrast, solutions of Ire1KR and Ire1KR24 remained clear at all concentrations with no signs of protein oligomerization, consistent with the lower cooperativity of their activation profiles (Fig. 1d).
a, Observation of visible self-association of Ire1KR32 that can be reversed by salt (NaCl). b, Analytical ultracentrifugation reveals monomers and dimers for Ire1KR as well as dimers and higher-order assemblies for Ire1KR32. Conditions were as in Fig. 1d; open symbols, 13.5 μM Ire1 (20 °C). c, Salt inhibits the RNase activity of Ire1KR32. d, Ire1KR32 has higher RNase activity against HP21 and Xbp1 RNA compared to Ire1KR and Ire1KR24 (Supplementary Fig. 1b; 2). Error bars show variability between single-exponential fits from two to five independent measurements. Conditions similar to those used in Fig. 1d are marked * and **.
Ire1KR32 cleaved HP21 ∼100-fold faster than did Ire1KR and Ire1KR24 (Fig. 2d, left panel). The observed rate constants were compared at 1 μM concentration of the enzymes, at which reactions occur in the same kinetic regime characterized by a log-linear concentration response of the observed rate constant. The catalytic advantage and the highly cooperative activation of Ire1KR32 were even more apparent with the Xbp1 443-base polymer, which more closely mimics the natural mRNA substrate of Ire1 (Fig. 2d, right panel, and Supplementary Fig. 2). These observations demonstrate that the N-terminal linker domain, particularly the eight amino acids that constitute the difference between Ire1KR32 and Ire1KR24 (Supplementary Fig. 1a), defines the self-association properties and the RNase activity of the cytosolic domains of Ire1. Notably, point mutations within these eight amino acids abrogate Ire1 signalling in vivo19. This functionally important linker extension was absent in the Ire1 variant used previously to obtain the back-to-back dimer structure14. The use of Ire1 that includes the extended N terminus resulted in the crystal structure of the oligomeric state of Ire1.
Structure of the Ire1 oligomer
To establish the mechanism of Ire1 oligomerization and activation, we used X-ray crystallography. Because efforts to crystallize Ire1KR32 with ADP produced crystals unsuitable for X-ray data collection, we attempted to co-crystallize Ire1KR32 with structurally diverse protein kinase inhibitors. Remarkably, several kinase inhibitors activated the RNase function revealing synthetic activators of wild-type Ire1 (Fig. 3a, b and Supplementary Fig. 3). These results have profound implications for therapeutic uses of kinase inhibitors (see Conclusions).
a, Activation of Ire1KR32 (3 µM) in the presence of different kinase inhibitors. b, Inhibitor structures, with probable hydrogen bonds shown by dashed lines. c, σA-weighted 3Fobs–2Fcalc map for APY29 bound to Ire1KR32Δ28 contoured at 1.5σ. d, The network of probable hydrogen bonds between APY29 and Ire1. e, The network of interactions between ADṖMg and Ire1 (PDB ID 2RIO). f, Chelation of magnesium inhibits Ire1 RNase in the presence of ADP, but not of APY29. Error bars show variability between single-exponential fits from two independent measurements. Reactions contained 2 mM ADP or 100 µM APY29.
Crystals obtained with the inhibitor APY29 allowed determination of the structure of the Ire1KR32·APY29 complex at 3.9 Å resolution. The resolution improved to 3.2 Å with a mutant version of Ire1KR32, Ire1KR32Δ28·APY29, in which we deleted the αF–αEF loop (28 amino acids, 865–892). The αF–αEF loop is not evolutionary conserved and was disordered in the 3.9-Å structure. Its deletion had no effect on the RNase activity of Ire1 (Supplementary Fig. 4). Electron density for the APY29 molecule was found in the ATP-binding pocket of the Ire1 kinase domain (Fig. 3c). The position of APY29 indicates that it could form three hydrogen bonds with residues Glu 746 and Cys 748 of the main chain and two additional hydrogen bonds or van der Waals contacts with the side chains Asn 751 and Asp 828 at the active site (Fig. 3d).
Although all tested compounds can potentially form hydrogen bonds with the protein backbone (Fig. 3b), the most potent activators, APY29 and APY24, also interact with the side chain Asn 751 and insert bulky aromatic rings in place of the ribose-phosphate moiety of ADP. Manual fitting of the FDA-approved anti-cancer drug Sunitinib guided by known structures of kinasėinhibitor complexes (Protein Data Bank (PDB) IDs 2G9X and 2F4J) predicts that the compound fills the adenine-binding site, but not the ribose and the phosphate subsites. Such partial occupancy could explain the fairly good binding of Sunitinib to Ire1 accompanied by partial activation of the enzyme (Fig. 3a). AIN54 could not be fit to the ATP pocket owing to steric clashes with the β1 strand.
The interactions of APY29 with the nucleotide-binding pocket closely mimic those of ADP except that APY29 does not use a divalent metal ion for docking (Fig. 3d, e). Accordingly, addition of EDTA inhibits the RNase activity of Ire1 for reactions stimulated by ADP but not APY29 (Fig. 3f). These findings support a model first proposed based on Ire1 mutants16: that ADP and kinase inhibitors activate Ire1 RNase by filling the ATP pocket. For maximum activity the adenine and the ribose subsites should be occupied, apparently to stabilize the active open conformation of the kinase that favours self-association of Ire1. Electrostatic interactions due to coordination of the magnesium ion and the phosphate groups of ADP do not have an indispensable role as the charged moieties can be replaced with neutral space-filling groups.
In contrast to Ire1, which lacks the oligomerization-inducing N-terminal segment and crystallizes as a back-to-back dimer14, Ire1KR32 and Ire1KR32Δ28 crystallize as a symmetric high-order assembly (Fig. 4a, b). Fourteen Ire1 molecules constitute the asymmetric unit in the crystal lattice. Formation of the oligomer can be described by incremental addition of symmetric back-to-back Ire1 dimers to an end of a growing filament, with a simultaneous clockwise turn of 51.4° per dimer, with a complete 360° turn every 14 molecules.
a, Assembly of Ire1KR32Δ28˙APY29. A parallel filament in the crystal packing is shown above the main filament. Domains are coloured as in Fig. 1a. The inset shows crystal packing of Ire1 dimers (PDB ID 2RIO). Letters A–N below the structure refer to individual monomers in the asymmetric unit. K, kinase; R, ribonuclease. b, Three intermolecular interfaces of Ire1KR32Δ28 in the oligomer. c, Dimer formed via interface IF1c. d, Dimer formed via interface IF2c. e, Dimer formed via interface IF3c (left). Close view of the activation loop (right). Phosphates are shown in ball representation. Arrows in b and e show the direction of the activation loop donation. Regions with previously unknown structures are coloured green.
The use of 14-fold non-crystallographic symmetry (NCS) improved the quality of averaged electron density maps and helped the modelling of all of the regions missing from the starting model (Supplementary Fig. 5). The structure of the kinase/RNase domain in the oligomer is similar to that in the Ire1˙ADP dimer14. However, tight packing of Ire1 in the oligomer compared to the crystal packing of the Ire1˙ADP dimers (Fig. 4a, inset) orders several fragments of Ire1 absent in the previous model (coloured green in Figs 4c–e). None of the new elements belong to the interface IF1c defined previously in the back-to-back dimer14 (Fig. 4b, c). Two new interfaces, IF2c and IF3c, form in addition to the interface IF1c in the oligomer. Interface IF2c has a two-fold symmetry and forms by contacts between the RNase domains of monomers A–D, C–F, and so on (Fig. 4d). Interface IF3c creates a linear side-to-side arrangement of monomers into filaments (B → D → F and, with opposite polarity, A ← C ← E). Interface IF3c is formed by contacts between the kinase domains and involves two new elements, the αD′ helix and the activation loop (Fig. 4e). The oligomerization-inducing N-terminal extension (residues 641–662) was disordered. Its structure and the mechanism of facilitating Ire1 oligomerization remain to be determined. It is possible that part of the N-tail contacts a dimerization interface, as proposed recently for the arginine-rich linker extension of epidermal growth factor receptor20.
Architecturally, the oligomer resembles the double helix of DNA (Fig. 4b and Supplementary Fig. 6), where interface IF1c parallels the interaction between nucleobases of opposing strands and interface IF3c parallels phosphodiester linkages between nucleotides of the same strand.
The trans-autophosphorylation complex of Ire1
In the Ire1 oligomer, each kinase offers its activation loop to a new partner, thereby extending the filamentous oligomeric assembly. This interaction resembles the side-to-side arrangement of kinase dimers implicated in trans-autophosphorylation reactions21,22. Ire1KR32 used in this work contained 17 phosphorylated residues (Supplementary Fig. 7). Phosphorylation was not observed on expression of Ire1 with a kinase-inactivating mutation (D828A), indicating that all Ire1 phosphates derive from its own kinase activity as the protein is expressed in Escherichia coli. Mass spectrometric analyses localized the phosphorylation sites to the activation loop and the αEF–αF loop (Supplementary Table 1), both of which face interface IF3c. Together, the oligomer structure and mass spectrometry support a model wherein IF3c serves for transfer of the phosphates in trans, resolving the difficulty in explaining trans-autophosphorylation of Ire1 in the back-to-back dimer14. The tightly packed oligomer makes it highly unlikely that kinases other than Ire1 have access to the phospho-acceptor sites. This feature can explain the specific phosphorylation of sites in Ire1 that are not part of any recognizable consensus motif and the apparent absence of other kinases known to phosphorylate Ire1.
Three phosphorylated residues important for Ire1 activation in vivo11—Ser 840p, Ser 841p and Thr 844p—are resolved in the crystal structure (Fig. 4e). Thr 844p forms two intramolecular salt bridges positioned to stabilize the open state of the activation loop and conserved among kinases23. Ser 840p and Ser 841p form two additional intramolecular salt bridges, and Ser 841p forms a unique intermolecular salt bridge with an adjacent Ire1 molecule at interface IF3c. All three phosphates are ideally placed to help Ire1 oligomerization by stabilizing the oligomerization-compatible open state of Ire1 kinase and positioning Ser 841p to stabilize interface IF3c.
Three Ire1 interfaces control the RNase activity
The presence of the three distinct interfaces in the oligomer structure raised questions about their relative contribution to activation of the Ire1 RNase. Thus, we characterized Ire1 variants with each interface selectively impaired by mutations. For IF1c, we prepared Ire1 with an E988Q mutation, which had the strongest deleterious effect on the RNase activity among the tested RNase IF1c mutants14. For IF2c and IF3c, we identified previously uncharacterized contacts and mutated relevant residues to destabilize these contacts (Fig. 5a, b).
a, Schematic representation of the Ire1 oligomer packing. Stars mark the ATP-binding pocket of the Ire1 kinase. Lower panel shows a single monomer; upper panel shows packing of four monomers. b, Contacts at the intermolecular interfaces of the oligomer. c, Mutations of the predicted interface residues designed to weaken IF1c, IF2c and IF3c inhibit the RNase activity of Ire1KR32. Reactions contained 5′-32P-HP21, 3 μM Ire1KR32 and 2 mM ADP. WT, wild type. Error bars show variability between single-exponential fits from two independent measurements. The colour of the bars matches that in a and b.
In the standard cleavage assay (3 µM Ire1, HP21 substrate), mutations at all three interfaces had significant deleterious effects (Fig. 5c). Mutations mapping to IF2c and IF3c exhibited as strong or stronger effects on the RNase activity as did the mutation mapping to IF1c. Sedimentation profiles and activation profiles show that mutations at each of the interfaces weaken the self-association properties of Ire1KR32 (Supplementary Fig. 8). The functional importance of residues at all three interfaces indicates a conjoint effort from IF1c, IF2c and IF3c in activation of the RNase.
The activation mechanism of the Ire1 RNase
It has been suggested that dimerization activates the RNase of Ire1 by complementing the pair of splice sites in the HAC1/Xbp1 mRNA14. In principle, this mechanism could explain why the stem-loop HP21 is cleaved slowly compared to HAC1/Xbp1 mRNA (Fig. 2d). However, several pieces of evidence do not support the proposed model. Only Ire1KR32 shows a large preference for cleavage of HAC1/Xbp1 mRNA over stem-loop HP21, whereas Ire1KR and Ire1KR24 show no discrimination (Fig. 2d). Furthermore, we prepared a 354-nucleotide RNA substrate that contains only a single stem-loop but reacts with Ire1KR32 at the rate of HAC1 and Xbp1 mRNA (Fig. 6a, b). We also prepared a 58-nucleotide RNA substrate that contains two stem-loops but reacts with Ire1KR32 at a rate of HP21 (Fig. 6c). These findings show that substrates with dual stem-loops do not have catalytic advantage compared to substrates with a single stem-loop and that self-association activates the Ire1 RNase by a mechanism different from steric complementation of the dual splice sites. In the oligomer structure, the RNase domains are linked into a continuous ribbon by two interfaces, IF1c and IF2c (Supplementary Fig. 9). IF2c places the α3′ helices from the adjacent RNase monomers in reciprocal contact (Fig. 6d). The α3′ helix as well as the adjacent α3′–α4 loop (coloured green in Fig. 6d, e and Supplementary Fig. 9) are disordered in the back-to-back dimer structure14, indicating that IF2c stabilizes this helix-loop element (designated HLE). Location of HLE near a dimerization interface may provide a dynamic switch that controls the RNase activity of Ire1. Indeed, HLE completes the proposed RNase active site and creates a cavity characteristic for substrate-binding pockets of enzymes (Fig. 6e), and point mutations in the HLE inactivate the RNase14 .
a, Time courses for cleavage of Xbp1 (lanes 1–6) and of Xbp1/PstI (lanes 7–12) with 5 nM Ire1KR32. b, Quantification of the gel in a. c, Cleavage of RNA with one and two splice sites by Ire1KR32. Error bars show variability between single-exponential fits from two to five independent measurements. nt, nucleotide. d, Position of the HLE at the RNase–RNase interface IF2c. e, Molecular surface representation of the RNase domain in the oligomer and in the dimer structures. Putative catalytic residues in d and e are coloured orange; HLE is coloured green. f, Revised model of Ire1 activation during the UPR.
An important additional contribution of oligomerization to the RNase activation may result from the extensive molecular surface of the oligomer, which would provide interactions with the substrate mRNA not possible with a monomer or a dimer. Xbp1 mRNA binds to Ire1KR32 several orders of magnitude better than HP21 (Supplementary Fig. 10), indicating that protein–mRNA binding interactions spread beyond a stem-loop binding site of Ire1. These interactions could explain why Ire1KR and Ire1KR24, which do not form oligomers, do not discriminate between large and small RNA substrates (Fig. 2d). We conclude that yet to be characterized extended contacts between the Ire1 oligomer and mRNA feature prominently in Ire1 function.
Mechanistic implications
Key attributes of Ire1 activation emerged soon after its discovery and include Ire1 self-association, trans-autophosphorylation and the binding of ADP as a cofactor (Fig. 1a). Our present functional and structural data rationalize each of these events. In particular, we show that the primary step activating the Ire1 RNase is the self-assembly of the cytosolic region into a helical rod structure (Fig. 4a). The self-association equilibrium built into the cytosolic kinase/RNase module must be subservient to the ligand-controlled oligomerization of the ER-lumenal domain of Ire1 to establish the flow of the UPR signal from the ER lumen towards the cytosol. Therefore, aggregation of the ER-lumenal domain of Ire1 by unfolded proteins would serve to increase the local concentrations of the kinase/RNase domains on the cytosolic side of the ER membrane, passing the threshold for oligomerization and, consequently, RNase activation.
The roles and the temporal separation of trans-autophosphorylation and ADP binding are now clear. Oligomerization of the unphosphorylated Ire1 opens the kinase domain and positions it for trans-autophosphorylation (Supplementary Fig. 11a). ATP enters the opened kinase and phosphorylates the activation loop in trans to lock it in the oligomerization-compatible open state and to introduce a phosphate-mediated salt bridge at the interface IF3c. These events provide positive feedback for oligomer assembly (Fig. 6f). Binding of a cofactor occurs in the open state of Ire1 kinase, shifts the equilibrium from monomers towards multimers and provides an additional, phosphorylation-independent level of positive modulation for the activating transition (Fig. 6f). At increased concentrations, Ire1 self-associates and becomes activated independent of phosphorylation (Supplementary Fig. 11b) and cofactor binding (Fig. 1d, open circles), directly supporting the model wherein oligomerization is the earliest and centremost step of Ire1 activation. Cofactor binding and phosphorylation enhance the self-association properties of Ire1 but neither is strictly required.
A model for the structure of the UPR-induced Ire1 foci12,13 emerges from our work. Oligomers formed by the ER-lumenal domain of Ire1 and the cytoplasmic domains can be arranged to give similar periodicity of monomers on both sides of the ER membrane (Supplementary Fig. 12a). The resulting mesh could provide a platform for the formation and growth of supramolecular Ire1 foci in two dimensions. The length of the linkers connecting the functional domains of Ire1 to the transmembrane region permits this arrangement (Supplementary Fig. 12b). Such an assembly would allow a cooperative response to unfolded proteins and a prolonged time to mount and extinguish the UPR.
Conclusions
Our knowledge of the multi-domain signalling proteins built around protein kinases is fairly immature. This work shows how one of these molecules, Ire1, operates by forming a supramolecular structure not observed previously. We found that kinase inhibitors—including Sunitinib—act as potent activators of the Ire1 RNase. Because Ire1 provides cytoprotective function24,25 from which cancer cells may benefit, it may be of therapeutic value to separate the intended function of kinase inhibitors towards the targets for which they were designed from activation of Ire1. Conversely, Ire1 activation might contribute to the beneficial effects of kinase inhibitors, including Sunitinib, in mouse models of type 1 diabetes26, and the cytoprotective effect of the Ire1 activators may be harnessed to combat protein-folding diseases.
Methods Summary
Proteins were expressed in E. coli and purified using glutathione S-transferase (GST)-affinity purification and size-exclusion chromatography. The DNA oligonucleotides were made by PCR or purchased from IDT. RNA oligonucleotides were purchased from Dharmacon Inc. or prepared by in vitro transcription with T7 RNA polymerase. All kinetic assays were done at 30 °C and neutral pH. Diffraction data were collected from cryo-preserved crystals at a beamline 8.3.1 (Advanced Light Source, Berkeley National Laboratories). The structure was solved at 3.2 Å resolution by molecular replacement followed by refinement in CNS27 and PHENIX28. The 2.4-Å structure of Ire1 dimer (PDB ID 2RIO14) was used as a molecular replacement search model in PHASER29. The final model containing amino acids 663–864 and 893–1115 of Ire1 has R/Rfree of 0.235/0.283 and excellent stereochemistry (PDB ID 3FBV; Supplementary Fig. 13 and Supplementary Tables 2–5). A part of the N-tail (residues 641–662) is disordered.
Online Methods
Experimental errors
All quantitative parameters were measured two or more times. The rate variations between measurements done on different days were within twofold and were always small compared to the effects we describe as significant. Errors and experimental uncertainties are indicated where applicable.
Expression and purification of Ire1 constructs
The plasmids for Ire1 expression were prepared using PCR with Pfu polymerase and pGEX-6P-2 vector encoding the cytoplasmic domain of Ire1 (ref. 18). DNA primers for mutagenesis were designed using Biochem Lab Solutions 3.5 and purchased from IDT. Proteins were expressed in BL21 CodonPlus (RIPL) E. coli cells (Stratagene). Expression and purification was conducted as described previously30. Bacteria were grown at 22 °C and lysis and FPLC buffers contained at least 300 mM NaCl to prevent aggregation of Ire1. Protein concentrations were determined from ultraviolet spectra using absorption peak at 280 nm and calculated extinction coefficients (Biochem Lab Solutions 3.5). Stocks of purified Ire1 had concentrations 10–70 mg ml-1 and were at least 99% pure as judged by Coomassie blue staining and quantification of FPLC traces.
Preparation of RNA substrates
HP21 21- and HAC1 28-base polymers were purchased from Dharmacon Inc. Other RNA substrates were prepared from restriction-digested plasmids encoding HAC1 and Xbp1 mRNA or from PCR-amplified products. Preparative amounts of long RNA were made using MegashortScript kit (Ambion). Before use, the oligonucleotides were purified by a denaturing (8 M urea) 5–20% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE). Cross-linked 29:1 polyacrylamide (40%) was purchased from National Diagnostics. Gel slices containing RNA were eluted in TE buffer and ethanol-precipitated. Substrates labelled with 32P at the 5′-terminus were prepared using T4 PNK (NEB) and γ-32P-ATP (Perkin Elmer). The 32P-body-labelled substrates were prepared by transcription with T7 RNA polymerase (Promega) in the presence of α-32P-UTP (Perkin Elmer). All 32P-labelled substrates were purified by denaturing 5–20% PAGE, eluted in TE and ethanol-precipitated before using.
Preparation of kinase inhibitors
Kinase inhibitors were obtained by chemical synthesis. The synthetic schemes will be reported in an upcoming publication.
The RNase cleavage assay
RNA cleavage reactions were conducted at 30 °C in buffer containing 20 mM HEPES (pH 7.0 at 30 °C), 70 mM NaCl, 2 mM ADP (pH 7.0), 2 mM Mg(OAc)2, 5 mM DTT, 5% glycerol, less than 1 nM 32P-labelled RNA substrate and 3 nM to 20 μM Ire1. Ire1 cleaves HAC1- and Xbp1-derived RNA substrates with similar kinetics (Fig. 6b). Xbp1 mRNA reacts to lower end points and has a more robust kinetic behaviour compared to that of HAC1 mRNA, presumably owing to better folding, and was used in most of the experiments. Reaction solutions and buffers were designed using Biochem Lab Solutions 3.5. Reactions were prepared such that 1 μl of RNA was added to 9 μl of pre-warmed reaction mixture containing all components except RNA. Typically, 3–10-min time courses were collected starting from 5 s for the first time point. At time intervals, 1 μl aliquots were withdrawn from each reaction and mixed with 6 μl stop solution containing 10 M urea, 0.1% SDS, 0.1 mM EDTA, 0.05% xylene cyanol and 0.05% bromophenol blue. The samples were separated by a denaturing 10–15% PAGE and exposed on a phosphor storage screen. The screens were scanned on a Storm or a Typhoon instruments and quantified using ImageQuant 5.0 or GelQuant.NET 1.4 programs. The data were plotted and fit in SigmaPlot 6.1. Hill equation with one added constant that describes the low-enzyme plateau was used to fit the cooperative activation profiles.
Analytical ultracentrifugation
Ire1 samples (13.5 μM) were loaded to a 400 μl cell in buffer for the RNase cleavage assay. Centrifugation was carried out on a Beckmann XL-A analytical ultracentrifuge at 129,024g (20 °C). A total of 60–80 scans were collected. Sedimentation traces were analysed in UltraScan 9.8 using C(s) model.
Mass spectrometry
A gold-coated plate was washed with 100% methanol and water. Solution A (10 mg 4-HCCA in 0.7 ml of acetonitrile, 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid) was quickly spread in a layer and allowed to dry. The residue was removed gently with a tissue. 0.5 μl of a mixture containing 1 μl Ire1 sample (0.1–1 mg ml-1) and 5 μl solution B (300 μl formic acid, 100 μl H2O, 200 μl iso-propanol, 10 mg 4-HCCA) was spotted over the dried surface and allowed to dry. The sample was washed twice with 2 μl of 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid and used for MALDI analysis on a Voyager mass spectrometer. The spectra were analysed using MoverZ (Genomic Solutions).
Crystallization
Initially Ire1KR32 (10 mg ml-1) was crystallized as a complex with ADP (2 mM) by vapour diffusion in hanging drops from 1.0 M sodium citrate. These co-crystals were disordered in one direction preventing their use in diffraction studies. A different crystal form was found by replacing the ADP with a kinase inhibitor APY29. Ire1KR32˙APY29 crystals were also obtained by vapour diffusion in hanging drops. Drops were prepared by mixing 1 μl of Ire1KR32 (12 mg ml-1) and APY29 (1 mM) in buffer containing 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.0 (20 °C), 500 mM NaCl, 2 mM DTT and 5% glycerol with 1 μl of solution containing 0.27 M Na2SO4, 8% PEG-3350, 10 mM EDTA and 2 mM TCEP. Well solution contained 200 µl of 0.085 M Na2SO4, 2.33% PEG-3350 and 5% tert-amyl alcohol. Single crystals grew at room temperature (20 °C) to a maximum size of 0.1 × 0.4 × 0.2 mm3 during three to four days. For data collection, the crystals were flash-frozen in solution containing 0.085 M Na2SO4, 3% tert-amyl alcohol, 5% PEG-3350 and 30% ethylene glycol. Crystals of Ire1KR32Δ28, were grown as described previously, except well solution contained 90 mM Na-citrate, pH 5.6.
Data collection and analysis
X-ray diffraction data were recorded on a beam line BL 8.3.1 at the Advanced Light Source (Berkeley National Laboratory). The data set, obtained using an X-ray wavelength of 1.11587 Å and an oscillation angle of 1 degree, was indexed and integrated using the XDS package31 (Supplementary Table 2). The data set was scaled with SCALA32. Five per cent of the reflections were marked as a test set. To reduce possible bias in Rfree towards R due to the high NCS, we have selected test-set reflections in thin shells rather than randomly33, so that the symmetry-related reflections belong either to the test or to the working set. A molecular replacement solution was found using PHASER29. Fourteen copies of monomer A from the X-ray structure of the Ire1 dimer14 were used as a starting model for refinement. Simulated annealing and grouped B-factor refinement were carried out in CNS27 followed by simulated annealing (starting at 10,000K) and TLS refinement in PHENIX28, using 14-fold NCS. One NCS group was comprised of one Ire1 monomer. HLE of monomer A was excluded from NCS treatment because its conformation differed from that in other monomers due to a close crystallographic contact. Fourier σA-weighted34 Fobs–Fcalc difference maps were used for interpretation of the parts of the model missing from the starting structure. The model of the ligand was created using ChemSketch 10.0 from Advanced Chemistry Development, Inc. (ACD/Labs). Model building and local real-space refinement were performed in Coot35, PyMol (DeLano Scientific) and RSRef36. The resulting model has excellent stereochemical parameters (Supplementary Table 2), no Ramachandran plot outliers (0 residues in disallowed regions) and low crystallographic R/Rfree of 0.235/0.283, indicating good agreement with diffraction data.
References
Cox, J. S. & Walter, P. A novel mechanism for regulating activity of a transcription factor that controls the unfolded protein response. Cell 87, 391–404 (1996)
Yoshida, H., Matsui, T., Yamamoto, A., Okada, T. & Mori, K. XBP1 mRNA is induced by ATF6 and spliced by IRE1 in response to ER stress to produce a highly active transcription factor. Cell 107, 881–891 (2001)
Koong, A. C., Chauhan, V. & Romero-Ramirez, L. Targeting XBP-1 as a novel anti-cancer strategy. Cancer Biol. Ther. 5, 756–759 (2006)
Ma, Y. & Hendershot, L. M. The role of the unfolded protein response in tumour development: friend or foe? Nature Rev. Cancer 4, 966–977 (2004)
Zheng, Y. et al. Hepatitis C virus non-structural protein NS4B can modulate an unfolded protein response. J. Microbiol. 43, 529–536 (2005)
Kudo, T. et al. The unfolded protein response is involved in the pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 977, 349–355 (2002)
Bartoszewski, R. et al. Activation of the unfolded protein response by {Delta}F508 CFTR. Am. J. Respir .Cell. Mol. Biol. 39, 448–457 (2008)
Naidoo, N., Giang, W., Galante, R. J. & Pack, A. I. Sleep deprivation induces the unfolded protein response in mouse cerebral cortex. J. Neurochem. 92, 1150–1157 (2005)
Atkin, J. D. et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and induction of the unfolded protein response in human sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 30, 400–407 (2008)
Credle, J. J., Finer-Moore, J. S., Papa, F. R., Stroud, R. M. & Walter, P. On the mechanism of sensing unfolded protein in the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 102, 18773–18784 (2005)
Shamu, C. E. & Walter, P. Oligomerization and phosphorylation of the Ire1p kinase during intracellular signaling from the endoplasmic reticulum to the nucleus. EMBO J. 15, 3028–3039 (1996)
Kimata, Y. et al. Two regulatory steps of ER-stress sensor Ire1 involving its cluster formation and interaction with unfolded proteins. J. Cell Biol. 179, 75–86 (2007)
Aragón, T et al. Messenger RNA targeting to endoplasmic reticulum stress signalling sites. Nature 10.1038/nature07641 (this issue)
Lee, K. P. et al. Structure of the dual enzyme Ire1 reveals the basis for catalysis and regulation in nonconventional RNA splicing. Cell 132, 89–100 (2008)
Zhang, X., Gureasko, J., Shen, K., Cole, P. A. & Kuriyan, J. An allosteric mechanism for activation of the kinase domain of epidermal growth factor receptor. Cell 125, 1137–1149 (2006)
Papa, F. R., Zhang, C., Shokat, K. & Walter, P. Bypassing a kinase activity with an ATP-competitive drug. Science 302, 1533–1537 (2003)
Gonzalez, T. N. & Walter, P. Ire1p: a kinase and site-specific endoribonuclease. Methods Mol. Biol. 160, 25–36 (2001)
Sidrauski, C. & Walter, P. The transmembrane kinase Ire1p is a site-specific endonuclease that initiates mRNA splicing in the unfolded protein response. Cell 90, 1031–1039 (1997)
Goffin, L. et al. The unfolded protein response transducer Ire1p contains a nuclear localization sequence recognized by multiple beta importins. Mol. Biol. Cell 17, 5309–5323 (2006)
Thiel, K. W. & Carpenter, G. Epidermal growth factor receptor juxtamembrane region regulates allosteric tyrosine kinase activation. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 104, 19238–19243 (2007)
Pirruccello, M. et al. A dimeric kinase assembly underlying autophosphorylation in the p21 activated kinases. J. Mol. Biol. 361, 312–326 (2006)
Pike, A. C. et al. Activation segment dimerization: a mechanism for kinase autophosphorylation of non-consensus sites. EMBO J. 27, 704–714 (2008)
Yonemoto, W. et al. Autophosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase in Escherichia coli. Identification of phosphorylation sites in the recombinant catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Protein Eng. 10, 915–925 (1997)
Lin, J. H. et al. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 318, 944–949 (2007)
Han, D. et al. A kinase inhibitor activates the IRE1α RNase to confer cytoprotection against ER stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 365, 777–783 (2008)
Louvet, C. et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors reverse type 1 diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 105, 18895–18900 (2008)
Brunger, A. T. et al. Crystallography & NMR system: A new software suite for macromolecular structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 54, 905–921 (1998)
Adams, P. D. et al. PHENIX: building new software for automated crystallographic structure determination. Acta Crystallogr. D 58, 1948–1954 (2002)
McCoy, A. J. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Cryst. 40, 658–674 (2007)
Nock, S., Gonzalez, T. N., Sidrauski, C., Niwa, M. & Walter, P. Purification and activity assays of the catalytic domains of the kinase/endoribonuclease Ire1p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Methods Enzymol. 342, 3–10 (2001)
Kabsch, W. Automatic processing of rotation diffraction data from crystals of initially unknown symmetry and cell constants. J. Appl. Cryst. 26, 795–800 (1993)
Evans, P. Scaling and assessment of data quality. Acta Crystallogr. D 62, 72–82 (2006)
Fabiola, F., Korostelev, A. & Chapman, M. S. Bias in cross-validated free R factors: mitigation of the effects of non-crystallographic symmetry. Acta Crystallogr. D 62, 227–238 (2006)
Read, R. J. Coefficients for maps using phases from partial structures with errors. Acta Crystallogr. A 42, 140–149 (1986)
Emsley, P. & Cowtan, K. Coot: model-building tools for molecular graphics. Acta Crystallogr. D 60, 2126–2132 (2004)
Korostelev, A., Bertram, R. & Chapman, M. S. Simulated-annealing real-space refinement as a tool in model building. Acta Crystallogr. D 58, 761–767 (2002)
Acknowledgements
We thank A. Krutchinsky for the help with MALDI instruments and for the tryptic digest analysis of Ire1KR32, F. Gruswitz for useful discussions, C. Waddling for managing the protein crystallization facility of the molecular structure group (MSG) at UCSF, and to the staff of the beamline 8.3.1 at the Advanced Light Source (Berkeley). We thank members of the Walter laboratory for critical review of the manuscript. A.V.K. is a recipient of Jane Coffin Childs fellowship. C.Z. was supported by a grant from the National Parkinson Foundation. R.M.S., J.F.-M. and P.F.E. were supported by an NIH grant RO1 GM60641. P.W. and K.M.S. are Investigators of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute.
Author Contributions A.V.K. designed and prepared protein and RNA constructs and carried out kinetic and biophysical analyses. A.V.K. and P.F.E. carried out crystallization and data collection. A.A.K. performed structure determination. J.F.-M. and A.V.K. contributed to crystallographic data processing and model building. C.Z. and K.M.S. selected and provided the kinase inhibitors. P.W. and R.M.S. supervised the work. A.V.K. and P.W. wrote the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Information
This file contains Supplementary Figures 1-13 with Legends and Supplementary Tables 1-5. (PDF 8492 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Korennykh, A., Egea, P., Korostelev, A. et al. The unfolded protein response signals through high-order assembly of Ire1. Nature 457, 687–693 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07661
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07661
This article is cited by
-
ER Ca2+ overload activates the IRE1α signaling and promotes cell survival
Cell & Bioscience (2023)
-
Dual RNase activity of IRE1 as a target for anticancer therapies
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling (2023)
-
IRE1α: from the function to the potential therapeutic target in atherosclerosis
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2023)
-
Pharmacological targeting of endoplasmic reticulum stress in disease
Nature Reviews Drug Discovery (2022)
-
Pumilio protects Xbp1 mRNA from regulated Ire1-dependent decay
Nature Communications (2022)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.