Abstract
Objective:
The Japan Public Health Center-based prospective Study examined the association of body mass index (BMI) and weight change with incident stroke in Japanese individuals, for whom BMI levels are generally low.
Methods:
We used initial data from 1990 to 1994 and 5-year follow-up surveys from 1995 to 1999. We calculated weight change over a 5-year period for 32 847 men and 38 875 women, aged 45–74 years, with no history of cardiovascular disease or cancer. Subjects were followed from the 1995–1999 survey to the end of 2005, and hazard ratios of self-reported BMI levels and weight change for incident stroke were estimated using Cox's proportional hazard models adjusted for potential confounders.
Results:
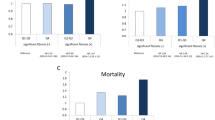
During the follow-up period (median 7.9 years) there were 2019 incident strokes, including subtypes. Multivariable-adjusted hazard ratios for all stroke events by BMI levels of 27.0–29.9 and ⩾30 kg m–2 versus 23.0–24.9 kg m–2 were 1.09 (95% confidence interval 0.88, 1.36) and 1.25 (0.86, 1.84) in men (P for trend=0.22), and 1.29 (1.01, 1.65) and 2.16 (1.60, 2.93) in women (P for trend <0.001), respectively. A weight change of ⩾10% in the previous 5 years was associated with total strokes and ischemic strokes in women.
Conclusion:
Higher BMI levels and a weight gain of ⩾10% over 5 years were associated with an increased risk of stroke in women, whereas this association was weak in men.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurth T, Gaziano JM, Rexrode KM, Kase CS, Cook NR, Manson JE et al. Prospective study of body mass index and risk of stroke in apparently healthy women. Circulation 2005; 111: 1992–1998.
Kurth T, Gaziano JM, Berger K, Kase CS, Rexrode KM, Cook NR et al. Body mass index and the risk of stroke in men. Arch Intern Med 2002; 162: 2557–2562.
Hu G, Tuomilehto J, Silventoinen K, Sarti C, Mannisto S, Jousilahti P . Body mass index, waist circumference, and waist-hip ratio on the risk of total and type-specific stroke. Arch Intern Med 2007; 167: 1420–1427.
Jood K, Jern C, Wilhelmsen L, Rosengren A . Body mass index in mid-life is associated with a first stroke in men: a prospective population study over 28 years. Stroke 2004; 35: 2764–2769.
Rexrode KM, Hennekens CH, Willett WC, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Rich-Edwards JW et al. A prospective study of body mass index, weight change, and risk of stroke in women. JAMA 1997; 277: 1539–1545.
Yatsuya H, Folsom AR, Yamagishi K, North KE, Brancati FL, Stevens J . Race- and sex-specific associations of obesity measures with ischemic stroke incidence in the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Stroke 2010; 41: 417–425.
Matsuzawa Y, Funahashi T, Kihara S, Shimomura I . Adiponectin and metabolic syndrome. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2004; 24: 29–33.
Song YM, Sung J, Davey Smith G, Ebrahim S . Body mass index and ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke: a prospective study in Korean men. Stroke 2004; 35: 831–836.
Zhou M, Offer A, Yang G, Smith M, Hui G, Whitlock G et al. Body mass index, blood pressure, and mortality from stroke: a nationally representative prospective study of 212 000 Chinese men. Stroke 2008; 39: 753–759.
Stevens J, Truesdale KP, McClain JE, Cai J . The definition of weight maintenance. Int J Obes (Lond) 2006; 30: 391–399.
Wannamethee SG, Shaper AG, Walker M . Weight change, body weight and mortality: the impact of smoking and ill health. Int J Epidemiol 2001; 30: 777–786.
Reed D, Jacobs Jr DR, Hayashi T, Konishi M, Nelson J, Iso H et al. A comparison of lesions in small intracerebral arteries among Japanese men in Hawaii and Japan. Stroke 1994; 25: 60–65.
Konishi M, Komachi Y, Iso H, Iida M, Naito Y, Sato S et al. Secular trends in atherosclerosis of coronary arteries and basal cerebral arteries in Japan. The Akita pathology study. Arteriosclerosis 1990; 10: 535–540.
Walker AE, Robins M, Weinfeld FD . The national survey of stroke. Clinical findings. Stroke 1981; 12: I13–I44.
Manson JE, Willett WC, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Hunter DJ, Hankinson SE et al. Body weight and mortality among women. N Engl J Med 1995; 333: 677–685.
Pham TM, Fujino Y, Tokui N, Ide R, Kubo T, Shirane K et al. Mortality and risk factors for stroke and its subtypes in a cohort study in Japan. Prev Med 2007; 44: 526–530.
Funada S, Shimazu T, Kakizaki M, Kuriyama S, Sato Y, Matsuda-Ohmori K et al. Body mass index and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japan: the Ohsaki study. Prev Med 2008; 47: 66–70.
Cui R, Iso H, Toyoshima H, Date C, Yamamoto A, Kikuchi S et al. Body mass index and mortality from cardiovascular disease among Japanese men and women: the JACC study. Stroke 2005; 36: 1377–1382.
Furukawa Y, Kokubo Y, Okamura T, Watanabe M, Higashiyama A, Ono Y et al. The relationship between waist circumference and the risk of stroke and myocardial infarction in a Japanese urban cohort: the Suita study. Stroke 2010; 41: 550–553.
Saito I, Sato S, Nakamura M, Kokubo Y, Mannami T, Adachi H et al. A low level of C-reactive protein in Japanese adults and its association with cardiovascular risk factors: the Japan NCVC-collaborative inflammation cohort (JNIC) study. Atherosclerosis 2007; 194: 238–244.
Saito I, Konishi M, Iso H, Inoue M, Tsugane S . Impact of weight change on specific-cause mortality among middle-aged Japanese individuals. J Epidemiol Community Health 2009; 63: 447–454.
Acknowledgements
We thank all staff members in each study area and in the central offices for their cooperation and technical assistance during the study (Appendix). This study was supported by grants-in-aid for Cancer Research and the 3rd Term Comprehensive 10-Year-Strategy for Cancer Control from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Appendix
Appendix
Members of the JPHC Study Group (principal investigator: S Tsugane): S Tsugane, M Inoue, T Sobue and T Hanaoka, Research Center for Cancer Prevention and Screening, National Cancer Center, Tokyo; J Ogata, S Baba, T Mannami, A Okayama and Y Kokubo, National Cardiovascular Center, Suita; K Miyakawa, F Saito, A Koizumi, Y Sano, I Hashimoto and T Ikuta, Iwate Prefectural Ninohe Public Health Center, Ninohe; Y Miyajima, N Suzuki, S Nagasawa, Y Furusugi and N Nagai, Akita Prefectural Yokote Public Health Center, Yokote; H Sanada, Y Hatayama, F Kobayashi, H Uchino, Y Shirai, T Kondo, R Sasaki, Y Watanabe, Y Miyagawa and Y Kobayashi, Nagano Prefectural Saku Public Health Center, Saku; Y Kishimoto, E Takara, T Fukuyama, M Kinjo, M Irei and H Sakiyama, Okinawa Prefectural Chubu Public Health Center, Okinawa; K Imoto, H Yazawa, T Seo, A Seiko, F Ito and F Shoji, Katsushika Public Health Center, Tokyo; A Murata, K Minato, K Motegi and T Fujieda, Ibaraki Prefectural Mito Public Health Center, Mito; T Abe, M Katagiri, M Suzuki and K Matsui, Niigata Prefectural Kashiwazaki and Nagaoka Public Health Center, Kashiwazaki and Nagaoka; M Doi, A Terao, Y Ishikawa and T Tagami, Kochi Prefectural Chuo-higashi Public Health Center, Tosayamada; H Doi, M Urata, N Okamoto, F Ide and H Sueta, Nagasaki Prefectural Kamigoto Public Health Center, Arikawa; H Sakiyama, N Onga, H Takaesu and M Uehara, Okinawa Prefectural Miyako Public Health Center, Hirara; F Horii, I Asano, H Yamaguchi, K Aoki, S Maruyama, M Ichii and M Takano, Osaka Prefectural Suita Public Health Center, Suita; S Matsushima and S Natsukawa, Saku General Hospital, Usuda; M Akabane, Tokyo University of Agriculture, Tokyo; I Saito, Ehime University, Toon; H Iso, Osaka University, Suita; Y Honda and K Yamagishi, Tsukuba University, Tsukuba; H Sugimura, Hamamatsu University, Hamamatsu; Y Tsubono, Tohoku University, Sendai; M Kabuto, National Institute for Environmental Studies, Tsukuba; S Tominaga, Aichi Cancer Center Research Institute, Nagoya; M Iida, W Ajiki and A Ioka, Osaka Medical Center for Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease, Osaka; S Sato, Osaka Medical Center for Health Science and Promotion, Osaka; N Yasuda, Kochi University, Nankoku; K Nakamura, Niigata University, Niigata; S Kono, Kyushu University, Fukuoka; K Suzuki, Research Institute for Brain and Blood Vessels Akita, Akita; Y Takashima, Kyorin University, Mitaka; E Maruyama, Kobe University, Kobe; M Yamaguchi, Y Matsumura, S Sasaki and S Watanabe, National Institute of Health and Nutrition, Tokyo; T Kadowaki, Tokyo University, Tokyo; M Noda, International Medical Center of Japan, Tokyo; Y Kawaguchi, Tokyo Medical and Dental University, Tokyo; and H Shimizu, Sakihae Institute, Gifu.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, I., Iso, H., Kokubo, Y. et al. Body mass index, weight change and risk of stroke and stroke subtypes: the Japan Public Health Center-based prospective (JPHC) study. Int J Obes 35, 283–291 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2010.131
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Risk factors for stroke among anthropometric indices and lipid profiles in the Korean population: a large-scale cross-sectional study
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Obesity and cardiovascular disease in women
International Journal of Obesity (2020)
-
Synthesis of clinical prediction models under different sets of covariates with one individual patient data
BMC Medical Research Methodology (2015)
-
Association between different obesity measures and the risk of stroke in the EPIC Spanish cohort
European Journal of Nutrition (2015)
-
Risk Factors of Stroke in Western and Asian Countries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Prospective Cohort Studies
BMC Public Health (2014)