Abstract
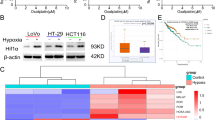
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α) is a main responder to intracellular hypoxia and is overexpressed in many human cancers, including renal cell carcinoma (RCC). To better understanding of the role of HIF-1α in the tumorigenicity of RCC, we used short-hairpin RNA (shRNA) interference to inhibit HIF-1α expression in the human renal cancer cell line, Caki-1 and OS-RC-2. Silencing of HIF-1α significantly reduced the expression of HIF-1α in both of renal cancer cell lines. In vitro downregulation of HIF-1α inhibited Caki-1 and OS-RC-2 cell growth, migration and invasion. The results further showed that HIF-1α silencing resulted in caspase-dependent apoptosis of Caki-1 and OS-RC-2 through regulation of PI3K/Akt pathway and Bcl-2-related proteins expression. In vivo animal studies showed that tumor growth was significantly inhibited in HIF-1α shRNA-transfected RCC. Intratumor gene therapy with polyethylenimine-loaded HIF-1α shRNA also resulted in tumor growth suppression. Thus, this study demonstrates that downregulation of HIF-1α could suppress tumorigenicity of RCC through induction of apoptosis, and HIF-1α shRNA may be a promising strategy for the treatment of RCC.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RNAi:
-
RNA interference
- shRNA:
-
short-hairpin RNA
- RCC:
-
renal cell carcinoma
References
McLaughlin JK, Lipworth L . Epidemiologic aspects of renal cell cancer. Semin Oncol 2000; 27: 115–123.
Murai M, Oya M . Renal cell carcinoma: etiology, incidence and epidemiology. Curr Opin Urol 2004; 14: 229–233.
Yagoda A, Petrylak D, Thompson S . Cytotoxic chemotherapy for advanced renal cell carcinoma. Urol Clin North Am 1993; 20: 303–321.
Motzer RJ, Bacik J, Murphy BA, Russo P, Mazumdar M . Interferon-α as a comparative treatment for clinical trials of new therapies against advanced renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 2002; 20: 289–296.
Bukowski RM . Natural history and therapy of metastatic renal cell carcinoma: the role of interleukin-2. Cancer 1997; 80: 1198–1220.
Yagoda A . Phase II cytotoxic chemotherapy trials in renal cell carcinoma: 1983–1988. Prog Clin Biol Res 1990; 350: 227–241.
Ke QD, Max C . Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol 2006; 70: 1469–1480.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ et al. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 411–421.
Zhong H, De Marzo AM, Laughner E, Lim M, Hilton DA, Zagzag D et al. Overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α in common human cancers and their metastases. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 5830–5835.
Talks KL, Turley H, Gatter KC, Maxwell PH, Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ et al. The expression and distribution of the hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α in normal human tissues, cancers, and tumor-associated macrophages. Am J Pathol 2000; 157: 411–421.
Beasley NJ, Leek R, Alam M, Turley H, Cox GJ, Gatter K et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors HIF-1α and HIF-2α in head and neck cancer: relationship to tumor biology and treatment outcome in surgically resected patients. Cancer Res 2002; 62: 2493–2497.
Volm M, Koomagi R . Hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) and its relationship to apoptosis and proliferation in lung cancer. Anticancer Res 2002; 20: 1527–1533.
Harris AL . Hypoxia-α key regulatory factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 38–47.
Pugh CW, Ratcliffe PJ . Regulation of angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med 2003; 9: 677–684.
Thomas R, Kim MH . HIF-1 alpha: a key survival factor for serum-deprived prostate cancer cells. Prostate 2008; 68: 1405–1415.
Wang Y, Pakunlu RI, Tsao W, Pozharov V, Minko T . Bimodal effect of hypoxia in cancer: role of hypoxia inducible factor in apoptosis. Mol Pharmacol 2004; 1: 156–165.
Sun X, Kanwar JR, Leung E, Lehnert K, Wang D, Krissansen GW . Gene transfer of antisense hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha enhances the therapeutic efficacy of cancer immunotherapy. Gene Therapy 2001; 8: 638–645.
Maemura K, Hsieh CM, Jain MK, Fukumoto S, Layne MD, Liu Y et al. Generation of a dominant-negative mutant of endothelial PAS domain protein 1 by deletion of a potent C-terminal transactivation domain. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 31565–31570.
Mizuno T, Nagao M, Yamada Y, Narikiyo M, Ueno M, Miyagishi M et al. Small interfering RNA expression vector targeting hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha inhibits tumor growth in hepatobiliary and pancreatic cancers. Cancer Gene Ther 2006; 13: 131–140.
Wiesener MS, Munchenhagen PM, Berger I, Morgan NV, Roigas J, Schwiertz A et al. Constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible genes related to overexpression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1a in clear cell renal carcinoma. Cancer Res 2001; 61: 5215–5222.
Klatte T, Seligson DB, Riggs SB, Leppert JT, Berkman MK, Kleid MD et al. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2007; 13: 7388–7393.
Lidgren A, Hedberg Y, Grankvist K, Rasmuson T, Vasko J, Ljungberg B . The expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is a favorable independent prognostic factor in renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 1129–1135.
Yao M, Yoshida M, Kishida T, Nakaigawa N, Baba M, Kobayashi K et al. VHL tumor suppressor gene alterations associated with good prognosis in sporadic clear-cell renal carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 2002; 20: 1569–1575.
Mehlen P, Puisieux A . Metastasis: a question of life or death. Nat Rev Cancer 2006; 6: 449–458.
Igney FH, Krammer PH . Death and anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 277–288.
Wang J, Yang J, Kuropatwinski K, Wang W, Liu XQ, Hauser J et al. Transforming growth factor beta induces apoptosis through repressing the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT/survivin pathway in colon cancer cells. Cancer Res 2008; 68: 3152–3160.
Fan KX, Dai JX, Wang H, Wei HF, Cao ZG, Hou S et al. Treatment of collagen-induced arthritis with an anti-osteopontin monoclonal antibody through promotion of apoptosis of both murine and human activated T cells. Arthritis Rheum 2008; 58: 2041–2052.
Jia SF, Worth LL, Densmore CL, Xu B, Zhou Z, Kleinerman ES . Eradication of osteosarcoma lung metastases following intranasal interleukin-12 gene therapy using a nonviral polyethylenimine vector. Cancer Gene Ther 2002; 9: 260–266.
Semenza GL . Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2003; 3: 721–732.
Qiao J, Kang J, Ishola TA, Rychahou PG, Evers BM, Chung DH . Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor silencing suppresses the tumorigenesis and metastatic potential of neuroblastoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2008; 105: 12891–12896.
Jeong SJ, Pise-Masison CA, Radonovich MF, Park HU, Brady JN . Activated AKT regulates NF-kappaB activation, p53 inhibition and cell survival in HTLV-1-transformed cells. Oncogene 2005; 24: 6719–6728.
Tang ED, Nuñez G, Barr FG, Guan KL . Negative regulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR by Akt. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 16741–16746.
Tsujimoto Y . Cell death regulation by the Bcl-2 protein family in the mitochondria. J Cell Physiol 2003; 195: 158–167.
Gross A, Jockel J, Wei MC, Korsmeyer SJ . Enforced dimerization of BAX results in its translocation, mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis. EMBO J 1998; 17: 3878–3885.
Ruffolo SC, Breckenridge DG, Nguyen M, Goping IS, Gross A, Korsmeyer SJ et al. BID-dependent and BID-independent pathways for BAX insertion into mitochondria. Cell Death Differ 2000; 7: 1101–1108.
Weiss JN, Korge P, Honda HM, Ping P . Role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in myocardial disease. Circ Res 2003; 93: 292–301.
Boussif O, Lezoualc’h F, Zanta A, Mergny MD, Scherman D, Demeneix B et al. A versatile vector for gene and oligonucleotide transfer into cells in culture and in vivo: polyethylenimine. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 7297–7301.
Urban-Klein B, Werth S, Abuharbeid S, Czubayko F, Aigner A . RNAi-mediated gene-targeting through systemic application of polyethylenimine (PEI)-complexed siRNA in vivo. Gene Therapy 2005; 12: 461–466.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, K., Ding, Q., Fang, Z. et al. Silencing of HIF-1α suppresses tumorigenicity of renal cell carcinoma through induction of apoptosis. Cancer Gene Ther 17, 212–222 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2009.66
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cgt.2009.66