Abstract
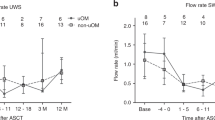
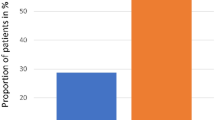
In this multicenter study, 30 patients undergoing matched related or unrelated allogeneic stem-cell transplantation for leukemia were treated with palifermin, and retrospectively compared to a matched control group. Palifermin recipients transplanted with an unrelated donor showed a significant reduction of severity, incidence and duration of oral mucositis WHO grades 2–4. In addition, in the palifermin group the use of opioid analgesics and the duration of total parenteral nutrition decreased, whether stem cells were used from matched related or unrelated donors. No beneficial influence of palifermin on the incidence and severity of acute GVHD (aGVHD) was apparent. The incidence and duration of febrile neutropenia, documented infections, hematopoietic recovery or overall survival remained unchanged. The most common adverse effects included rash or erythema, generally mild and transient in appearance. Thus, the administration of palifermin was generally well tolerated and safe, and significantly reduced oral mucositis whereas—regardless of donor status—no effect on the incidence and severity of aGVHD was seen.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woo SB, Sonis ST, Monopoli MM, Sonis AL . A longitudinal study of oral ulcerative mucositis in bone marrow transplant recipients. Cancer 1993; 72: 1612–1617.
Sonis ST, Oster G, Fuchs H, Bellm L, Bradford WZ, Edelsberg J et al. Oral mucositis and the clinical and economic outcomes of hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. J Clin Oncol 2001; 19: 2201–2205.
Elting LS, Cooksley C, Chambers M, Cantor SB, Manzullo E, Rubenstein EB . The burdens of cancer therapy. Clinical and economic outcomes of chemotherapy-induced mucositis. Cancer 2003; 98: 1531–1539.
Keefe DM, Schubert MM, Elting LS, Sonis ST, Epstein JB, Raber-Durlacher JE et al. Updated clinical practice guidelines for the prevention and treatment of mucositis. Cancer 2007; 109: 820–831.
Spielberger R, Stiff P, Bensinger W, Gentile T, Weisdorf D, Kewalramani T et al. Palifermin for oral mucositis after intensive therapy for hematologic cancers. N Engl J Med 2004; 351: 2590–2598.
Krijanovski OI, Hill GR, Cooke KR, Teshima T, Crawford JM, Brinson YS et al. Keratinocyte growth factor separates graft-versus-leukemia effects from graft-versus-host disease. Blood 1999; 94: 825–831.
Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Lacey DL, Vallera DA, Blazar BR . Keratinocyte growth factor administered before conditioning ameliorates graft-versus-host disease after allogeneic bone marrow transplantation in mice. Blood 1998; 92: 3960–3967.
Blazar BR, Weisdorf DJ, Defor T, Goldman A, Braun T, Silver S et al. Phase 1/2 randomized, placebo-control trial of palifermin to prevent graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Blood 2006; 108: 3216–3222.
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A . Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981; 47: 207–214.
Przepiorka D, Weisdorf D, Martin P, Klingemann HG, Beatty P, Hows J et al. 1994 Consensus Conference on Acute GVHD Grading. Bone Marrow Transplant 1995; 15: 825–828.
Buchheidt D, Bohme A, Cornely OA, Fatkenheuer G, Fuhr HG, Heussel G et al. Diagnosis and treatment of documented infections in neutropenic patients—recommendations of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Hematology and Oncology (DGHO). Ann Hematol 2003; 82 (Suppl 2): S127–S132.
Kruger WH, Bohlius J, Cornely OA, Einsele H, Hebart H, Massenkeil G et al. Antimicrobial prophylaxis in allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Guidelines of the Infectious Diseases Working Party (AGIHO) of the German Society of Haematology and Oncology. Ann Oncol 2005; 16: 1381–1390.
Nasilowska-Adamska B, Rzepecki P, Manko J, Czyz A, Markiewicz M, Federowicz I et al. The influence of palifermin (Kepivance) on oral mucositis and acute graft versus host disease in patients with hematological diseases undergoing hematopoietic stem cell transplant. Bone Marrow Transplant 2007; 40: 983–988.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All authors declare that there was no funding or financial support by the company for this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Langner, S., Staber, P., Schub, N. et al. Palifermin reduces incidence and severity of oral mucositis in allogeneic stem-cell transplant recipients. Bone Marrow Transplant 42, 275–279 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.157
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bmt.2008.157
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Systematic review of growth factors and cytokines for the management of oral mucositis in cancer patients and clinical practice guidelines
Supportive Care in Cancer (2020)
-
Efficacy and safety of keratinocyte growth factor (palifermin) for prevention of oral mucositis in TBI-based allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
Bone Marrow Transplantation (2018)
-
Prevention and treatment of oral mucositis pain following cancer therapy
Drugs & Therapy Perspectives (2018)
-
CD34+ selection and the severity of oropharyngeal mucositis in total body irradiation-based allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Supportive Care in Cancer (2016)
-
Palifermin for prevention of oral mucositis in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a single-institution retrospective evaluation
Supportive Care in Cancer (2015)