Abstract
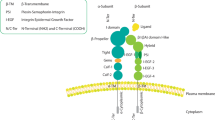
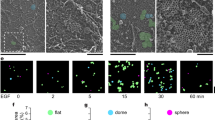
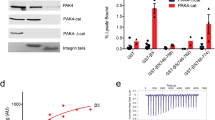
In the present study we have used fluorocytometry and immunoprecipitation to characterize the expression of alphav-containing integrins in a panel of eight human breast cancer cell lines and one normal human mammary epithelial line. We show that the classical vitronectin receptor alphavbeta3 is expressed in only one cell line (MDA-MB-231), whereas alphavbeta5 is expressed on all breast cancer cell lines and alphavbeta1 is expressed on the majority. Using adherence assays to purified ligands in the presence and absence of function-blocking monoclonal antibodies, we have demonstrated that alphavbeta5 mediates adhesion to vitronectin in the majority of these cells. In one cell line, ZR75-1, alphavbeta1 contributes significantly to adhesion to immobilized vitronectin. The formation of focal adhesions containing the alphav and beta1 subunits on vitronectin is also demonstrated by indirect immunofluorescence.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meyer, T., Marshall, J. & Hart, I. Expression of αv integrins and vitronectin receptor identity in breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer 77, 530–536 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.86
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1998.86
This article is cited by
-
NDRG4 promoter hypermethylation is a mechanistic biomarker associated with metastatic progression in breast cancer patients
npj Breast Cancer (2019)
-
BPIFB1 (LPLUNC1) inhibits migration and invasion of nasopharyngeal carcinoma by interacting with VTN and VIM
British Journal of Cancer (2018)
-
Metastasis review: from bench to bedside
Tumor Biology (2014)
-
Integrin β5 contributes to the tumorigenic potential of breast cancer cells through the Src-FAK and MEK-ERK signaling pathways
Oncogene (2013)
-
Cilengitide affects tumor compartment, vascularization and microenvironment in experimental bone metastases as shown by longitudinal 18F-FDG PET and gene expression analysis
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)