Abstract
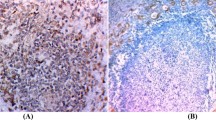
In this study of papillary thyroid carcinomas, immunopositivity for EGF-receptor was present in a majority of the cases (96%), although different staining patterns were observed. A distinct membraneous reaction was found in 46%, whereas cytoplasmatic positivity of various degrees was present in 90% of the cases. Strong cytoplasmic EGF-receptor staining was significantly associated with extra-thyroidal growth of the primary tumour (P = 0.009), and it was furthermore related to decreased recurrence free survival (P = 0.006). Membraneous EGF-receptor staining was not associated with recurrence free survival or patient survival. Multivariate Cox analysis showed that lymph node metastases (P = 0.0009) and cytoplasmic EGF-receptor staining (P = 0.0048) was independent indicators of tumour recurrences in this group of surgically treated papillary thyroid carcinomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akslen, L., Myking, A., Salvesen, H. et al. Prognostic impact of EGF-receptor in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Br J Cancer 68, 808–812 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.432
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1993.432
This article is cited by
-
Cell membrane and cytoplasmic epidermal growth factor receptor expression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma
Medical Oncology (2012)
-
In thyroid cancer cell lines expression of periostin gene is controlled by p73 and is not related to epigenetic marks of active transcription
Cellular Oncology (2011)
-
Differential effects of cetuximab and AEE 788 on epidermal growth factor receptor (EGF-R) and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGF-R) in thyroid cancer cell lines
Endocrine (2007)
-
Targeting the EGF/VEGF-R system by tyrosine-kinase inhibitors—a novel antiproliferative/antiangiogenic strategy in thyroid cancer
Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery (2006)
-
Significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor in development of papillary thyroid cancer
Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery (2005)