Abstract
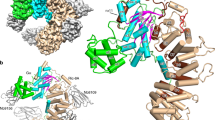
Small G proteins transduce signals from plasma-membrane receptors to control a wide range of cellular functions1,2. These proteins are clustered into distinct families but all act as molecular switches, active in their GTP-bound form but inactive when GDP-bound. The Rho family of G proteins, which includes Cdc42Hs, activate effectors involved in the regulation of cytoskeleton formation, cell proliferation and the JNK signalling pathway3,4,5,6,7,8,9. G proteins generally have a low intrinsic GTPase hydrolytic activity but there are family-specific groups of GTPase-activating proteins (GAPs) that enhance the rate of GTP hydrolysis by up to 105times10,11. We report here the crystal structure of Cdc42Hs, with the non-hydrolysable GTP analogue GMPPNP, in complex with the GAP domain of p50rhoGAP at 2.7 å resolution. In the complex Cdc42Hs interacts, mainly through its switch I and II regions, with a shallow pocket on rhoGAP which is lined with conserved residues. Arg 85 of rhoGAP interacts with the P-loop of Cdc42Hs, but from biochemical data and by analogy with the G-protein subunit Giα1 (ref. 12), we propose that it adopts a different conformation during the catalytic cycle which enables it to stabilize the transition state of the GTP-hydrolysis reaction.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. The GTPase superfamily: a conserved switch for diverse cell functions. Nature 348, 125–132 (1990).
Bourne, H. R., Sanders, D. A. & McCormick, F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature 349, 117–127 (1991).
Paterson, H. F. et al. Microinjection of recombinant p21rho induces rapid changes in cell morphology. J. Cell. Biol. 111, 1001–1007 (1990).
Hall, A. The cellular functions of small GTP-binding proteins. Science 249, 635–640 (1990).
Ridley, A. J. & Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 70, 389–399 (1992).
Qiu, R. -G., Chen, J., Kirn, D., McCormick, F. & Symns, M. An essential role for Rac in Ras transformation. Nature 374, 457–459 (1995).
Ridley, A. J. Rho: theme and variations. Curr. Biol. 6, 1256–1264 (1996).
Coso, O. A. et al. The small GTP-binding proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 regulate the activity of the JNK/SAPK signaling pathway. Cell 81, 1137–1146 (1995).
Minden, A., Lin, A., Claret, F. -X., Abo, A. & Karin, M. Selective activation of the JNK signaling cascade and c-Jun transcriptinal activity by the small GTPases Rac and Cdc42Hs. Cell 81, 1147–1157 (1995).
Lancaster, C. A. et al. Characterization of rhoGAP. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 1137–1142 (1994).
Lamarche, N. & Hall, A. GAPs for rho-related GTPases. Trends Genet. 10, 436–440 (1994).
Coleman, D. E. et al. Structures of active conformations of Giα1and the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. Science 265, 1405–1412 (1994).
Pai, E. F. et al. Refined crystal structure of the triphosphate conformation of H-ras p21 at 1.35A resolution: implications for the mechanism of GTP hydrolysis. EMBO J. 9, 2351–2359 (1990).
Schlichting, I. et al. Time-resolved X-ray crystallographic study of the conformational change in Ha-Ras p21 protein on GTP hydrolysis. Nature 345, 309–315 (1990).
Prive, G. G. et al. X-ray crystal structures of transforming p21 ras mutants suggest a transition-state stabilization mechanism for GTP hydrolysis. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 89, 3649–3653 (1992).
Hirshberg, M., Stockley, R. W., Dodson, G. & Webb, M. R. The crystal structure of human rac1, a member of the rho-family complexed with a GTP analogue. Nature Struct. Biol. 4, 147–152 (1997).
Scheffzek, K., Lautwein, A., Kabsch, W., Ahmadian, M. R. & Wittinghoferr, A. Crystal structure of the GTPase-activating domain of human p120GAP and implications for the interaction with Ras. Nature 384, 591–596 (1996).
Barrett, T. et al. The structure of the GTPase-activating domain from p50rhoGAP. Nature 385, 458–461 (1997).
Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. & Sigler, P. B. The 2.2 å crystal structure of transducin-α complexed with GTP-γS. Nature 366, 654–663 (1993).
Sondek, J., Lambright, D. G., Noel, J. P., Hamm, H. E. & Sigler, P. B. GTPase mechanism of G-proteins from the 1.7 å crystal structure of transducinα·GDP AlF44−. Nature 372, 276–279 (1994).
Tesmer, J. J. G., Berman, D. M., Gilman, A. G. & Sprang, S. R. Structure of RGS4 bound to AlF44−-activated Giα1: Stabilization of the transition state for GTP hydrolysis. Cell 89, 251–261 (1997).
Milburn, M. V. et al. Molecular switch for signal transduction: Structural differences between active and inactive forms of protooncogenic ras proteins. Science 247, 939–945 (1990).
Goody, R. S. et al. Studies on the structure and mechanism of H-ras p21. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 336, 3–11 (1992).
Mittal, R., Ahmadian, M. R., Goody, R. S. & Wittinghoferr, A. Formation of a transition-state analog of Ras GTPase reaction by Ras GDP, tetrafluoroaluminate, and GTPase-activating proteins. Science 273, 115–117 (1996).
Smith, D. B. & Johnson, K. S. Single-step purification of polypeptides expressed in Escherichia coli as fusions with glutathione S-transferase. Gene 67, 31–40 (1988).
Otwinowski, Z. & Minor, W. Data Collection and Processing (eds Sawyer, L., Isaacs, N. & Bailey, S.) 556–562 (SERC Daresbury Laboratory, Warrington, 1993).
CCP4 The CCP4 suite: programs for protein crystallographyActa Crystallogr. D 50 760–763 (1994).
Jones, T. A., Zhou, J. Y., Cowan, S. W. & Kjeldgaard, M. Improved methods for building protein models in electron density maps and the location of errors in these models. Acta Crystallogr. A 47, 110–119 (1991).
Kraulis, P. J. MOLSCRIPT: a program to produce both detailed and schematic plots of protein structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 24, 946–950 (1991).
Acknowledgements
We thank M. Hirshberg for making coordinates of Rac1 available before general release, E. Skordalakes for assistance with data collection, A. Hall for the gift of rhoA and rhoGAP expression systems, E. Manser and L. Lim for construction and characterization of the Cdc42HsΔ7 expression system, G. Dodson and D. Trentham for critical reading of this manuscript, and A. Savoia (Trieste) and A. Thompson (ESRF) for beamline assistance. D.O. and E.L. Thank the European commission for financial support and the BBSRC and Welcome Trust for support to the Cambridge Centre for Molecular Recognition. K.R. is funded by an EEC TMR fellowship.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rittinger, K., Walker, P., Eccleston, J. et al. Crystal structure of a small G protein in complex with the GTPase-activating protein rhoGAP. Nature 388, 693–697 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/41805
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/41805
This article is cited by
-
Assembly of the Non-Canonical Myo9a-RhoGAP and RhoA·GDP Transition State Complex in the Presence of MgF3−
The Protein Journal (2021)
-
SYD-1 Promotes Multiple Developmental Steps Leading to Neuronal Connectivity
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
MicroRNA-125b promotes invasion and metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting STARD13 and NEU1
Tumor Biology (2016)
-
Regulation of cytokinesis by Rho GTPase flux
Nature Cell Biology (2009)
-
The Rho-activating CNF1 toxin from pathogenic E. coli: A risk factor for human cancer development?
Infectious Agents and Cancer (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.