Abstract
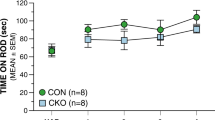
The nervous mouse mutation causes a relatively selective degeneration of Purkinje cells in the cerebellar cortex. The mutants were compared to age-matched controls of the same background strain in tests of motor activity and coordination, spontaneous alternation, and spatial learning in the Morris water maze. As expected from their ataxia, the nervous mutants were impaired in stationary beam, coat-hanger, and rotorod tests of motor coordination. The nervous mutants were also impaired in the submerged but not in the visible platform condition of the Morris water maze, attributable to a spatial deficit, and displayed a higher level of motor activity in an automated chamber. The deficit in spontaneous alternation rates seen in nervous mutants is accountable by reduced motivation, disinhibition, or spatial disorientation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berrebi, A. S., and Mugnaini, E. (1988). Effects of the murine mutation “nervous” on neurons in cerebellum and dorsal cochlear nucleus. J. Neurocytol. 17:465-484.
Bliss, T. V., and Errington, M. L. (1977). “Reeler” mutant mice fail to show spontaneous alternation. Brain Res. 124:168-170.
Botez-Marquard, T., and Botez, M. I. (1993). Cognitive behavior in heredodegenerative ataxias. Eur. Neurol. 33:351-357.
Caston, J., Jones, N., and Stelz, T. (1995). Role of preoperative and postoperative sensorimotor training on restoration of the equilibrium behavior in adult mice following cerebellectomy. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 64:195-202.
Caston, J., Vasseur, F., Delhaye-Bouchaud, N., and Mariani, J. (1997). Delayed spontaneous alternation in intact and cerebellectomized control and Lurcher mutant mice: Differential role of cerebellar cortex and deep cerebellar nuclei. Behav. Neurosci. 111:214-218.
de Bruin, J. P. C., Moita, M. P., de Brabander, H. M., and Joosten, R. N. J. M. A. (2001). Place and response learning in a Morris water maze: Differential effects of fimbria fornix and medial prefrontal cortex. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 75:164-178.
Dember, W. N. (1958). Stimulus alternation in peripherally blinded rats. Can. J. Psychol. 12:219-221.
Douglas, R. J., Clark, G. M., Erway, L. C., Hubbard, D. G., and Wright, C. G. (1979). Effects of genetic vestibular defects on behavior related to spatial orientation and emotionality. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 93:467-480.
Fehrenbach, R. A., Wallesch, C.-W., and Claus, D. (1984). Neuropsychologic findings in Friedreich's ataxia. Arch. Neurol. 41:306-308.
Fortier, P., Smith, A. M., and Rossignol, S. (1987). Locomotor deficits in the cerebellar mutant mouse, Lurcher. Exp. Brain Res. 66:271-286.
Goodlett, C. R., Hamre, K. M., and West, J. R. (1992). Dissociation of spatial navigation and visual guidance performance in Purkinje cell degeneration (pcd) mutant mice. Behav. Brain Res. 47:129-141.
Isseroff, A. (1979). Limited recovery of spontaneous alternation after extensive hippocampal damage: Evidence for a memory impairment. Exp. Neurol. 64:284-294.
Joyal, C. C., Strazielle, C., and Lalonde, R. (2001). Effects of dentate nucleus lesions on spatial and postural sensorimotor learning in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 122:131-137.
Joyal, C. C., Meyer, C., Jacquart, G., Mahler, P., Caston, J., and Lalonde, R. (1996). Effects of midline and lateral cerebellar lesions on motor coordination and spatial orientation. Brain Res. 739:1-11.
Lalonde, R. (1987). Exploration and spatial learning in staggerer mutant mice. J. Neurogenet. 4:285-292.
Lalonde, R. (2002). The neurobiological basis of spontaneous alternation. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 26:91-104.
Lalonde, R., and Botez, M. I. (1985a). Exploration and habituation in nervous mutant mice. Behav. Brain Res. 17:83-86.
Lalonde, R., and Botez, M. I. (1985b. Exploration of a hole-board matrix in nervous mutant mice. Brain Res. 343:356-359.
Lalonde, R., and Strazielle, C. (2001). Motor coordination and regional brain metabolism in spontaneous mouse mutations with cerebellar atrophy. Behav. Brain Res. 125:103-108.
Lalonde, R., Botez, M. I., and Boivin, D. (1986). Spontaneous alternation and habituation in a t-maze in nervous mutant mice. Behav. Neurosci. 100:350-352.
Landis, S. C. (1973). Ultrastructural changes in the mitochondria of cerebellar Purkinje cells of nervous mutant mice. J. Cell Biol. 57:782-797.
LaVail, M. M., White, M. P., Gorrin, G. M., Yasumura, D., Porrello, K. V., and Mullen, R. J. (1993). Retinal degeneration in the nervous mutant mouse: I. Light microscopic cytopathology and changes in the interphotoreceptor matrix. J. Comp. Neurol. 333:168-181.
Le Marec, N., Dahhaoui, M., Stelz, T., Bakalian, A., Delhaye-Bouchaud, N., Caston, J., and Mariani, J. (1997). Effect of cerebellar granule cell depletion on spatial learning and memory and in an avoidance conditioning task: Studies in postnatally Xirradiated rats. Dev. Brain Res. 99:20-28.
Morris, R. G. M., Garrud, P., Rawlins, J. N. P., and O'Keefe, J. (1982). Place navigation impaired in rats with hippocampal lesions. Nature 292:681-683.
Mullen, R. J., and Lavail, M. M. (1975). Two new types of retinal degeneration in cerebellar mutant mice. Nature 258:528-530.
Newman, P. P., and Reza, H. (1979). Functional relationships between the hippocampus and the cerebellum: An electrophysiological study in the cat. J. Physiol. (London) 287:405-426.
Pelligrino, L. J., and Altman, J. (1979). Effects of differential interference with postnatal cerebellar neurogenesis on motor performance, activity level, and maze learning of rats: A developmental study. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 93:1-33.
Petrosini, L., Molinari, M., and Dell'Anna, M. E. (1996). Cerebellar contribution to spatial event processing: Morris water maze and T-maze. Eur. J. Neurosci. 8:1882-1896.
Price, J. L. (1995). Thalamus. In: Paxinos, G. (Ed.) The Rat Nervous System (2nd Ed), Academic Press, New York, pp. 629-648.
Rubertone, J. A., Mehler, W. R., and Voogd, J. (1995). The vestibular nuclear complex. In: Paxinos, G. (Ed.), The Rat Nervous System (2nd Ed), Academic Press, New York, pp. 773-796.
Saint-Cyr, J. A., and Woodward, D. J. (1982). Activation of mossy and climbing fiber pathways to the cerebellar cortex by stimulation of the fornix in the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 45:333-348.
Savage, L. M., Sweet, A. J., Castillo, R., and Langlais, P. J. (1997). The effects of lesions to thalamic lateral internal medullary lamina and posterior nuclei on learning, memory and habituation in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 82:133-147.
Schmahmann, J. D., and Sherman, J. C. (1998). The cerebellar cognitive affective syndrome. Brain 121:561-579.
Sidman, R. L., and Green, M. C. (1970). “Nervous,” a new mutant mouse with cerebellar disease. In: Sabourdy, M. (Ed.), Les mutants pathologiques chez l'animal. CNRS, Paris, pp. 69-79.
Sotelo, C., and Triller, A. (1979). Fate of presynaptic afferents of Purkinje cells in adult nervous mutant mice: A model to study presynaptic stabilization. Brain Res. 175:11-36.
Stubley-Weatherly, L., Harding, J. W., and Wright, J. W. (1996). Effects of discrete kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions on spatial and contextual learning and memory in rats. Brain Res. 716:29-38.
Wassef, M., Sotelo, C., Cholley, B., Brehier, A., and Thomasset, M. (1987). Cerebellar mutations affecting the postnatal survival of Purkinje cells in the mouse disclose a longitudinal pattern of differentially sensitive cells. Dev. Biol. 124:379-389.
Whishaw, I. Q., Mittleman, G., Bunch, S. T., and Dunnett, S. B. (1987). Impairments in the acquisition, retention and selection of spatial navigational strategies after medial caudate-putamen lesions in rats. Behav. Brain Res. 24:125-138.
White, M. P., Gorrin, G. M., Mullen, R. J., and LaVail, M. M. (1993). Retinal degeneration in the nervous mutant mouse: II. Electron microscopic analysis. J. Comp. Neurol. 333:182-198.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lalonde, R., Strazielle, C. Motor Coordination, Exploration, and Spatial Learning in a Natural Mouse Mutation (nervous) with Purkinje Cell Degeneration. Behav Genet 33, 59–66 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021003600900
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1021003600900