Abstract
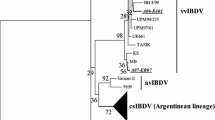
Eleven infectious bursal disease virus (IBDV) strains isolated recently from China were compared with the early classical virulent strain CJ801, the chicken embryo fibroblast-adapted (CEF) variant strain GZ902, and the attenuated vaccine strains BJ836, BK912, and LM to discern the evolutionary characteristics of IBDV in China at both antigenic and genetic levels. Virus neutralization (VN) assay showed that all ten very virulent (vv) IBDV strains belong to the same subtype as attenuated strains, whereas the other variant isolate strain BX could be attributed to other subtype of the variant strain GZ902. Antigen-capture ELISA (AC-ELISA) determined by a panel of monoclonal antibodies (Mabs) against classical and variant strains showed further that among these vv strains, nine strains except for strain NC had no reaction with neutralizing Mab B69. The vv strains SC and YV had no reaction with non-neutralizing Mabs 2B8 and 2C4, respectively, whose epitopes were located in classical IBDV strains. On the other hand, there is no alteration in antigenic epitopes located in the variant strain BX as that of the variant GZ902. Sequence comparison of the highly variable region (HVR) of the VP2 proteins showed that these vv strains had 98.6–100.0% identities to European and Asian vv strains at amino acid level. For the vv strains NC, SC, and YV, all had one amino acid substitution at the major hydrophilic domains, indicating that new vv strains are evolving. In addition, the vv strains DMS and NC had amino acid residue 279N as well, showing that the substitution of amino acid at this position might not be related to the virulence of IBDV. The variant strain BX had one amino acid substitution in the two major hydrophilic domains and two unique amino acids 249K and 254S as the other early variant strains, and shared 97.3% of amino acid identity to the variant strain VarE. Phylogenetic analysis suggests that the recent Chinese vvIBDVs and the previous European and Asian vv strains still belong to a genetic group and the variant strain BX to the other genetic group, which is more closely related to the European classical virulent strain F52/70 and the American classical virulent strain STC than to the early Chinese classical virulent strain CJ801, showing that the recent vv and variant strains that spread widely in the country might be derived from Europe and America than from early Chinese classical virulent strains.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lukert P.D. and Saif Y.M. (eds), Infectious Bursal Disease, in Diseases of Poultry. 10th, Iowa State University Press, pp. 721-738, 1997.
Saif Y.M., Vet Immunol Immunopathol 30, 45-50, 1991.
Ismail N.M., Saif Y.M., and Moorhead P.D., Avian Dis 32, 757-759, 1988.
Jackwood D.J. and Saif Y.M., Avian Dis 31, 766-770, 1987.
Snyder D.B., Vakharia V.N., and Savage P.K., Arch Virol 127, 89-101, 1992.
Chette N., Stuart J.C., and Wyeth P.J., Vet Rec 125, 291-272, 1989.
Van den Berg T.P., Gonze M., and Meulemans G., Avian Pathol 20, 133-143, 1991.
Eterradossi N., Picault J.P., Drouin P., Guittet M., L'Hospitalier R., and Bennejean G., J Vet Med B39, 683-691, 1992.
Tsukamoto K., Tanimura N., Hihara H., Shirai J., Imai K., Nakamura K., and Maeda M., J Vet Med Sci 54, 153-155, 1992.
Azad A.A., Jagadish M.N., Brown M.A., and Hudson P.J., Virology 161, 145-152, 1985.
Hudson P.J., McKern N.M., Power B.E., and Azad A.A., Nucleic Acids Res 14, 5001-5012, 1986.
Müller H. and Nitschke R., Virology 159, 174-177, 1987.
Mundt E., Beyer J., and Müller H., J Gen Virol 76, 437-443, 1995.
Spies U., Müller H., and Becht H., Virus Res 8, 127-140, 1987.
Spies U. and Müller H., J Gen Virol 71, 977-981, 1990.
Becht H., Müller H., and Müller H.K., J Gen Virol 69, 631-640, 1988.
Azad A.A., Jagadish M.N., Brown M.A., and Hudson P.J., Virology 161, 145-152, 1987.
Bayliss C.D., Spies U., Shaw K., Peters R.W., Papageorgiou A., Müller H., and Boursnell M.E.G., J Gen Virol 71, 1303-1312, 1990.
Heine H.G., Haritou M., Failla P., Fahey K., and Azad A., J Gen Virol 72, 1835-1843, 1991.
Schnitzler D., Bernstein F., Müller H., and Becht H., J Gen Virol 74, 1563-1571, 1993.
Vakharia V.N., He J., Ahamed B., and Snyder D.B., Virus Res 31, 265-273, 1994.
Van den Berg T.P., Gonze M., Morales D., and Meulemans G., Avian Pathol 25, 751-768, 1996.
Zhou J., Liu F.Z., Tao S.H., and Wang H.J., Chin J Vet Med 8, 25-26, 1982.
Li D.S., Wu Z., and Chan G., Chin J Husbandry Poult Pathol 6, 57-61, 1991.
Li S.G., Huang S., Lin Z., and Bi Y.Z., Chin J Husbandry Poult Pathol 5, 7-11, 1991.
Cao Y.C., Bi Y.Z., and Law M., Chin J Vet Med 9, 3-6, 1997.
Cao Y.C., Yeung W.S., Law M., Bi Y.Z., Leung F.C., and Lim B.L., Avian Dis 42, 340-351, 1998.
Chen H.Y., Zhou Q., Zhang M.F., and Giambrone J.J., Avian Dis 42, 762-769, 1998.
Liu J., Liu Y.C., and Zhou J., Chin J Vet Med 10, 39-41, 1997.
Lim B.L., Cao Y.C., Yu T., and Mo C.W., J Virology 73, 2854-2862, 1999.
Snyder D.B., Lana D.P., Savage P.K., Yancey F.S., Mengel S.A., and Marquardt W.W., Avian Dis 32, 535-539, 1988.
Tao S.H., We L., Xui Y.T., and Qian Y.R., Beijing Agr Sci 13, 15-17, 1995.
Eterradossi N., Toquin D., Rivallan G., and Guittet M., Arch Virol 142, 255-270, 1997.
Eterradossi N., Rivallan G., Toquin D., and Guittet M., Arch Virol 142, 2079-2087, 1997.
Eterradossi N., Arnauld C., Toquin D., and Rivallan G., Arch Virol 143, 1627-1636, 1998.
Pitcovski J., Goldberg D., Levi B.Z., DiCastro D., Azriel A., Krispel S., Maray T., and Shaaltiel Y., Avian Dis 42, 497-506, 1998.
Zierenberg K., Nieper H., van den Berg T.P., Ezeokoli C.D., Voß M., and Müller H., Arch Virol 145, 113-125, 2000.
Islam M.R., Zierenberg K., Eterradossi N., Toquin D., Rivallan G., and Müller H., J Vet Med B Infect Dis Vet Public Health 48, 211-221, 2001.
Ikuta N., El-Attrache J., Villegas P., Garcia E.M., Lunge V.R., Fonseca A.S., Oliveira C., and Marques E.K., Avian Dis 45, 297-306, 2001.
Jackwood D.J. and Jackwood R.J., Avian Dis 41, 97-104, 1997.
Yamaguchi T., Ogawa M., Inoshima Y., Mitoshi M., Fukushi H., and Hirai K., Virology 223, 219-223, 1996.
Sapats S.I. and Ignjatovic J., Arch Virol 145, 773-785, 2000.
Dormitorio T.V., Giambrone J.J., and Duck L.W., Avian Dis 41, 36-44, 1997.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Zhou, J. & Kwang, J. Antigenic and Molecular Characterization of Recent Infectious Bursal Disease Virus Isolates in China. Virus Genes 24, 135–147 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014568532292
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1014568532292