Abstract
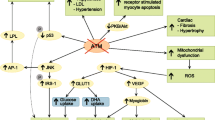
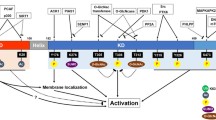
Akt/PKB is a serine/threonine kinase, which controls vital cellular functions such as cell survival/apoptosis, cell cycle progression and glucose metabolism. Akt/PKB acts down-stream from growth factors and hormones and is a key mediator of their pro-survival, proliferative and metabolic effects. Akt/PKB carries out these diverse tasks through phosphorylation of a number of cellular substrates. The substrates of Akt/PKB, which promote the inhibition of apoptosis after being phosphorylated by Akt, include the Forkhead transcription factors and the Bcl-2 family member Bad. The cyclin dependent kinase inhibitors are substrates of Akt which when phosphorylated relinquish their inhibitory influence on cell cycle progression. Akt mediates many of the stimulatory effects of insulin on glucose metabolism through deactivation of glycogen synthase kinase, activation of phosphofructokinase, and modulation of glucose transporter activity. Consequently, Akt can be implicated in the pathological processes, which are associated with defects in regulation of apoptosis/survival and energy metabolism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Datta SR, Brunet A, Greenberg ME: Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev 13: 2905-2927, 1999
Lawlor MA, Alessi DR: PKB/Akt: A key mediator of cell proliferation, survival and insulin response? J Cell Sci 114: 2903-2910, 2001
Talapatra S, Thompson CB: Growth factor signaling in cell survival: Implications for cancer treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298: 873-878, 2001
Downward J: Mechanisms and consequences of activation of protein kinase B/Akt. Curr Opin Cell Biol 10: 262-267, 1998
Brazil DP, Hemmings BA: Ten years of protein kinase B signaling: A hard Akt to follow. Trends Biochem Sci 26: 657-663, 2001
Staal SP, Hartley JW, Rowe WP: Isolation of transforming murine leukemia viruses from mice with a high incidence of spontaneous lymphoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74: 3065-3067, 1977
Staal SP: Molecular cloning of the akt oncogene and its human homologs Akt1 and Akt2: Amplification of Akt1 in a primary gastric adenocarcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84: 5034-5037, 1987
Bellacosa A, Testa JR, Staal SP, Tsichlis PN: A retroviral oncogene akt, encoding a serine threonine kinase containing an SH2-like region. Science 254: 274-277, 1991
Coffer PJ, Woodgett JR: Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel putative protein serine kinase related to the c-AMP dependent and protein kinase C families. Eur J Biochem 201: 475-481, 1991
Jones PF, Jakubowicz T, Pitossi FJ, Maurer F, Hemmings BA: Molecular cloning and identification of a serine/threonine protein kinase of the second-messenger subfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88: 4171-4175, 1991
Frech M, Andjelkovic M, Ingley E, Reddy KK, Falck JR, Hemmings BA: High affinity binding of inositol phosphates and phosphoinositides to the pleckstrin homology domain of RAC/protein kinase B and their influence on kinase activity. J Biol Chem 272: 8474-8481, 1997
Franke TF, Yang SI, Chan TO, Datta K, Kazlauskas A, Morrison DK, Kaplan DR, Tsichlis PN: The protein kinase encoded by the Akt protooncogene is a target of the PDGF-activated phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cell 81: 727-736, 1995
Franke TF, Kaplan DR, Cantley LC, Toker A: Direct regulation of the Akt proto-oncogene product by phosphatidylinositol-3,4-bisphosphate. Science 275: 665-668, 1997
Bellacosa A, Chan TO, Ahmed NN, Datta K, Malstrom S, Stokoe D, McCormick F, Feng J, Tsichlis P: Akt activation by growth factors is a multiple-step process: The role of the PH domain. Oncogene 17: 313-325, 1998
Auger Kr, Serunian LA, Soltoff Sp, Libby P, Cantley LC: PDGF-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation stimulates production of novel polyphosphoinositides in intact cells. Cell: 167-175, 1989
Ruderman NB, Kapellar R, White MF, Cantley LC: Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase by insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 1411-1415, 1990
Andjelkovic M, Alessi DR, Meier R, Fernandez A, Lamb NJC, Frech M, Cron P, Cohen P, Lucocq M, Hemmings BA: Role of translocation in the activation and function of protein kinase B. J Biol Chem 272: 31515-31524, 1997
Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P: Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase B alpha. Curr Biol 7: 261-269, 1997
Alessi DR, Deak M, Casamayor A, Caudwell FB, Morrice N, Norman DG, Gaffney P, Reese CB, MacDougall CN, Harbison D, Ashworth A, Bownes M: 3-Phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDK1): Structural and functional homology with the Drosophila DSTPK61 kinase. Curr Biol 7: 776-789, 1997
Alessi DR, Andjelkovic M, Caudwell B, Cron P, Morrice N, Cohen P, Hemmings BA: Mechanism of activation of protein kinase B by insulin and IGF-1. EMBO J 15: 6541-6551, 1996
Currie RA, Walker KS, Gray A, Deak M, Casamayor A, Downes CP, Cohen P, Alessi DR, Lucocq J: Role of phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate in regulating the activity and localization of 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1. Biochem J 337: 575-583, 1999
Yamada KM, Araki M: Tumor suppressor PTEN: Modulator of cell signaling, growth, migration and apoptosis. J Cell Sci 114: 2375-2382, 2001
Maehama T, Dixon JE: The tumor suppressor, PTEN/MMAC1, dephosphorylates the lipid second messenger, phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem 273: 13375-13378, 1998
Li DM, Sun H: PTEN/MMAC1/TEP1 suppresses the tumorigenicity and induces G1 cell cycle arrest in human glioblastoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 15406-15411, 1998
Myers MP, Pass I, Batty IH, Van der Kaay J, Stolarov JP, Hemmings BA, Wigler MH, Downes CP, Tonks NK: The lipid phosphatase activity of PTEN is critical for its tumor suppressor function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95: 13513-13518, 1998
Davies MA, Lu Y, Sano T, Fang X, Tang P, LaPushin R, Koul D, Bookstein R, Stokoe D, Yung WK, Mills GB, Steck PA: Adenoviral transgene expression of MMAC/PTEN in human glioma cells inhibits Akt activation and induces anoikis. Cancer Res 58: 5285-5290, 1998
Davies MA, Koul D, Dhesi H, Berman R, McDonnell TJ, McConkey D, Yung WK, Steck PA: Regulation of Akt/PKB activity, cellular growth, and apoptosis in prostate carcinoma cells by MMAC/PTEN. Cancer Res 59: 2551-2556, 1999
Datta SR, Dudek H, Tao X, Masters S, Fu H, Gotoh Y, Greenberg ME: Akt phosphorylation of BAD couples survival signals to the cell-intrinsic death machinery. Cell 91: 231-241, 1997
del Peso L, Gonzalez-Garcia M, Page C, Herrera R, Nunez G: Interleukin-3-induced phosphorylation of BAD through the protein kinase Akt. Science 278: 687-689, 1997
Tang ED, Nunez G, Barr FG, Guan KL: Negative regulation of the forkhead transcription factor FKHR by Akt. J Biol Chem 274: 16741-16746, 1999
Kops GJ, de Ruiter ND, De Vries-Smits AM, Powell DR, Bos JL, Burgering BM: Direct control of the Forkhead transcription factor AFX by protein kinase B. Nature 398: 630-634, 1999
Brunet A, Bonni A, Zigmond MJ, Lin MZ, Juo P, Hu LS, Anderson MJ, Arden KC, Blenis J, Greenberg ME: Akt promotes cell survival by phosphorylating and inhibiting a Forkhead transcription factor. Cell 96: 857-868, 1999
Biggs WH, Meisenhelder J, Hunter T, Cavenee WK, Arden KC: Protein kinase B/Akt-mediated phosphorylation promotes nuclear exclusion of the winged helix transcription factor FKHR1. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96: 7421-7426, 1999
Chen WS, Xu PZ, Gottlob K, Chen ML, Sokol K, Shiyanova T, Roninson I, Weng W, Suzuki R, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Hay N: Growth retardation and increased apoptosis in mice with homozygous disruption of the Akt1 gene. Genes Dev 15: 2203-2208, 2001
Blair LA, Bence-Haneluc KK, Mehta S, Franke T, Kaplan D, Marshall J: Akt-dependent potentiation of L channels by insulin-like growth factor-1 is required for neuronal survival. J Neurosci 19: 1940-1951, 1999
Barber AJ, Nakamura M, Wolpert EB, Reiter CE, Seigel GM, Antonetti DA, Gardner TW: Insulin rescues retinal neurons from apoptosis by a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-mediated mechanism that reduces the activation of caspase-3. J Biol Chem 276: 32814-32821, 2001
Humbert S, Bryson EA, Cordelieres FP, Connors NC, Datta SR, Finkbeiner S, Greenberg ME, Saudou F: The IGF-1/Akt pathway is neuroprotective in Huntington's disease and involves Huntingtin phosphorylation by Akt. Dev Cell 2: 831-837, 2002
Zhou BP, Liao Y, Xia W, Spohn B, Lee MH, Hung MC: Cytoplasmic localization of p21Cip1/WAF1 by Akt-induced phosphorylation in HER-2/neu-overexpressing cells. Nat Cell Biol 3: 245-52, 2001
Medema RH, Kops GJ, Bos JL, Burgering BM: AFX-like Forkhead transcription factors mediate cell-cycle regulation by Ras and PKB through p27kip1. Nature 404: 782-787, 2000
Muise-Helmericks RC, Grimes HL, Bellacosa A, Malstrom SE, Tsichlis PN, Rosen N: Cyclin D expression is controlled post-transcriptionally via a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 273: 29864-29872, 1998
Graff JR, Konicek BW, McNulty AM, Wang Z, Houck K, Allen S, Paul JD, Hbaiu A, Goode RG, Sandusky GE, Vessella RL, Neubauer BL: Increased AKT activity contributes to prostate cancer progression by dramatically accelerating prostate tumor growth and diminishing p27Kip1 expression. J Biol Chem 275: 24500-24505, 2000
Brognard J, Clark AS, Ni Y, Dennis PA: Akt/protein kinase B is constitutively active in non-small cell lung cancer cells and promotes cellular survival and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Cancer Res 61: 3986-3997, 2001
Miwa W, Yasuda J, Murakami Y, Yashima K, Sugano K, Sekine T, Kono A, Egawa S, Yamaguchi K, Hayashizaki Y, Sekiya T: Isolation of DNA sequences amplified at chromosome 19q13.1-q13.2 including the AKT2 locus in human pancreatic cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 225: 968-974, 1996
Liu W, Li J, Roth RA: Heregulin regulation of Akt/protein kinase B in breast cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261: 897-903, 1999
Roy HK, Olusola BF, Clemens DL, Karolski WJ, Ratashak A, Lynch HT, Smyrk TC: AKT proto-oncogene overexpression is an early event during sporadic colon carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 23: 201-205, 2002
Lynch HT, Casey MJ, Lynch J, White TE, Godwin AK: Genetics and ovarian carcinoma. Semin Oncol 25: 265-280, 1998
Cross DA, Alessi DR, Cohen P, Andjelkovich M, Hemmings BA: Inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase-3 by insulin mediated by protein kinase B. Nature 378: 785-789, 1998
Czech MP, Corvera S: Signaling mechanisms that regulate glucose transport. J Biol Chem 274: 1865-1868, 1999
Deprez J, Vertommen D, Alessi DR, Hue L, Rider MH: Phosphorylation and activation of heart 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase by protein kinase B and other protein kinases of the insulin signaling cascades. J Biol Chem 272: 17269-17275, 1997
Pessin JE, Saltiel AR: Signaling pathways in insulin action: Molecular targets of insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 106: 165-169, 2000
Ducluzeau PH, Fletcher LM, Vidal H, Laville M, Tavare JM: Molecular mechanisms of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in adipocytes. Diabetes Metab 28: 85-92, 2002
Wang Q, Somwar R, Bilan PJ, Liu Z, Jin J, Woodgett JR, Klip A: Protein kinase B/Akt participates in GLUT4 translocation by insulin in L6 myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol 19: 4008-4018, 1999
Hernandez R, Teruel T, Lorenzo M: Akt mediates insulin induction of glucose uptake and up-regulation of GLUT4 gene expression in brown adipocytes. FEBS Lett 494: 225-231, 2001
Plas DR, Talapatra S, Edinger AL, Rathmell JC, Thompson CB: Akt and Bcl-xL promote growth factor-independent survival through distinct effects on mitochondrial physiology. J Biol Chem 276: 12041-12048, 2001
Gottlob K, Majewski N, Kennedy S, Kandel E, Robey RB, Hay N: Inhibition of early apoptotic events by Akt/PKB is dependent on the first committed step of glycolysis and mitochondrial hexokinase. Genes Dev 15: 1406-1418, 2001
Cho H, Mu J, Kim JK, Thorvaldsen JL, Chu Q, Crenshaw EB, Kaestner KH, Bartolomei MS, Shulman GI, Birnbaum MJ: Insulin resistance and a diabetes mellitus-like syndrome in mice lacking the protein kinase Akt2 (PKB beta). Science 292: 1728-1731, 2001
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sen, P., Mukherjee, S., Ray, D. et al. Involvement of the Akt/PKB signaling pathway with disease processes. Mol Cell Biochem 253, 241–246 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026020101379
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1026020101379