Abstract
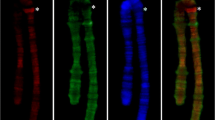
The Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) is a conserved protein which is best known for its strong association with the heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. We previously demonstrated that another important property of HP1 is its localization to the telomeres of Drosophila, a feature that reflects its critical function as a telomere capping protein. Here we report our analysis of the euchromatic sites to which HP1 localizes. Using an anti-HP1 antibody, we compared immunostaining patterns on polytene chromosomes of the Ore-R wild type laboratory strain and four different natural populations. HP1 was found to accumulate at specific euchromatic sites, with a subset of the sites conserved among strains. These sites do not appear to be defined by an enrichment of known repetitive DNAs. Comparisons of HP1 patterns among several Drosophila species revealed that association with specific euchromatic regions, heterochromatin and telomeres is a conserved characteristic of HP1. Based on these results, we argue that HP1 serves a broader function than typically postulated. In addition to its role in heterochromatin assembly and telomere stability, we propose that HP1 plays an important role in regulating the expression of many different euchromatic regions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasland, R. & A.F. Stewart, 1995. The chromo shadow domain, a second chromo domain in heterochromatin-binding protein 1, HP1. Nucl. Acid. Res. 23: 3168-3173.
Bannister, A.J., P. Zegerman, J.F. Partridge, E.A. Miska, J.O. Thomas, R.C. Allshire & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromodomain. Nature 410: 120–124.
Delattre, M., A. Spierer, C.H. Tonka & P. Spierer, 2000. The genomic silencing of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster: interaction between the heterochromatinassociated proteins Su(var)3-7 and HP1. J. Cell Sci. 23: 4253-4261.
Eissenberg, J.C. & T. Hartnett, 1993. A heat shock-activated cDNA rescues the recessive lethality of mutations in the heterochromatin-associated protein HP1 of Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Gen. Genet. 240: 333–338.
Eissenberg, J.C., T.C. James, D.M. Foster-Hartnett, T. Hartnett, V. Ngan & S.C.R. Elgin, 1990. Mutation in a heterochromatin-specific chromosomal protein is associated with suppression of position-effect variegation in Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 9923-9927.
Elgin, S.C.R., 1996. Heterochromatin and gene regulation in Drosophila. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 6: 193–202.
Fanti, L., D.R. Dorer, M. Berloco, S. Henikoff & S. Pimpinelli, 1998a. Heterochromatin Protein 1 binds transgene arrays. Chromosoma 107: 286–292.
Fanti, L., G. Giovinazzo, M. Berloco & S. Pimpinelli, 1998b. The Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) prevents telomere fusions in Drosophila melanogaster. Mol. Cell. 2: 1–20.
Furuta, K., E.K.L. Chan, K. Kiyosawa, G. Reimer, C. Luderschmidt & E.M. Tan, 1997. Heterochromatin protein HP1Hsβ (p25β) and its localization with centromeres in mitosis. Chromosoma 106: 11–19.
Horsley, D., A. Hutchings, G.W. Butcher & P.B. Singh, 1996. M32, a murine homologue of Drosophila Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1), localises to euchromatin within interphase nuclei and is largely excluded from constitutive heterochromatin. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 73: 308–311.
Huang, D.W., L. Fanti, D.T. Pak, M.R. Botchan, S. Pimpinelli & R. Kellum, 1998. Distinct cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions of Drosophila Heterochromatin Protein 1: their phosphorylation levels and associations with origin recognition complex proteins. J. Cell Biol. 142: 307–318.
Hwang, K.K., J.C. Eissenberg & H.J. Worman, 2001. Transcriptional repression of euchromatic genes by Drosophila Heterochromatin Protein 1 and histone modifiers. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98: 11423–11427.
James, T.C.& S.C.R. Elgin, 1986. Identification of nonhistone chromosomal protein associated with heterochromatin in Drosophila and its gene. Mol. Cell. Biol. 6: 3862-3872.
James, T.C., J.C. Eissenberg, C. Craig, V. Dietrich, A. Hobson & S.C.R. Elgin, 1989. Distribution patterns of HP1, a hetero-chromatin-associated nonhistone chromosomal protein of Drosophila. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 50: 170–180.
Jones, D.O., I.G. Cowell & P. Singh, 2000. Mammalian chromodomain proteins: their role in genome organisation and expression. Bioessays 22: 124–137.
Kaufmann, B.P., 1939. Distribution of induced breaks along the X chromosome of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 25: 571–577.
Lachner, M., D. O'Carroll, S. Rea, K. Mechtler & T. Jenuwein, 2001. Methylation of histone H3 Lysine9 creates a binding site for HP1 proteins. Nature 410: 116–120.
Miklos, G.L. & J.N. Cotsell, 1990. Chromosome structure at interfaces between major chromatin types: alpha-and betaheterochromatin. Bioessays 12: 1–6.
Miklos, G.L., M. Yamamoto, J. Davis & V. Pirrotta, 1988. Microcloning reveals a high frequency of repetitive sequences characteristic of chromosome 4 and the β-heterochromatin of Drosophila melanogaster. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 85: 2051-2055.
Minc, E., J.C. Courvalin & B. Buendia, 2000. HP1 gamma associates with euchromatin and heterochromatin in mammalian nuclei and chromosomes. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 90: 279–284.
Minc, E., Y. Allory, H.J. Worman, J.C. Courvalin & B. Buendia, 1999. Localization and phosphorylation of HP1 proteins during the cell cycle in mammalian cells. Chromosoma 108: 220–234.
Minc, E., Y. Allory, J.C. Courvalin & B. Buendia, 2001. Immunolocalization of HP1 proteins in metaphasic mammalian chromosomes. Meth Cell Sci. 23: 173–176.
Nielsen, S.J., R. Schneider, U.M. Bauer, A.J. Bannister, A. Morrison, D. O'Carroll, R. Firestein, M. Cleary, T. Jenuwein, R.E. Herrera & T. Kouzarides, 2001. Rb targets histone H3 methylation and HP1 to promoters. Nature 412: 561–565.
Pak, D.T.S., M. Pflumm, I. Chesnokov, D.W. Huang, R. Kellum, J. Marr, P. Romanowski & M.R. Botchan, 1997. Association of the origin recognition complex with heterochromatin and HP1 in higher eukaryotes. Cell 91: 311–323.
Paro, R. & D.S. Hogness, 1991. The polycomb protein shares a homologous domain with a heterochromatin-associated protein of Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 263–267.
Pimpinelli, S., M. Berloco, L. Fanti, P. Dimitri, S. Bonaccorsi, E. Marchetti, R. Caizzi, C. Caggese & M. Gatti, 1995. Transposable elements are stable structural components of Drosophila melanogaster heterochromatin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 92: 3804-3808.
Pimpinelli, S., S. Bonaccorsi, L. Fanti & M. Gatti, 2000. Preparation and analysis of mitotic chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster, pp. 1-24 in Drosophila: A Laboratory Manual, edited by W. Sullivan, M. Ashburner & S. Hawley. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Scholzen, T., E. Endl, C. Wohlenberg, S. van Der Sar, I.G. Cowell, J. Gerdes & P.B. Singh, 2002. The Ki-67 protein interacts with members of the Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) family: a potential role in the regulation of higher-order chromatin structure. J. Pathol. 196: 135–144.
Singh, P.B., J.R. Miller, J. Pearce, R. Kothary, R.D. Burton, R. Paro, T.C. James & S.J. Gaunt, 1991. A sequence motif found in a Drosophila heterochromatin protein is conserved in animal and plants. Nucl. Acid. Res. 19: 789–794.
Smothers, J.F. & S. Henikoff, 2001. The hinge and chromo shadow domain impart distinct targeting of HP1-like proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 21: 2555-2569.
Song, K., Y. Jung, D. Jung & I. Lee, 2001. Human Ku70 interacts with Heterochromatin Protein 1 alpha. J. Biol. Chem. 276: 8321-8327.
Vaury, C., A. Bucheton & A. Pelisson, 1989. The beta heterochromatic sequences flanking the I elements are themselves defective transposable elements. Chromosoma 98: 215–224.
Wreggett, K.A., F. Hill, P.S. James, A. Hutchings, G.W. Butcher & P.B. Singh, 1994. A mammalian homologue of Drosophila Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) is a component of constitutive heterochromatin. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 66: 99–103.
Zhimulev, I.F., V.F. Semeshin, V.A. Kulichkov & E.S. Belyaeva, 1982. Intercalary heterochromatin in Drosophila. I. Localization and general characteristics. Chromosoma 87: 197–228.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fanti, L., Berloco, M., Piacentini, L. et al. Chromosomal Distribution of Heterochromatin Protein 1 (HP1) in Drosophila: a Cytological Map of Euchromatic HP1 Binding Sites. Genetica 117, 135–147 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022971407290
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1022971407290