Abstract
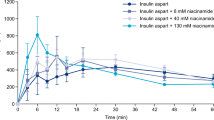
The intranasal absorption enhancing and histological effects of a range of lysophospholipids has been investigated in the rat. Blood glucose levels fell rapidly following the administration of insulin (8 IU/kg) in combination with lysophosphatidylcholines (LPC; 0.625% w/v) which had ten or more carbon groups in their fatty acid chain. The effect of the LPC-caproyl (C6) was comparable to that of an unenhanced insulin formulation; the enhancing effect of LPC-decanoyl (C10) was similar to that of an LPC-palmitoyl/stearoyl (C16/C18) for similar concentrations. The effect of LPC-decanoyl was reduced with concentration but was still significant at 0.2% w/v (5mM). Lysophosphatidylglycerol (LPG) had a marked insulin absorption enhancing effect even at 0.0625% w/v. The histological effects of LPC-caproyl were similar to those of an unenhanced insulin formulation, while co-administration of LPC-decanoyl resulted in evidence of epithelial interaction. LPG (0.5% w/v) resulted in similar histological changes as LPC (0.625% w/v) (1), but at 0.0625% w/v no significant changes in epithelial integrity were observed. The length of the fatty acid residue of lysophospholipids was identified as an important factor for intranasal absorption enhancing activity. The nature of the polar head group may also have an influence. Increased insulin absorption was not necessarily accompanied by severe disruption of the nasal epithelium. Careful selection of lysophospholipid type and concentration may enable therapeutic drug levels to be achieved via the nasal route without prohibitive toxic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
S. G. Chandler, L. Illum and N. W. Thomas. Nasal absorption in rats. II Effect of enhancers on insulin absorption and nasal histology. Int. J. Pharm. 76: 61–70 (1991)
S. Hirai, T. Yashiki, T. Matsuzawa and H. Mima. Absorption of drugs from the nasal mucosa of rat. Int. J. Pharm., 7: 317–325 (1981)
S. Hirai, t. Yashiki and H. Mima. Effect of surfactants on the nasal absorption of insulin in rats. Int. J. Pharm., 9: 165–172 (1981)
G.S.M.J.E Duchateau, J. Zuidema and F.W.H.M. Merkus. Bile salts and intranasal drug absorption. Int. J. Pharm., 31: 193–199 (1986)
S.J. Hersey and R.T. Jackson. Effect of bile salts on nasal permeability in vitro. J. Pharm. Sci., 76: 876–879 (1987)
A.L. Daugherty, H.D. Liggitt, J.G. McCabe, J.A. Moore and J.S. Patton. Absorption of recombinant methionyl-human growth hormone (Met-hGH) from rat nasal mucosa. Int. J. Pharm., 45: 197–206 (1988)
W.A.J.J. Hermens, M.J.M. Deurloo, S.G. Romeyn, J.C. Verhoef and F.W.H.M. Merkus. Nasal absorption enhancement of 17B-estradiol by dimethyl-beta-cyclodextrin in rabbits and rats. Pharm. Res., 7: 500–503 (1990)
A. Yamamoto, T. Morita, M. Hashida and H. Sezaki. Effect of absorption promotors on the nasal absorption of drugs with various molecular weights. Int. J. Pharm. 93: 91–99 (1993)
G-B Park, Z. Shao and A.K. Mitra. Acyclovir permeation enhancement across intestinal and nasal mucosae by bile salt-acylcarnitine mixed micelles. Pharm. Res. 9: 1262–1267 (1992)
S. G. Chandler, L. Illum and N. W. Thomas. Nasal absorption in the rat I. A method to demonstrate the histological effects of nasal formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 70: 19–27 (1991)
F.W.H.M. Merkus, N.G.M. Schipper, W.A.J.J. Hermens, S.G. Romeijin and J.C. Verhoef. Absorption enhancers in nasal drug delivery: efficacy and safety. J. Con. Rel. 24: 201–208 (1993)
L. Illum, N.F. Farraj, H. Critchley, B. R. Johansen and S. S. Davis. Enhanced nasal absorption of insulin in rats using lysophosphatidylcholine. Int. J. Pharm., 57: 49–54 (1989)
J. L. Richardson, L. Illum and N. W. Thomas. Vaginal absorption of insulin in the rat. Pharm. Res. 9: 878–883 (1992)
G. S. Gordon, A.C. Moses, R.D. Silver, J.S. Flier and M.C. Carey. Nasal absorption of insulin: enhancement by hydrophobic bile salts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA., 82 7419–7423 (1985)
J.A. Fix, K. Engle, P. A. Porter, P.S. Leppert, S. J. Selk, C. R. Gardner and J. Alexander. Acylcarnitines: drug absorption-enhancing agents in the gastrointestinal tract. Am. J. Physiol., 251: G332–G340 (1986)
M. Linton and P.S. Gallo. The Practical Statistician: Simplified Handbook of Statistics, Wadsworth Publishing Company, Inc., Belmont, California, (1975)
K. D. Hopkins and G. V. Glass. Basic Statistics for the Behavioural Sciences, Prentice-Hall Inc., New Jersey (1978)
E. L. LeCluyse, L. E. Appel and S.C. Sutton. Relationship between drug absorption enhancing activity and membrane perturbing effects of acylcarnitines. Pharm. Res., 8: 84–87 (1991)
K. S. Cho and P. Proulx. Studies on the mechanism of haemolysis by acylcarnitines, lysolecithins and acylcholines. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 225: 214–223 (1971)
P. A. Karlquist, L. Franzen, R. Sjodahl and C. Tagesson. Lysophosphatidylcholine and taurodeoxycholate increase stomach permeability to different-sized molecules. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 21: 1039–1045 (1986)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chandler, S.G., Thomas, N.W. & Illum, L. Nasal Absorption in the Rat. III. Effect of Lysophospholipids on Insulin Absorption and Nasal Histology. Pharm Res 11, 1623–1630 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018970006935
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1018970006935