Abstract
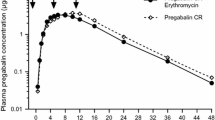
To determine the role of acid hydrolysis on the gastrointestinal absorption of erythromycin, six healthy subjects received erythromycin as a 240 mg intravenous dose, a 250 mg oral solution administered via endoscope directly into the duodenum and bypassing the stomach, and an enteric-coated 250 mg capsule. Blood samples were collected for 6 hours and serum erythromycin quantified by a microbiological method. The time to achieve maximum serum concentrations for the solution was 0.25 ± 0.08 (mean ± SD) hours and for the capsule was 2.92 ± 0.55 hours. The absolute bioavailability of erythromycin from the capsule was 32 ± 7% and for the duodenal solution 43 ± 14%. The ratio of the areas under the serum erythromycin concentration-time curve of capsule to solution was 80 ± 28% (range 38 to 110%). There is substantial loss of erythromycin apart from gastric acid hydrolysis, which cannot be accounted for by hepatic first-pass metabolism. Attempts to further improve the oral bioavailability of erythromycin beyond 50% by manipulation of formulation are likely to be futile.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
L.E. Josselyn, and J.C. Sylvester. Absorption of erythromycin. Antibiot. Chemother. 3:63–66 (1953).
B.G. Boggiano and M. Gleeson. Gastric acid inactivation of erythromycin stearate in solid dosage forms. J. Pharm. Sci., 65:497–502 (1976).
P.J. McDonald, L.E. Mather and M.J. Story. Studies on absorption of a newly developed enteric-coated erythromycin base. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 17:601–606 (1977).
E. Triggs and M. A. Neaverson. Bioavailability of erythromycin. Med. J. Aust. 2:344 (1973)
E. J. Triggs and J. J. Ashley. Oral administration of erythromycin stearate: effect of dosage form and plasma levels. Med.J. Aust. 2:121–123 (1978).
A.-S. Malmborg. Bioavailability of erythromycin ethylsuccinate from tablet and mixture forms: a comparison with equivalent doses of erythromycin stearate. Curr. Ther. Res. 27:733–740 (1980).
A. Digranes, K. Josefsson, and A. Schreiner. Influence of food on the absorption of erythromycin from enteric-coated pellets and stearate tablets. Curr. Ther. Res. 35:313–320 (1984).
T. Hovi, K. Josefsson and O.V. Renkonen. Erythromycin absorption in healthy volunteers from single and multiple doses of enteric-coated pellets and tablets. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 25: 271–273 (1983).
K. Josefsson, M.J. Levitt, J. Jann, and C. Bon. Erythromycin absorption from enteric-coated pellets given in multiple doses to volunteers, in comparison with enteric-coated tablets and film coated stearate tablets. Curr. Ther. Res. 39:131–142 (1986).
J. Rutland, N. Berend and G.E. Marlin. The influence of food on the bioavailability of new formulations of erythromycin stearate and base. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 38:343–347 (1979).
L.S. Sansom, R.J. West, D.B. Williams, G. Boehm, and M.J. Fong Lim. Pharmacokinetic comparison of enteric-coated erythromycin base pellets 175 mg and erythromycin stearate tablets 250 mg in healthy volunteers. (Unpublished).
T.B. Tjandramaga, A. Van Hecken, A. Mullie, R. Verbesselt, P.J. De Schepper, L. Verbist, and K. Josefsson. Relative bioavailability of enteric coated pellets, stearate and ethylsuccinate formulations of erythromycin. Pharmacology 29:305–311 (1984).
G.J. Yakatan, C.E. Rasmussen, P.J. Feis, and S. Wallen. Bioinequivalence of erythromycin ethylsuccinate and enteric-coated erythromycin pellets following multiple oral doses. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 25: 36–42 (1985).
P.B. Watkins, S.A. Murray, L.G. Winkelman, D.M. Heuman, S.A. Wrighton, and P.S. Guzelian. Erythromycin breath test as an assay of glucocorticoid-induced liver cytochromes P-450. J. Clin. Invest. 83: 688–697 (1989)
M. Gibaldi. Biopharmaceutics and Clinical Pharmacokinetics, Lea and Febiger, Philadelphia, 1991.
P.G. Welling and W.A. Craig. Pharmacokinetics of intravenous erythromycin. J. Pharm. Sci., 67:1057–1059 (1978).
K.L. Austin, L.E. Mather, C.R. Philpot, and P.J. McDonald. Intersubject and dose related variability after intravenous administration of erythromycin. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 10:273–279 (1980).
J. Barre, A. Mallat, J. Rosenbaum, L. Deforges, G. Houin, D. Dhumeaux, and J.-P. Tillement. Pharmacokinetics of erythromycin in patients with severe cirrhosis. Respective influence of decreased serum binding and impaired liver metabolic capacity. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 23: 753–757 (1987).
A.H.C. Chun and J.A. Seitz. Pharmacokinetics and biological availability of erythromycin. Infection, 5(suppl. 1): 14–22 (1977)
B. Lake and S.M. Bell. Variations in absorption of erythromycin. Med. J. Aust. i: 449–451 (1969).
A.C. Moffat. Clarke's Isolation and Identification of Drugs, The Pharmaceutical Press, London, 1986
E. Lunell, K.-E. Andersson, O, Borgå, P.-O. Fagerström, G. Kjellin, C.G.A. Persson, and K. Sjölund. Absorption of enprofylline from the gastrointestinal tract in healthy subjects. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 27: 329–333 (1984).
D. Brockmeier, H.-G. Grigoleit, and H. Leonhardt. The absorption of piretanide from the gastro-intestinal tract is site-dependent. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 30: 79–82 (1986).
K.M. Downey, and D.M. Chaput de Saintonge. Gastrointestinal side effects after intravenous erythromycin lactobionate. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 21: 295–299 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somogyi, A.A., Bochner, F., Hetzel, D. et al. Evaluation of the Intestinal Absorption of Erythromycin in Man: Absolute Bioavailability and Comparison with Enteric Coated Erythromycin. Pharm Res 12, 149–154 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016215510223
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1016215510223