Abstract
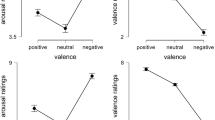
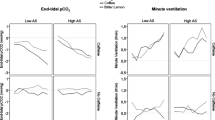
Psychophysiological assessments measuring heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and skin resistance level were conducted on 7 male compulsive gamblers and on 7 age and gender matched controls while both groups performed mental arithmetic and listened to individualized tapes of the gamblers' preferred form of gambling and an individualized fear tape. Heart rate responses of the gamblers to the 2 gambling audiotapes were significantly greater than those found for the controls whereas the groups did not differ on mental arithmetic or the fear provoking scene, confirming some degree of cue-specific arousal in gamblers. The other physical responses did not yield such strong results. If physiological arousal provides the motivational basis for gambling and is maintained on an intermittent schedule of reinforcement, the findings may have implications for the treatment of compulsive gambling.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Abrams, D. B., Monti, P. M., Carey, K. B., Pinto, R. P., & Jacobus, S. I. (1988). Reactivity to smoking cues and relapse: Two studies of discriminant validity. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 26, 225–233.
American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th Ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
Anderson, G., & Brown, R. I. F. (1984). Real and laboratory gambling, sensation-seeking and arousal. British Journal of Psychology, 75, 401–410.
Blanchard, E. B., Hickling, E. J., Buckley, T. C., Taylor, A. E., Vollmer, A., & Loos, W. R. (1996). The psychophysiology of motor vehicle accident related post-traumatic stress disorder: Replication and extension. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64, 742–751.
Blanchard, E. B., Hickling, E. J., Taylor, A. E., Loos, W. R., & Gerardi, R. J. (1994). The psychophysiology of motor vehicle accident related post-traumatic stress disorder. Behavior Therapy, 25, 453–467.
Blakey, R., & Baker, R. (1980). An exposure approach to alcohol abuse. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 18, 319–325.
Binkoff, J. A., Abrams, D. B., Collins, R. L., Liepman, M. R., Monti, P. M., Nirenberg, T. D., & Zwick, W. R. (1984, November). Exposure to alcohol cues: Impact of reactivity and non-problem drinkers. Paper presented at the annual convention of the Association for the Advancement of Behavior Therapy, Philadelphia.
Childress, A. R., McLellan, A. T., & O'Brien, C. P. (1985). Assessment and extinction of conditioned withdrawal-like responses in an integrated treatment for opiate dependence. In L. S. Harris (Ed.), Problems of drug dependence, 1984 (National Institute of Drug Abuse Research Monograph 55, pp. 202–210). Washington, DC: U.S. Government Printing Office.
Cooney, N. L., Litt, M. D., Morse, P. A., Bauer, L. O., & Gautt, L. (1997). Alcohol cue reactivity, negative mood reactivity, and relapse in treated alcoholic men. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 106, 243–250.
Coventry, K. R., & Norman, A. C. (1997). Arousal, sensation-seeking and frequency of gambling in off-course horse racing bettors. British Journal of Psychology, 88, 671–681.
Dougher, M. J., Auguston, E., Markham, M. R., & Wulfert, E. (1994). The transfer of respondent eliciting and avoidance evoking functions through stimulus equivalence classes. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 62, 331–351.
Drummond, D. C., & Glautier, S. (1994). A controlled trial of cue exposure treatment in alcohol dependence. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62, 809–817.
Dymond, S., & Barnes, D. (1994). A transfer of self-discrimination response functions through the arbitrarily applicable relations of sameness, opposition, more than, and less than. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 62, 251–267.
First, M. B., Gibbon, M., Spitzer, R. L., & Williams, J. B. W. (1996, February, Final version). User's Guide for Structured Clinical Interview for DSM-IV Axis I Disorders-Research Version (SCID-I, Version 2.0), New York: Biometrics Research Department, NY State Psychiatric Institute.
First, M. B., Spitzer, R. L., Gibbon, M., & Williams, J. B. W. (1994). Structured Clinical Interview for Axis II Personality Disorders, Version 2.0 (July 1994 Draft). New York: Biometrics Research Department.
Franken, I. H. A., de Haan, H. A., van der Meer, C. W., Haffmans, P. M. J., & Hendriks, V. M. (1999). Cue reactivity and effects of cue exposure in abstinent posttreatment drug users. Journal of Substance Abuse Treatment, 16, 81–85.
Hayes, S. C., & Wilson, K. G. (1995). The role of cognition in complex human behavior: A contextualistic perspective. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry, 26(3), 241–248.
Hodgson, R. J., & Greene, J. B. (1980). The saliva priming effect, eating speed, and the measurement of hunger. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 18, 243–247.
Hodgson, R. J., & Rankin, H. J. (1976). Modification of excessive drinking by cue exposure. Behaviour Research and Therapy, 14, 305–307.
Ladouceur (1998). La passion du jeu. (unpublished treatment manual). Centre Quebecois d'excellence pour la prevention et le traitement du jeu. Quebec, Canada.
Lang, P. (1979). A bio-informational theory of emotional imagery. Psychophysiology, 16, 495–512.
Lesieur, H. R., & Blume, S. B. (1987). The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): A new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. American Journal of Psychiatry, 144, 1184–1188.
Ludwig, A. M., & Stark, L. H. (1974). Alcohol craving: Subjective and situational aspects. Quarterly Journal of Studies on Alcohol, 35, 899–905.
Marlatt, G. A. (1987). Craving Notes. British Journal of Addiction, 82, 42–44.
Marlatt, G. A., & Gordon, J. R. (Eds). (1985). Relapse prevention: Maintenance strategies in the treatment of addictive behaviors. New York: Guilford Press.
McConaghy, N., Blaszczynski, A., & Frankova, A. (1991). Comparison of imaginal desensitization with other behavioural treatments of pathological gambling: A two-to nine-year follow-up. British Journal of Psychiatry, 159, 390–393.
Michael, J. (1982). Distinguishing between discriminative and motivational functions of stimuli. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 37, 149–155.
Michael, J. (1994). Establishing operations. The Behavior Analyst, 16, 191–206.
Monti, P. M., Binkoff, J. A., Abrams, D. B., Zwick, W. R., Nirenberg, T. D., & Liepman, M. R. (1987). Reactivity of alcoholics and non-alcoholics to drinking cues. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 96, 1–5.
Niaura, R. S., Rohsenow, D. J., Binkoff, J. A., Monti, P. M., Pedraza, M., & Abrams, D. B. (1988). Relevance of cue reactivity to understanding alcohol and smoking relapse. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 97, 133–152.
Nirenberg, T. D., & Miller, P. M. (1982). Salivation: An assessment of food craving? Behaviour Research and Therapy, 20, 405–407.
Notterman, J. M., Schoenfeld, W. N., & Bersh, P. J. (1952). A comparison of three extinction procedures following heart rate conditioning. Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 47, 674–677.
Pitman, R. K., Orr, S. P., Forgue, D. F., deJong, J. B., & Claiborn, J. M. (1987). Psychophysiologic assessment of post-traumatic stress disorder imagery in Vietnam combat veterans. Archives of General Psychiatry, 44, 970–975.
Pomerleau, O. F., Fertig, J., Baker, L., & Cooney, N. (1983). Reactivity to alcohol cues in alcoholics and non-alcoholics: Implications for a stimulus control analysis of drinking. Addicitive Behaviors, 8, 1–10.
Rohsenow, D. J., Monti, P. M., Abrams, D. B., Rubonis, A. V., Niaura, R. S., Sirota, A. D., & Colby, S. M. (1992). Cueeleicited urge to drink and salivation in alcoholics: Relationship to individual differences. Advances in Behavior Research and Therapy, 14, 195–210.
Rohsenow, D. J., Monti, P. M., Rubonis, A. V., Sirota, A. D., et al. (1997). Cue reactivity as a predictor of drinking among male alcoholics. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 62, 620–626.
Shadel, W. G., Niaura, R., Abrams, D. B., Goldstein, M. G., Rohsenow, D. J., Sirota, A. D., & Monti, P. M. (1998). Scripted imagery manipulations and smoking cue reactivity in a clinical sample of self-quitters. Experimental & Clinical Psychopharmacology, 6, 179–186.
Sitharthan, T., Sitharthan, G. Hough, M. J., & Kavanagh, D. J. (1997). Cue exposure in moderation drinking. A comparison with cognitive-behavior therapy. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 878–882.
Stewart, J., de-Wit, H., & Eikelboom, R. (1984). Role of unconditioned and conditioned drug effects in the self-administration of opiates and stimulants. Psychological Review, 91(2), 251–268.
Sylvain, C., Ladouceur, R., & Boisvert, J. (1997). Cognitive and behavioral treatment of pathological gambling: A controlled study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 65, 727–732.
Symes, B. A., & Nicki, R. M. (1997). A preliminary consideration of cue-exposure, response-prevention treatment for pathologial gambling behaviour: Two case studies. Journal of Gambling Studies, 13, 145–157.
Volberg, R. (1996). Prevalence studies of problem gambling in the United States. Journal of Gambling Studies, 12, 111–128.
Walker, M. B. (1992). The psychology of gambling. New York: Pergamon Press.
Wise, R. A. (1988). The neurobiology of craving: Implications for the understanding and treatment of addiction. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 97, 118–132.
Wulfert, E., Dougher, M. J., & Greenway, D. E. (1991). Protocol analysis of the correspondence of verbal behavior and equivalence formation. Journal of the Experimental Analysis of Behavior, 56, 489–504.
Wulfert, E., Greenway, D. E., & Dougher, M. J. (1996). A logical functional analysis of reinforcement-based disorders: Alcoholism and pedophilia. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 64, 1140–1151.
Wulfert, E., Greenway, D. E., Farkas, P., Hayes, S. C., & Dougher, M. J. (1994). Correlation between a personality test for rigidity and performance on an operant schedule. Journal of Applied Behavior Analysis, 27, 659–671.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blanchard, E.B., Wulfert, E., Freidenberg, B.M. et al. Psychophysiological Assessment of Compulsive Gamblers' Arousal to Gambling Cues: A Pilot Study. Appl Psychophysiol Biofeedback 25, 155–165 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009550724836
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009550724836