Abstract
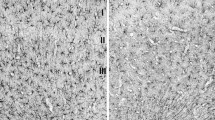
The distribution and morphology of GFAP-immunoreactive cells was investigated in two elasmobranch species, Scyliorhinus canicula and Torpedo marmorata, in an attempt to distinguish between Horstmann's (1954) hypothesis that the presence of cells resembling mammalian astrocytes is a function of the thickness of the ventricular walls, and Cajal's (1911) hypothesis that astrocytes are a phylogenetic novelty found only in birds and mammals. Two types of GFAP-reactive elements were observed, but the distribution of these differed markedly between the two species. In Scyliorhinus, radial glial cells were predominant and astrocytes relatively rare. In Torpedo, on the other hand, a species in which the ventricles are atrophied and the ventricular walls extremely thick, the overwhelming majority of GFAP-labelled structures strongly resembled astrocytes; occasionally, GFAP-positive cells were observed in the ependyma of the spinal cord. These findings, together with previous results obtained by others in hagfish, provide strong evidence in favour of Horstmann's hypothesis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
AchÙcarro, N. (1915) De l′évolution de la névroglie,et spécialement de ses relations avec l′appareil vasculaire. Trabajos del Laboratorio de Investigaciones Biol´ogicas de la Universidad de Madrid 13, 169-212.
Amrendra & Sensharma, G. C. (1981) Neuroglia in the Teleost (Channa striatus). Zeitschrift f ür mikroskopischanatomische Forschung 95, 108-112.
Anderson, M. J., Swanson, K. A., Waxman, S. G. & Eng, L. F. (1984) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in regenerating teleost spinal cord. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 32, 1099-1106.
BÄckstrÖm, K. (1924) Contributions to the forebrain morphology in selachians. Acta Zoologica 5, 120-240.
Balaton, A. J. (1993) Application des micro-ondes dans les techniques immunohistochimiques. Annales Pathologiques 3, 145-150.
Bauchot, R., Platel, R. & Ridet, J.-M. (1976) Brainbody weight relationships in Selachii. Copeia 2, 305-309.
Bell, P. B. JR, Rundquist, I., Svensson, I. & Collins, V. P. (1987) Formaldehyde sensitivity of a GFAPepitope, removed by extraction of the cytoskeleton with high salt. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 35, 1375-1380.
BjÖrklund, H., Bignami, A. & Dahl, D. (1985) Immunohistochemical demonstration of glial fibrillary acidic protein in normal rat Müller glia and retinal astrocytes. Neuroscience Letters 54, 363-368.
Bodega, G., Suarez, I., Rubio, M. & Fernandez, B. (1990) Distribution and characteristics of the different astroglial cell types in the adult lizard (Lacerta lepida) spinal cord. Anatomy and Embrology 181, 567-575.
Bodega, G., Suarez, I., Rubio, M. & Fernandez, B. (1994) Ependyma: phylogenetic evolution of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and vimentin expression in vertebrate spinal cord. Histochemistry 102, 113-122.
Bodega, G., Suarez, I., Rubio, M., Villalba, R. M. & Fernandez, B. (1993) Astroglial pattern in the spinal cord of the adult barbel (Barbus comiza). Anatomy and Embrology 187, 385-395.
Cameron-curry, P., Viglietti-panzica, A. C. & Panzica, G. C. (1991) Immunocytochemical distribution of glial fibrillary acidic protein in the central nervous system of the Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica). Anatomy and Embryology 184, 571-581.
Cardone, B. & Roots, B. I. (1990) Comparative immunohistochemical study of glial filament proteins (glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin) in goldfish, octopus and snail. Glia 3, 180-192.
Craigie, E. H., (1939) Vascularity in the brains of tailed amphibians. I. Ambystoma tigrinum (Green). Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 81, 21-27.
Craigie, E. H. (1940a)Vascularity in the brains of tailed amphibians. II. Necturus maculosus Rafinesque. Proceedings of the American Philosophical Society 82, 395-410.
Craigie, E. H. (1940b) The capillary bed of the central nervous system of Dermophis (Amphibia, Gymnophiona). Journal of Morphology 67, 477-487.
Craigie, E. H. (1941a) Vascularization in the brains of reptiles. II. The cerebral capillary bed in Sphenodon punctatum. Journal of Morphology 69, 263-277.
Craigie, E. H. (1941b) The capillary bed of the central nervous system in a member of a second genus of Gymnophiona-Siphonops. Journal of Anatomy 76, 56-64.
Craigie, E. H. (1943) The architecture of the cerebral capillary bed in lungfishes. Journal of Comparative Neurology 79, 19-31.
Dahl, D. & Bignami, A. (1973) Immunochemical and immunofluorescence studies of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in vertebrates. Brain Research 61, 279-293.
Dahl, D; Crosby, C. J., Sethi, J. S. & Bignami, A. (1985) Glial fibrillary acidic (GFA) protein in vertebrates: immunofluorescence and immunoblotting study with monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Journal of Comparative Neurology 239, 75-88.
De guevara, R., Pairault, C. & Pinganaud, G. (1994) Expression de la vimentine et de la GFAP et développement de la rétine chez la truite. Comptes Rendus de l′Académie des Sciences 316, 455-458.
Ebbesson, S. O. E. & Northcutt, R. G. (1976) Neurology of anamniotic vertebrates. In Evolution of brain and behavior in vertebrates. (edited by Masterson, R. B., Bitterman, M. E., Campbell, C. B. G. and Hotton, N., pp. 115-146. Hillsdale, N.J.: Erlbaum.
Edinger, L. (1906) Über das Gehirn von Myxine glutinosa. Abhandlungen der Königlich Preussischen Akademie derWissenschaften aus dem Jahre 1906 1-36.
Eng, L. F., Vanderhaeghen, J. J., Bignami, A. & Gerstl, B. (1971) An acidic protein isolated from fibrous astrocytes. Brain Research 28, 351-354.
Eng, L. M. (1982) The glial fibrillary acidic protein: the major protein constituent of glial filaments. Scandinavian Journal of Immunology 15, 41-51.
Eurich, F. W. (1898) Contributions to the comparative anatomy of the neuroglia. Journal of Anatomy and Physiology 32, 688-708.
Evers, P. & Uylings, A. B. (1994) Microwave-stimulated antigen retrieval is pH and temperature dependent. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 42, 1555-1563.
Fox, C. H., Johnson, J. B., Whitting, J. & Roller, P. P. (1985) Formaldehyde fixation. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry 33, 845-853.
Gianonatti, C., Bodega, G. & Bardasano, J. L. (1987) Neuroglia of the optic tectum in the Bufo bufo (Amphibian Anura), First Trials. Journal für Hirnforschung 29, 139-143.
Horstmann, E. (1954) Die Faserglia des Selachiergehirns. Zeitschrift für Zellforschung 39, 588-617.
Kalman, M., Kiss, A. & Majorossy, K. (1994) Distribution of glial fibrillary acidic protein-immunopositive structures in the brain of the red-eared freshwater turtle (Pseudemys scripta elegans). Anatomy and Embryology 189, 421-434.
King, J. S. (1966) A comparative investigation of neuroglia in representative vertebrates: a silver carbonate study. Journal of Morphology 119, 435-466.
Klatzo, I. (1967) Cellular morphology of the lemon shark brain. In Sharks, Skates and Rays. (edited by Gilbert, P.W., Mathewson, R. F. and Rall, D. P.), pp. 341-359, Baltimore: The Johns Hopkins Press.
Kruger, L. & Maxwell, D. S. (1967) Comparative fine structure of vertebrate neuroglia: Teleosts and Reptiles. Journal of Comparative Neurology 129, 115-142.
Lauro, G. M., Fonti, R. & Margotta, V. (1991) Phylogenetic evolution of intermediate filament associated proteins in ependymal cells of several adult poïkilotherm vertebrates. Journal für Hirnforschung 32, 257-261.
Lazzari, M., Franceschini, V. & Ciani, F. (1997) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin in radial glia of Ambystoma mexicanum and Triturus carnifex: an immunocytochemical study. Journal of Brain Research 38, 187-194.
Long, D. M., Bodenheimer, G. S., Hartmann, J. F. & Klatzo, I. (1968) Ultrastructural features of the shark brain. American Journal of Anatomy 122, 209-236.
Margotta, V., Fonti, R., Palladini, G., Filoni, S. & Lauro, G. M. (1991) Transient expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) in the ependyma of the regenerating spinal cord in adult newts. Journal für Hirnforschung 32, 475-490.
Miller, R. H. & Liuzzi, F. J. (1986) Regional specialization of the radial glial cells of the adult frog spinal cord. Journal of Neurocytology 15, 187-196.
Monzon-mayor, M., Yannes, M. S., Ghandour, M. S., De Barry, J. & Gombos, G. (1990) Glial fibrillary acidic protein and vimentin immunohistochemistry in the developing and adult midbrain of the lizard Gallotia galloti. Journal of Comparative Neurology 295, 569-579.
Mysliveckova, A. (1978) Ultrastructural image of the neuroglia of Fishes, Amphibians and Reptiles. Folia Morphologica 26, 49-54.
Naujoks-manteuffel, B. & Roth, G. (1989) Astroglial cells in a salamander brain (Salamandra salamandra) as compared to mammals: a glial fibrillary acidic protein immunohistochemistry study. Brain Research 487, 397-401.
Nicholson, C. (1998) Structure and function of the cellular elements in the central nervous system. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates. Vol. 1. (edited by Nieuwenhuys, R., Ten donkelaar, H. J. and Nicholson, C.), pp. 1-24. Berlin: Springer
Northcutt, R. G. (1977) Elasmobranch central nervous system organization and its possible evolutionary signi-ficance. American Zoologist 17, 411-429.
Onteniente, B., Kimura, H. & Maeda, T. (1983) Comparative study of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in vertebrates by PAP immunohistochemistry. Journal of Comparative Neurology 215, 427-436.
Rakic, P. (1971) Neuron-glia relationship during granule cell migration in developing cerebellar cortex. A Golgi and electron microscopic study in Macacus rhesus. Journal of Comparative Neurology 141, 283-312.
Ramon Y., Cajal, S. (1911) Histologie du syst`eme nerveux de l'homme et des vertébrés. Vol I et II. Paris: A. Maloine.
Retzius, G. (1891) ZurKenntniss des zentralen Nervensystems von Myxine glutinosa.Biologische Untersuchungen, Neue Folge 19, 1-26.
Semple-rowland, S. L. (1991) Expression of glial fibrillary acidic protein by Müller cells in rd Chick retina. Journal of Comparative Neurology 305, 581-590.
Silver, M. L. (1942) The glial elements of the spinal cord of the frog. Journal of Comparative Neurology 77, 41-47.
Smeets, W. J. A. J. (1998) Cartilaginous fishes. In The Central Nervous System of Vertebrates. Vol. 1. (edited by Nieuwenhuys, R., TEN DONKELAAR, H. J. AND Nicholson, C), pp. 1-24. Berlin: Springer.
Smeets, W. J. A. J., Nieuwenhuys, R. & Roberts, B. L. (1983) The central nervous system of cartilaginous fishes. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Stensaas, L. J. (1977) The ultrastructure of astrocytes, oligodendrocytes and microglia in the optic nerve of urodele amphibians (A.punctatum, T.pyrrhogaster, T.viridescens). Journal of Neurocytology 6, 269-286.
Stensaas, L. J. & Stensaas, S. S. (1968) Light microscopy of glial cells in turtles and birds. Zeitschrift fur Zellforschung und mikroskopische Anatomie 91, 315-340.
Szaro, B. G. & Gainer, H. (1988) Immunocytochemical identification of non-neuronal intermediate filament proteins in the developing Xenopus laevis nervous system. Developmental Brain Research 43, 207-224.
Tapscott, S. J., Bennett, G. S., Toyama, Y., Kleinbart, F. & Holtzer, H. (1981) Intermediate filament proteins in the developing chick spinal cord. Developmental Biology 86, 40-54.
Van gehuchten, A. (1898) Neuroglie dans le cervelet de l'homme. Bibliographie Anatomique 2, 146-152.
Vaughan, D. K., Erickson, P. A. & Fisher, S. K. (1990) Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) immunoreactivity in rabbit retina: effect of fixation. Experimental Eye Research 50, 385-392.
Virgintino, D., Maiorano, E., Bertossi, M., Pollice, L., Ambrosi, G. & Roncali, L. (1992) GFAP-immunoreactive perivascular glia in the chick optic tectum. European Journal of Histochemistry 36, 445-454.
Wasowicz, M., Pierre, J., Reperant, J. Ward, R., Vesselkin, N. P. & Versaux-botteri, C. (1994) Immunoreactivity to Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP) in the brain and spinal cord of the lamprey (Lampetra fluviatilis). Journal of Brain Research 35, 834-837.
Wicht, H., Derouiche, A. & Korf, H.-W. (1994) An immunocytochemical investigation of glial morphology in the Pacific hagfish: radial and astrocyte-like glia have the same phylogenetic age. Journal of Neurocytology 23, 565-576.
Wicht, H. & Northcutt, R. G. (1992) The forebrain of the Pacific hagfish: a cladistic reconstruction of the ancestral craniate forebrain. Brain, Behavior and Evolution 40, 25-64.
Wright, S. (1940) The statistical consequences of Mendelian heredity in relation to speciation. In The New Systematics (edited by HUXLEYI), pp. 191-193. Oxford University Press.
Yanes, G., Monzon-mayor, M., Ghandour, M. S., De barry, J. & Gombos, G. (1990) Radial glia and astrocytes in developing and adult telencephalon of the lizard Gallotia galloti as revealed by immunohistochemistry with anti-GFAP and anti-vimentin antibodies. Journal of Comparative Neurology 295, 559-568.
Yen, S.-H., Dahl, D. Schachner, M. & Shelanski, M. L. (1976) Biochemistry of the filaments of brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA 73, 529-533.
Zamora, A. J. & Muttin, M. (1988) Vimentin and glial fibrillary acidic protein filaments in radial glia of the adult urodele spinal cord. Neuroscience 27, 279-288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wasowicz, M., Ward, R. & Repérant, J. An investigation of astroglial morphology in Torpedo and Scyliorhinus. J Neurocytol 28, 639–653 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007004714712
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007004714712