Abstract
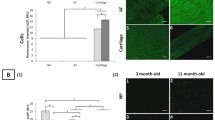
The expression of the matrix protein chondromodulin-I has been studied in human intervertebral discs of 101 people using immunohistochemical analyses. The purpose of this report is to present data on the metabolic changes that were found to occur in the chondrocytes of intervertebral discs during development and aging. Chondromodulin-I was highly expressed during the gestational period and gradually decreased after maturation. It was detected in both the extracellular matrix and chondrocytes in the zone of hypertrophic cartilage, the zone of proliferative cartilage and the zone of resting cartilage in fetal discs. It was also present in the annulus fibrosus, nucleus pulposus and end-plate cartilage in mature discs. In degenerative discs, chondromodulin-I immunoreactivity tended to be elevated in the remaining chondrocytes. Our findings suggest that the expression of the protein is developmentally regulated and upregulated through a defense mechanism against the degenerative processes of the aged intervertebral disc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Conventry MB, Ghormley RK, Kernohan JW (1945) The intervertebral disc: its microscopic anatomy and pathology. Part II. Changes in the intervertebral disc concomitant with age. J Bone Joint Surg 17: 233–247.
Dupuis PR, Yong-Hing K, Cassidy JD, Kirkaldy-Willis WH (1985) Radiologic diagnosis of degenerative lumbar spinal instability. Spine 10: 262–276.
Frymoyer JW, Hanley EN Jr, Howe J, Kuhlmann D, Matteri RE (1979) A comparison of radiographic findings in fusion and nonfusion patients ten or more years following lumbar disc surgery. Spine 4: 435–440.
Hayami T, Shukunami C, Mitui K, Endo N, Tokunaga K, Kondo J, Takahashi H, Hiraki Y (1999) Specific loss of Chondromodulin-I gene expression in chondrosarcoma and the suppression of tumor angiogenesis and growth by its recombinant protein in vivo. FEBS Letters 458: 436–440.
Hiraki Y, Tanaka H, Inoue H, Kondo J, Kamizono A, Suzuki F (1991) Molecular cloning of a new class of cartilage-specific matrix, chondromodulin-I, which stimulates growth of cultured chondrocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 175: 971–977.
Hiraki Y, Inoue H, Kondo J, Kamizono A, Yoshitake Y, Shukunami C, Suzuki F (1996) A novel growth-promoting factor derived from fetal bovine cartilage, chondromodulin-II-purification and amino acid sequence. J Biol Chem 271: 22657–22662.
Hiraki Y, Inoue H, Iyama K, Kamizono A, Ochiai M, Shukunami C, Iijima S, Suzuki F, Kondo J (1997a) Identification of chondromodulin-I as a novel endothelial cell growth inhibitor: purification and its localization in the avascular zone of epiphyseal cartilage. J Biol Chem 272: 32419–32426.
Hiraki Y, Kono T, Sato M, Shukunami C, Kondo J (1997b) Inhibition of DNA synthesis and tube morphogenesis of cultured vascular endothelial cells by chondromodulin-I. FEBS Letters 415: 321–324.
Hiraki Y, Mitui K, Endo N, Takahashi K, Hayami T, Inoue H, Shukunami C, Tokunaga K, Kono T, Yamada M, Takahashi HE, Kondo J (1999) Molecular cloning of human chondromodulin-I, a cartilage-derived growth modulating factor, and its expression in Chinese hamster ovary cells. Eur J Biochem 260: 869–878.
Inkinen RI, Lammi MJ, Agren U, Tammi K, Puustjrvi K, Tammi MI (1999) Hyaluronan distribution in the human and canine intervertebral disc and cartilage endplate. Histochem J 31: 579–587.
Inoue H, Kondo J, Koike T, Shukunami C, Hiraki Y (1997) Identification of an autocrine chondrocyte colony-stimulating factor-chondromodulin-I stimulates the colony formation of growth plate chondrocytes in agarose culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 241: 395–400.
Iwaki T, Kume-Iwaki A, Liem RKH, Goldman JE (1989) αB-crystallin is expressed in non-lenticular tissues and accumulates in Alexander's disease brain. Cell 57: 71–78.
Lindahl O (1996) Determination of sagittal mobility of the lumbar spine: a clinical method. Acta Orthop Scand 37: 241–254.
Markwell M, Hass S, Bieber L, Tolbert N (1978) A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem 87: 206–210.
Maroudas A (1988) Nutrition and metabolism of the intervertebral disc. In: Ghosh P, ed. The Biology of the Intervertebral Disc, Vol. 2, Boca Raton: CRC Press, pp. 1–37.
Nachemson AL (1960) Lumbar intervertebral pressure: Experimental studies on post-mortem material. Acta Orthop Scand (Suppl. 43) 43: 42–43.
Nachemson AL, Lewin T, Maroudas A, Freeman MAE (1970) In vitro diffusion of dye through the endplates and the annulus fibrosus of human lumbar intervertebral discs. Acta Orthop Scand 41: 589–607.
Parkkinen JJ, Hakkinen TP, Sayolainen S, Wang C, Tammi R, Agren UM, Lammi MJ, Arokoski J, Helminen HJ, Tammi MI (1996) Distribution of hyaluronan in articular cartilage as probed by a biotinylated binding region of aggrecan. Histochem Cell Biol 105: 187–194.
Shukunami C, Hiraki Y (1998) Expression of cartilage-specific functional matrix chondromodulin-I mRNA in rabbit growth plate chondrocytes and its responsiveness to growth stimuli in vitro. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 249: 885–890.
Shukunami C, Yamamoto S, Tanabe T, Hiraki Y (1999) Generation of multiple transcripts from the chicken chondromodulin-I gene and their expression during embryonic development. FFBS 456: 165–170.
Tammi R, Agren U, Tuhkanen A-L, Tammi M (1994) Hyaluronan metabolism in skin. Progr Histochem Cytochem 29: 1–81.
Yasuma T, Yamauchi Y, Arai K, Makino E (1989) Histopathologic study on tumor infiltration into the intervertebral disc. Spine 14: 1245–1248.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takao, T., Iwaki, T., Kondo, J. et al. Immunohistochemistry of Chondromodulin-I in the Human Intervertebral Discs with Special Reference to the Degenerative Changes. Histochem J 32, 545–550 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004150211097
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004150211097