Abstract
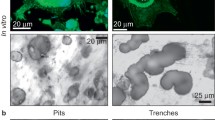
Osteoclasts resorb bone by a complex dynamic process that initially involves attachment, polarization and enzyme secretion, followed by their detachment and migration to new sites. In this study, we postulated that mineralized and osteoid bone matrix signal osteoclasts differently, resulting in the resorption of mineralized bone matrix only. We, therefore, compared the cytoplasmic distribution of cytoskeletal proteins F-actin and vinculin using confocal laser-scanning microscopy in osteoclasts cultured on mineralized and demineralized bone slices and correlated the observations with their functional activity. Our results have demonstrated significant differences in F-actin and vinculin staining patterns between osteoclasts cultured on mineralized bone matrix and those on demineralized bone matrix. In addition, the structural variations were accompanied by significant differences in bone resorbing activity between osteoclasts grown on mineralized bone matrix and those on demineralized bone matrix after 24 h of culture -- resorption only occurring in mineralized bone but not in demineralized bone. These results indicated that failure of osteoid bone resorption is caused by perturbation of osteoclast polarization. © 1998 Chapman & Hall
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baron, R. (1993) Cellular and molecular biology of the osteoclast. In Cellular and Molecular Biology of Bone (edited by Noda, M. ), pp. 445-95.
Baron, R. (1989) Polarity and membrane transport in osteoclasts. Conn. Tissue Res. 20, 109-20.
Baron, R., Neff, L., Louvard, D. & Courtoy, P.J. (1985) Cell-mediated extracellular acidification and bone resorption: evidence for a low pH in resorbing lacunae and localisation of a 100-kD lysosomal membrane protein at the osteoclast ruffled border. J. Cell Biol. 101, 2210-22.
Baron, R., Neff, L., Brown, W., Courtoy, P.J., Couvard, D. & Farquhar, M.G. (1988) Polarised secretion of lysosomal enzymes: co-distribution of cation-independent mannose-6-phosphate receptors and lysosomal enzymes along the osteoclast exocytic pathway. J. Cell Biol. 106, 1863-72.
Burridge, K. & Connell, L. (1983) A new protein of adhesion plaques and ruffling membranes. J. Cell Biol. 97, 359-67.
Chambers, T. J., Thomson, B.M. & Fuller, K. (1984) Effect of substrate composition on bone resorption by rabbit osteoclasts. J. Cell Sci. 70, 61-71.
Geiger, B., Tokuyasu, K.T., Dutton, A.H. & Singer, S. J. (1980) Vinculin, an intracellular protein localised at specialised sites where microfilament bundles terminate at cell membranes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 77, 4127-31.
Gupta, A., Edwards, J.C. & Hruska, K.A. (1996) Cellular distribution and regulation of NHE-1 isoform of the Na-H exchange in the avian osteoclast. Bone 18, 87-95.
Lakkakorpi, P., Tuukkanen, F., Hentunen, T., Jarvelin, K. & Vaananen, K. (1989) Organisation of the osteoclast microfilaments during the attachment to bone surface in vitro. J. Bone Min. Res. 4, 817-25.
Lucht, U. (1972) Osteoclasts and their relationship to bone as studied by electron microscopy. Zellforsch. Mikrosk. Anat. 135, 211-28.
Marchisio, P. (1984) Cell substratum interactions of cultured avain osteoclasts is mediated by specific adhesion structures. J. Cell Biol. 99, 1696-705.
Miller, S. (1977) Osteoclast cell surface changes during the egg laying cycle in Japanese quail. J. Cell Biol. 75, 104-18.
Nakamura, I., Takahashi, N., Sasaki, T., Kurokawa, T. & Suda, T. (1996) Chemical and physical properties of the extra cellular matrix are required for the actin ring formation in osteoclasts. J. Bone Min. Res. 11, 1873-9.
Oldberg, A., Franzen, A. & Heinegard, D. (1986) Cloning sequence analysis of rat bone sialoprotein (osteopontin) cDNA reveals an Arg-Gly-Asp cellbinding sequence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 83, 8819-323.
Oldberg, A., Franzen, A., Heinegard, D., Pierschbacher, M. & R UOSALAHTI, E. (1988) Identification of a bone sialoprotein receptor in osteocarcoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 263, 19433-6.
Palokangas, H., Mulari, M. & Vaananen, H.K. (1997) Endocytic pathway from the basal plasma membrane to the ruffled border membrane in bone-resorbing osteoclasts. J. Cell. Sci. 110, 1767-80.
Reinholt, F.P.K., Hullenby, A., Oldberg, A. & Heinegard, D. (1990) Osteopontin: a possible anchor of osteoclasts to bone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87, 4473-5.
Ross, F.P., Alvarez, J. I., Chappel, J., Sander, D., Butler, W.T., Farach-Carson, M.C., Mintz, K.A., Robey, P.G., Teitelbaum, S.L. & Cheresh, D.A. (1993) Interactions between matrix proteins osteopontin and bone sialoprotein and the osteoclast integrin αvβ3 potentiate bone resorption. J. Biol. Chem. 268, 9901-7.
Stevenson, S. & Horowitz, M. (1992) The response to bone allografts. J. Bone Joint Surg. 74A, 939-51.
Termine, J. (1993) Bone matrix proteins and the minerlisation process. In Primer on the Metabolic Bone Disease and Disorders of Mineral Metabolism. 2nd edn (edited by Favus, M. ), pp. 21-5. New York: Raven Press.
Teti, A., Blair, H.C., Schlesinger, P.H., Grano, M., Zambonin Zallone, A., Kahn, A. J., Teitelbaum, S.L. & H RUSKA, K.A. (1989) Extracellular protons acidify osteoclasts, reduce cytosolic calcium and promote expression of cell-matrix attachment structure. J. Clin. Invest. 84, 773-80.
Teti, A., Marchisio, P.C. & Zambonin Zallone, A. (1991) Clear zone in osteoclast function: role of podosomes in regulation of bone-resorbing activity. Am. J. Physiol. 261, C1-7.
Turksen, K., Kaneskia, J., Opas, M., H EERSCH, J.N. & Aubin, J.E. (1988) Adhesion patterns and cytoskeleton of rabbit osteoclasts on bone slices and glass. J. Bone Min. Res. 3, 389-400.
Urist, M. (1965) Bone: formation by autoinduction. Science 150, 893-9.
Wozney, J.M., Rosen, V., Celeste, A.F., Mitsock, L.M., Whitters, M.J., Kriz, R.W., Hewick, R.M. & Wang, E.A. (1988) Novel regulators of bone formation: molecular clones and activities. Science 242, 1528-34.
Zheng, M.H., Papadimitriou, J.M. & Nicholson, G.C. (1991a) RNA synthesis in isolated rat osteoclasts: inhibitory effect of calcitonin. Bone 12, 317-22.
Zheng, M.H., Papadimitriou, J.M. & Nicholson, G.C. (1991b) A quantitative cytochemical investigation of osteoclasts and multinucleate giant cells. Histochem. J. 23, 180-8.
Zheng, M.H., Wood, D. J. & Papadimitriou, J.M. (1992) What's new in role of cytokine in osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Pathol. Res. Pract. 188, 1104-21.
Zheng, M.H., Fan, Y., Wysocki, S., Wood, D.J. & Papadimitriou, J.M. (1993) Detection of mRNA for carbonic anhydrase II in human osteoblast-like cells by in-situ hybridisation. J. Bone Min. Res. 8, 111-16.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
YOVICH, S., SEYDEL, U., PAPADIMITRIOU, J.M. et al. Evidence that failure of osteoid bone matrix resorption is caused by perturbation of osteoclast polarization. Histochem J 30, 267–273 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003263907320
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003263907320