Abstract
Aim
To study the discomfort and fear associated with maxillary infiltration injections when using a combination of external cold and a commercially available vibrating device.
Methodology
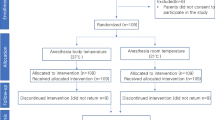
A total of 60 children aged 7 years old participated in this split mouth randomised crossover study. The control intervention comprised of the administration of 1.8 ml of 2% lidocaine with 1:100,000 adrenaline using a 24 mm 30 gauge needle, while the test intervention used external cold and a commercially available vibrating device in addition to the control protocol. The heart rate of the child at the time of injection was used as an objective measure and the Wong–Baker pain scale was used as a subjective measure of the child’s discomfort. The face, limbs, arms, cry and consolability (FLACC) scale was used to record the child’s pain as perceived by the dentist.
Results
Children reported a significantly lower Wong–Baker score and the operators observed a significantly lower heart rate and FLACC scores in the test visit than the control visit.
Conclusions
Combining external cold with vibrating devices might be effective in reducing discomfort and fear in children undergoing infiltration dental analgesia.
Clinical trials Identifier
NCT02675387.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baxter AL, Lawson ML. Methodological concerns comparing buzzy to transilluminator device. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2014;29:114.
Baxter AL, Cohen LL, Mcelvery HL, Lawson ML, Von Baeyer CL. An integration of vibration and cold relieves venipuncture pain in a pediatric emergency department. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2011;27:1151–6.
Bonjar AHS. Syringe micro vibrator (SMV) a new device being introduced in dentistry to alleviate pain and anxiety of intraoral injections, and a comparative study with a similar device. Ann Surg Innov Res. 2011;5:1–5.
Canbulat N, Ayhan F, Inal S. Effectiveness of external cold and vibration for procedural pain relief during peripheral intravenous cannulation in pediatric patients. Pain Manag Nurs. 2015a;16:33–9.
Canbulat ŞN, İnal S, Sevim AA. The effect of combined stimulation of external cold and vibration during immunization on pain and anxiety levels in children. J Perianesth Nurs. 2015b;30:228–35.
Ching D, Finkelman M, Loo CY. Effect of the DentalVibe injection system on pain during local anesthesia injections in adolescent patients. Pediatr Dent. 2014;36:51–5.
Czarnecki ML, Turner HN, Collins PM, et al. Procedural pain management: a position statement with clinical practice recommendations. Pain Manag Nurs. 2011;12:95–111.
Fakhruddin KS, Gorduysus MO, El Batawi H. Effectiveness of behavioral modification techniques with visual distraction using intrasulcular local anesthesia in hearing disabled children during pulp therapy. Eur J Dent. 2016;10:551–5.
Frankl S, Shiere F, Fogels H. Should the parent remain with the child in the dental operatory. J Dent Child. 1962;29:150–62.
Gonzalez-Martinez R, Jovani-Sancho MD, Cortell-Ballester I. Does psychological profile influence third molar extraction and postoperative pain? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2017;75:484–90.
Hosseini HR, Parirokh M, Nakhaee NP, Abbott VA, Samani S. Efficacy of articaine and lidocaine for buccal infiltration of first maxillary molars with symptomatic irreversible pulpitis: a randomized double-blinded clinical trial. Iran Endod J. 2016;11:79–84.
Jalevik B, Klingberg G. Pain sensation and injection techniques in maxillary dento-alveolar surgery procedures in children–a comparison between conventional and computerized injection techniques (The Wand). Swed Dent J. 2014;38:67–75.
Kandiah P, Tahmassebi JF. Comparing the onset of maxillary infiltration local analgesia and pain experience using the conventional technique vs. the Wand in children. Br Dent J. 2012;213:E15.
Kearl YL, Yanger S, Montero S, Morelos-Howard E, Claudius I. Does combined use of the J-tip(R) and buzzy(R) device decrease the pain of venipuncture in a pediatric population? J Pediatr Nurs. 2015;30(6):829–33.
Kilinc G, Akay A, Eden E, Sevinc N, Ellidokuz H. Evaluation of children’s dental anxiety levels at a kindergarten and at a dental clinic. Braz Oral Res. 2016. https://doi.org/10.1590/1807-3107BOR-2016.vol30.0072
Nanitsos E, Vartuli R, Forte A, Dennison P, Peck C. The effect of vibration on pain during local analgesia injections. Aust Dent J. 2009;54:94–100.
Pani SC, Alanazi GS, Albaragash A, Almosaihel M. Objective assessment of the influence of the parental presence on the fear and behavior of anxious children during their first restorative dental visit. J Int Soc Prev Community Dent. 2016;6:148–52.
Raghav K, Van Wijk AJ, Abdullah F, et al. Efficacy of virtual reality exposure therapy for treatment of dental phobia: a randomized control trial. BMC Oral Health. 2016;16:25.
Roeber B, Wallace DP, Rothe V, Salama F, Allen KD. Evaluation of the effects of the VibraJect attachment on pain in children receiving local anesthesia. Pediatr Dent. 2011;33:46–50.
Sharma A, Suprabha BS, Shenoy R, Rao A. Efficacy of lignocaine in gel and spray form during buccal infiltration anesthesia in children: a randomized clinical trial. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2014;15:750–4.
Shilpapriya M, Jayanthi M, Reddy VN, et al. Effectiveness of new vibration delivery system on pain associated with injection of local anesthesia in children. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent. 2015;33:173–6.
Voepel-Lewis T, Shayevitz JR, Malviya S. The FLACC: a behavioral scale for scoring postoperative pain in young children. Pediatr Nurs. 1997;23:293–7.
Whelan HM, Kunselman AR, Thomas NJ, Moore J, Tamburro RF. The impact of a locally applied vibrating device on outpatient venipuncture in children. Clin Pediatr (Phila). 2014;53:1189–95.
Wiederhold MD, Gao K, Wiederhold BK. Clinical use of virtual reality distraction system to reduce anxiety and pain in dental procedures. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw. 2014;17:359–65.
Wright G. Children’s behavior in the dental office. In: Wright GZ editor. Behavior management in dentistry for children. Philadelphia: WB Saunders Co; 1975. p. 55–72.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge the Ministry of Health, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia for supporting the lead author during his graduate study period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential sources of conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alanazi, K.J., Pani, S. & AlGhanim, N. Efficacy of external cold and a vibrating device in reducing discomfort of dental injections in children: A split mouth randomised crossover study. Eur Arch Paediatr Dent 20, 79–84 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-018-0399-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40368-018-0399-8