Abstract
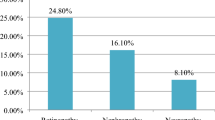
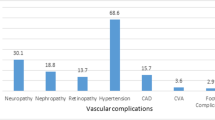
To determine the prevalence of microvascular complications and associated risk factors among subjects with type 2 diabetes reported at a tertiary care unit of Karachi, Pakistan. This retrospective observational study was carried out in the outpatient department of Baqai Institute of Diabetology and Endocrinology (BIDE), a tertiary care diabetes center of Karachi from January 2005 to April 2016. Data records of patients with type 2 diabetes at presentation were analyzed. Selected data was extracted from Health Management System (HMS) including basic demographics, anthropometric measurements, biochemical results, medical information, and microvascular complications results. Data analysis was performed on Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20.0. Overall, prevalence of at least one microvascular complication was 56.9%, retinopathy 15.8%, nephropathy 31.0%, and neuropathy 48.7% were noted. Male gender, age ≥ 40 years, duration of diabetes > 10 years, obesity, hypertension, HbA1c > 7%, and low HDL were found to be significant risk factors for microvascular complication. Hypertriglyceridemia and hypercholesterolemia were significantly associated with nephropathy and neuropathy, whereas no significant association of high LDL was found with any complication. High prevalence of microvascular complications was observed among type 2 diabetic subjects visited first time at a tertiary care hospital. Early identification and effective management are required at primary and secondary care levels to combat this situation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zimmet PZ. Diabetes and its drivers: the largest epidemic in human history? Clin Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;3(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40842-016-0039-3
International Diabetes Federation. IDF Atlas. 8th edition. retrieved from: http://www.diabetesatlas.org. (last accessed: Feb 2018).
Abougalambou SS, Hassali MA, Sulaiman SA, Abougalambou AS. Prevalence of vascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus outpatients at teaching hospital in Malaysia. J Diabetes Metab. 2011;2(115):1–4. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6156.1000115.
Valencia WM, Florez H. How to prevent the microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes beyond glucose control. BMJ. 2017;356:i6505. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i6505.
Agrawal R, Ola V, Bishnoi P, Gothwal S, Sirohi P, Agrawal R. Prevalence of micro and macrovascular complications and their risk factors in type-2 diabetes mellitus. JAPI. 2014;62:505.
Alaboud AF, Tourkmani AM, Alharbi TJ, Alobikan AH, Abdelhay O, Al Batal SM, et al. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of type 2 diabetic mellitus in central, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Saudi Med J. 2016;37(12):1408. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2016.12.17062.
Yokoyama H, Oishi M, Takamura H, Yamasaki K, Shirabe SI, Uchida D, et al. Large-scale survey of rates of achieving targets for blood glucose, blood pressure, and lipids and prevalence of complications in type 2 diabetes (JDDM 40). BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2016;4(1):e000294. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjdrc-2016-000294.
Rhee EJ. Diabetes in Asians. Endocrinol Metab. 2015;30(3):263–9.
So WY, Raboca J, Sobrepena L, Yoon KH, Deerochanawong C, Ho LT, et al. Comprehensive risk assessments of diabetic patients from seven Asian countries: the Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) program. J Diabetes. 2011;3(2):109–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1753-0407.2011.00115.x.
Shah AD, Kandula NR, Lin F, Allison MA, Carr J, Herrington D, et al. Less favorable body composition and adipokines in south Asians compared with other US ethnic groups: results from the MASALA and MESA studies. Int J Obes. 2016;40(4):639–45. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2015.219.
Chowdhury TA, Lasker SS. Complications and cardiovascular risk factors in south Asians and Europeans with early-onset type 2 diabetes. QJM. 2002;95(4):241–6.
Basit A, Hydrie MZ, Hakeem R, Ahmedani MY, Masood Q. Frequency of chronic complications of type 2 diabetes. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2004;14(2):79–83. 02.2004/JCPSP.7983.
Eboh C, Chowdhury TA. Management of diabetic renal disease. Ann Transl Med. 2015;3(11):154.
Ahmedani MY, Hydrie MZ, Iqbal A, Gul A, Mirza WB, Basit A. Prevalence of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetic patients in Karachi: Pakistan a multi-center study. Hypertension (n= 1226). 2005; 2194:99–7.
Ahsan S, Basit A, Ahmed KR, Ali L, Khanam R, Fawwad A, et al. Risk indicators of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes screened by fundus photographs: a study from Pakistan. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries. 2015;35(3):333–8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-014-0277-9.
Hydrie MZ, Basit A. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy. J Baqai Med Univ. 2002;5(2):6–11.
Ali A, Iqbal F, Taj A, Iqbal Z, Amin MJ, Iqbal QZ. Prevalence of microvascular complications in newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes. Pakistan J Med Sci. 2013;29(4):899–902.
ATP III Guidelines At-A-Glance Quick Desk Reference. Available at: https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/files/docs/guidelines/atglance.pdf (last assessed on March 15, 2018).
Let patients manage their own cholesterol. Available at: https://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/783728 (last assessed on 15 Mar 2018.
Santos AD, Cecílio HP, Teston EF, Arruda GO, Peternella FM, Marcon SS. Microvascular complications in type 2 diabetes and associated factors: a telephone survey of self-reported morbidity. Cien Saude Colet. 2015;20(3):761–70. https://doi.org/10.1590/1413-81232015203.12182014.
Pradeepa R, Anjana RM, Unnikrishnan R, Ganesan A, Mohan V, Rema M. Risk factors for microvascular complications of diabetes among South Indian subjects with type 2 diabetes—the Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study (CURES) eye study-5. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2010;12(10):755–61. https://doi.org/10.1089/dia.2010.0069
Pradeepa R, Rema M, Vignesh J, Deepa M, Deepa R, Mohan V. Prevalence and risk factors for diabetic neuropathy in an urban south Indian population: the Chennai urban rural epidemiology study (CURES-55). Diabet Med. 2008;25(4):407–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2008.02397.
Wani FA, Koul RK, Raina AA, Nazir A, Maqbool M, Bhat MH, et al. Prevalence of microvascular complications in newly diagnosed type-2 diabetes mellitus. Int J Sci Study. 2016;3(10):102–5. https://doi.org/10.17354/ijss/2016/21.
Kung K, Chow KM, Hui EM, Leung M, Leung SY, Szeto CC, et al. Prevalence of complications among Chinese diabetic patients in urban primary care clinics: a cross-sectional study. BMC Fam Pract. 2014;15(1):8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2296-15-8
Jamil K, Iqbal Y, Zia S, Khan QA. Frequency of retinopathy in newly diagnosed patients of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pakistan J Ophthalmol. 2014;30(1):38.
Sohail M. Prevalence of diabetic retinopathy among type–2 diabetes patients in Pakistan—vision registry. Pak J Ophthalmol. 2014;30(4):204–12.
Zoungas S, Woodward M, Li Q, Cooper ME, Hamet P, Harrap S, et al. Impact of age, age at diagnosis and duration of diabetes on the risk of macrovascular and microvascular complications and death in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2014;57(12):2465–74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00125-014-3369-7.
Bansal D, Gudala K, Esam HP, Nayakallu R, Vyamusani RV, Bhansali A. Microvascular complications and their associated risk factors in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Int J Chronic Dis. 2014;2014 https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/201423.
Haque HF, Afroz F, Afroze SR, Mitra P, Rahim MA, Ahmed AS, et al. Frequency and risk factors of diabetic complications among selected group of diabetic patients: real-life scenario from a developing country, Bangladesh. BIRDEM Med J. 2017;7(2):143–7.
Timar B, Timar R, Gaiță L, Oancea C, Levai C, Lungeanu D. The impact of diabetic neuropathy on balance and on the risk of falls in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study. PloS One. 2016;11(4):e0154654. from this region and from other parts of the world.
Vinik AI, Strotmeyer ES, Nakave AA, Patel CV. Diabetic neuropathy in older adults. Clin Geriatr Med. 2008;24(3):407–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cger.2008.03.011.
Dirani M, Xie J, Fenwick E, Benarous R, Rees G, Wong TY, et al. Are obesity and anthropometry risk factors for diabetic retinopathy?: the diabetes management project. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2011;52(7):4416–21. https://doi.org/10.1167/iovs.11-7208.
Hozumi J, Sumitani M, Matsubayashi Y, Abe H, Oshima Y, Chikuda H, et al. Pain Res Manag. 2016;2016 https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/2487924.
Themeli Y, Bajrami V, Barbullushi M, Idrizi A, Teferici D, Muka L, Ktona E. Diabetic nephropathy and risk factors associated with DM in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval for the study was obtained from the institutional review board (IRB) of BIDE.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abro, M., Zafar, A.B., Fawwad, A. et al. Prevalence of diabetic micro vascular complications at a tertiary care unit of Karachi, Pakistan. Int J Diabetes Dev Ctries 39, 325–330 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-018-0683-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13410-018-0683-5