Abstract
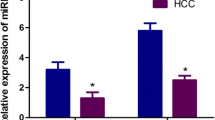
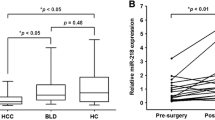
Aberrant expressions of the miR-148/152 family (miR-148a, miR-148b, and miR-152) have been documented in many tumor tissues, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). However, the expression pattern and clinical significance of circulating miR-148/152 family in HCC remain elusive. In this study, we conducted quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) to examine the levels of serum miR-148a, miR-148b, and miR-152 in 76 HCC cases, as well as 62 controls with benign liver diseases and 55 healthy volunteers. Our results showed that serum levels of three microRNAs (miRNAs) were significantly decreased in HCC cases than those in benign and healthy controls (all P < 0.05). Moreover, they showed strong correlations with each other in HCC group (r = 0.6716, 0.5381, and 0.7712; all P < 0.001). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis revealed that the combination of circulating miR-148/152 family had an increased area under the curve (AUC) = 0.940 (95 % confidence interval (CI), 0.886–0.973) with the sensitivity of 96.1 % and the specificity of 91.9 %, which were significantly higher than those of serum alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and three miRNAs alone in differentiating HCC from benign liver diseases. In addition, serum miR-148a and miR-148b were significantly associated with tumor size (P = 0.011 and 0.037) and tumor–node–metastasis (TNM) stage (P < 0.001 and P = 0.034), yet serum miR-152 was only correlated with TNM stage (P = 0.009). Also, dynamic monitoring three miRNAs can help us predict recurrence or metastasis in HCC cases after surgical resection. Besides, Kaplan–Meier analyses demonstrated that the decreased serum miR-148a (P < 0.001) and miR-152 (P = 0.012) was closely correlated with shorten overall survival of HCC patients. Additionally, Cox regression model further indicated that serum miR-148a was strongly associated with the prognosis of HCC patients. Our study suggests that downregulated circulating miR-148/152 family can provide positive diagnostic value for HCC. Moreover, serum miR-148a might be as independent prognostic factor for HCC patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63(1):11–30.
Njei B, Rotman Y, Ditah I, Lim JK. Emerging trends in hepatocellular carcinoma incidence and mortality. Hepatology. 2015;61(1):191–9.
Bodzin AS, Busuttil RW. Hepatocellular carcinoma: advances in diagnosis, management, and long term outcome. World J Hepatol. 2015;7(9):1157–67.
Yang N, Ekanem NR, Sakyi CA, Ray SD. Hepatocellular carcinoma and microRNA: new perspectives on therapeutics and diagnostics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;81:62–74.
Romero-Cordoba SL, Salido-Guadarrama I, Rodriguez-Dorantes M, Hidalgo- Miranda A. miRNA biogenesis: biological impact in the development of cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2014;15(11):1444–55.
Lan H, Lu H, Wang X, Jin H. MicroRNAs as potential biomarkers in cancer: opportunities and challenges. Biomed Res Int. 2015;2015:125094.
Jiang L, Cheng Q, Zhang BH, Zhang MZ. Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma screening: a validation set from China. Medicine (Baltimore). 2015;94(10):e603.
Khoury S, Tran N. Circulating microRNAs: potential biomarkers for common malignancies. Biomark Med. 2015;9(2):131–51.
Chen Y, Song YX, Wang ZN. The microRNA-148/152 family: multi-faceted players. Mol Cancer. 2013;12:43.
Zhai R, Kan X, Wang B, Du H, Long Y, Wu H, et al. miR-152 suppresses gastric cancer cell proliferation and motility by targeting CD151. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(11):11367–73.
Joshi P, Jeon YJ, Lagana A, Middleton J, Secchiero P, Garofalo M, et al. MicroRNA-148a reduces tumorigenesis and increases TRAIL-induced apoptosis in NSCLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2015;112(28):8650–5.
Zhang JP, Zeng C, Xu L, Gong J, Fang JH, Zhuang SM. MicroRNA-148a suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of hepatoma cells by targeting Met/Snail signaling. Oncogene. 2014;33(31):4069–76.
Zhang JG, Shi Y, Hong DF, Song M, Huang D, Wang CY, et al. MiR-148b suppresses cell proliferation and invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting WNT1/β-catenin pathway. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8087.
Huang J, Wang Y, Guo Y, Sun S. Down-regulated microRNA-152 induces aberrant DNA methylation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting DNA methyltransferase 1. Hepatology. 2010;52(1):60–70.
Sidhu K, Kapoor NR, Pandey V, Kumar V. The “Macro” World of microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2015;5:68.
Khare S, Zhang Q, Ibdah JA. Epigenetics of hepatocellular carcinoma: role of microRNA. World J Gastroenterol. 2013;19(33):5439–45.
Wang WT, Chen YQ. Circulating miRNAs in cancer: from detection to therapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2014;7(1):86.
Qi J, Wang J, Katayama H, Sen S, Liu SM. Circulating microRNAs (cmiRNAs) as novel potential biomarkers for hepatocellular carcinoma. Neoplasma. 2013;60(2):135–42.
Liao Q, Han P, Huang Y, Wu Z, Chen Q, Li S, et al. Potential role of circulating microRNA-21 for hepatocellular carcinoma diagnosis: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 2015;10(6):e0130677.
Yin J, Hou P, Wu Z, Wang T, Nie Y. Circulating miR-375 and miR-199a-3p as potential biomarkers for the diagnosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(6):4501–7.
Chen L, Chu F, Cao Y, Shao J, Wang F. Serum miR-182 and miR-331-3p as diagnostic and prognostic markers in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(10):7439–47.
Xu X, Fan Z, Kang L, Han J, Jiang C, Zheng X, et al. Hepatitis B virus X protein represses miRNA-148a to enhance tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(2):630–45.
Heo MJ, Kim YM, Koo JH, Yang YM, An J, Lee SK, et al. microRNA-148a dysregulation discriminates poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma in association with USP4 overexpression. Oncotarget. 2014;5(9):2792–806.
Yan H, Dong X, Zhong X, Ye J, Zhou Y, Yang X, et al. Inhibitions of epithelial to mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells-like properties are involved in miR-148a-mediated anti-metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 2014;53(12):960–9.
Jiang F, Mu J, Wang X, Ye X, Si L, Ning S, et al. The repressive effect of miR-148a on TGF beta-SMADs signal pathway is involved in the glabridin- induced inhibition of the cancer stem cells-like properties in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e96698.
Liu Q, Xu Y, Wei S, Gao W, Chen L, Zhou T, et al. miRNA-148b suppresses hepatic cancer stem cell by targeting neuropilin-1. Biosci Rep. 2015;35(4). doi:10.1042/BSR20150084.
Zhang Z, Zheng W, Hai J. MicroRNA-148b expression is decreased in hepato- cellular carcinoma and associated with prognosis. Med Oncol. 2014;31(6):984.
Huang S, Xie Y, Yang P, Chen P, Zhang L. HCV core protein-induced down-regulation of microRNA-152 promoted aberrant proliferation by regulating Wnt1 in HepG2 cells. PLoS One. 2014;9(1):e81730.
Dang YW, Zeng J, He RQ, Rong MH, Luo DZ, Chen G. Effects of miR-152 on cell growth inhibition, motility suppression and apoptosis induction in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(12):4969–76.
Li L, Chen YY, Li SQ, Huang C, Qin YZ. Expression of miR-148/152 family as potential biomarkers in non-small-cell lung cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2015;21:1155–61.
Yang JS, Li BJ, Lu HW, Chen Y, Lu C, Zhu RX, et al. Serum miR-152, miR-148a, miR-148b, and miR-21 as novel biomarkers in non-small cell lung cancer screening. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):3035–42.
Pan L, Huang S, He R, Rong M, Dang Y, Chen G. Decreased expression and clinical significance of miR-148a in hepatocellular carcinoma tissues. Eur J Med Res. 2014;19:68.
Le HB, Zhu WY, Chen DD, He JY, Huang YY, Liu XG, et al. Evaluation of dynamic change of serum miR-21 and miR-24 in pre- and post-operative lung carcinoma patients. Med Oncol. 2012;29(5):3190–7.
Fleming NH, Zhong J, da Silva IP, Vega-Saenz de Miera E, Brady B, Han SW, et al. Serum-based miRNAs in the prediction and detection of recurrence in melanoma patients. Cancer. 2015;121(1):51–9.
Acknowledgments
The project was supported by the National Nature Science Foundation of China (No. 81472027, 81172141, 81200401), Nanjing Science and Technology Committee Project (No. 201108025), and Nanjing Medical Science and Technique Development Foundation (ZKX11025, QRX11254, QRX11255).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Additional information
Feng Wang and Houqun Ying contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, F., Ying, H., He, B. et al. Circulating miR-148/152 family as potential biomarkers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Tumor Biol. 37, 4945–4953 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4340-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-4340-z