Abstract
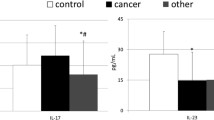
Many studies suggested that cytokines interleukin (IL)-29, IL-32, and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) are implicated in the pathogenesis of malignancies. The purpose of this study was to determine the clinical significance of the serum levels of IL-29, IL-32, and TNF-α in gastric cancer (GC) patients. Fifty-eight GC patients and 20 age- and sex-matched healthy controls were enrolled into this study. The median age at diagnosis was 59.5 years (range 32–82 years). Tumor localization of the majority of the patients was antrum (n = 42, 72.4 %), and tumor histopathology of the majority of the patients was diffuse (n = 43, 74.1 %). The majority of the patients had stage IV disease (n = 41, 70.7 %). Thirty-six (62.1 %) patients had lymph node involvement. The median follow-up time was 66 months (range 1 to 97.2 months). The baseline serum IL-29 concentrations were not different between patients and controls (p = 0.627). The baseline serum IL-32 and TNF-α concentrations of the GC patients were significantly higher (for IL-32, p = 0.014; for TNF-α, p = 0.001). Gender, localization, histopathology, tumor, and lymph node involvement were not found to be correlated with serum IL-29, IL-32, and TNF-α concentrations (p > 0.05). Patients without metastasis (p = 0.01) and patients who responded to chemotherapy (p = 0.04) had higher serum IL-29 concentrations. Patients older than 60 years had higher serum IL-32 (p = 0.002). Serum IL-29, IL-32, and TNF-α levels were not associated with outcome (p = 0.30, p = 0.51, and p = 0.41, respectively). In conclusion, serum levels of IL-32 and TNF-α may be diagnostic markers, and serum IL-29 levels may be associated with good prognosis in patients with GC.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
GLOBOCAN (2012) Estimated cancer incidence, mortality and prevalence worldwide in 2012.
Leaman DW. Mechanism of interferon action. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1998;20:101–42.
Pfeffer LM, Dinarello CA, Herberman RB, Williams BR, Borden EC, Bordens R, et al. Biological properties of recombinant alpha-interferons: 40th anniversary of the discovery of interferons. Cancer Res. 1998;58:2489–99.
Fujie H, Tanaka T, Tagawa M, Kaijun N, Watanabe M, Suzuki T, et al. Antitumor activity of type III interferon alone or in combination with type I interferon against human non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Sci. 2011;102:1977–90.
Stark GR, Kerr IM, Williams BR, Silverman RH, Schreiber RD. How cells respond to interferons. Annu Rev Biochem. 1998;67:227–64.
Pestka S, Krause CD, Walter MR. Interferons, interferon-like cytokines, and their receptors. Immunol Rev. 2004;202:8–32.
Kotenko SV, Gallagher G, Baurin VV, et al. IFN-lambdas mediate antiviral protection through a distinct class II cytokine receptor complex. Nat Immunol. 2003;4:69–77.
Dumoutier L, Lejeune D, Hor S, Fickenscher H, Renauld JC. Cloning of a new type II cytokine receptor activating signal transducer and activator of transcription (STAT)1, STAT2 and STAT3. Biochem J. 2003;370:391–6.
Witte K, Witte E, Sabat R, Wolk K. IL-28A, IL-28B, and IL-29: promising cytokines with type I interferon-like properties. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2010;21:237–51.
Zitzmann K, Brand S, Baehs S, et al. Novel interferon-lambdas induce antiproliferative effects in neuroendocrine tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2006;344:1334–41.
Brand S, Beigel F, Olszak T, Zitzmann K, Eichhorst ST, Otte JM, et al. IL-28A and IL-29 mediate antiproliferative and antiviral signals in intestinal epithelial cells and murine CMV infection increases colonic IL-28A expression. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G960–8.
Meager A, Visvalingam K, Dilger P, Bryan D, Wadhwa M. Biological activity of interleukins-28 and -29: comparison with type I interferons. Cytokine. 2005;31:109–18.
Kim SH, Han SY, Azam T, Yoon DY, Dinarello CA. Interleukin-32: a cytokine and inducer of TNF-alpha. Immunity. 2005;22:131–42.
Netea MG, Azam T, Ferwerda G, Girardin SE, Walsh M, Park JS, et al. IL-32 synergizes with nucleotide oligomerization domain (NOD) 1 and NOD2 ligands for IL-1beta and IL-6 production through a caspase 1-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:16309–14.
Li Y, Wang L, Pappan L, Galliher-Beckley A, Shi J. IL-1beta promotes stemness and invasiveness of colon cancer cells through Zeb1 activation. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:87.
Egberts JH, Cloosters V, Noack A, Schniewind B, Thon L, Klose S, et al. Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy inhibits pancreatic tumor growth and metastasis. Cancer Res. 2008;68:1443–50.
Sunaga N, Imai H, Shimizu K, Shames DS, Kakegawa S, Girard L, et al. Oncogenic KRAS-induced interleukin-8 overexpression promotes cell growth and migration and contributes to aggressive phenotypes of non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2012;130:1733–44.
Kollmar O, Scheuer C, Menger MD, Schilling MK. Macrophage inflammatory protein-2 promotes angiogenesis, cell migration, and tumor growth in hepatic metastasis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13:263–75.
Sullivan NJ, Sasser AK, Axel AE, Vesuna F, Raman V, Ramirez N, et al. Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene. 2009;28:2940–7.
Yu X, Zhou B, Zhang Z, Gao Q, Wang Y, Song Y, Pu Y, Chen Y, Duan R, Zhang L, Xi M. Significant association between IL-32 gene polymorphisms and susceptibility to endometrial cancer in Chinese Han women. Tumour Biol. 2015.
Seo EH, Kang J, Kim KH, Cho MC, Lee S, Kim HJ, et al. Detection of expressed IL-32 in human stomach cancer using ELISA and immunostaining. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2008;18:1606–12.
Ishigami S, Arigami T, Uchikado Y, Setoyama T, Kita Y, Sasaki K, et al. IL-32 expression is an independent prognostic marker for gastric cancer. Med Oncol. 2013;30:472.
Sorrentino C, Di Carlo E. Expression of IL-32 in human lung cancer is related to the histotype and metastatic phenotype. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2009;180:769–79.
Nishida A, Andoh A, Inatomi O, Fujiyama Y. Interleukin-32 expression in the pancreas. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:17868–76.
Kang YH, Park MY, Yoon DY, Han SR, Lee CI, Ji NY, et al. Dysregulation of overexpressed βα in hepatocellular carcinoma suppresses cell growth and induces apoptosis through inactivation of NF-κB and Bcl-2. Cancer Lett. 2012;318:226–33.
Yousif NG, Al-Amran FG, Hadi N, Lee J, Adrienne J. Expression of IL-32 modulates NF-κB and p38 map kinase pathways in human esophageal cancer. Cytokine. 2013;61:223–7.
Park JS, Choi SY, Lee JH, Lee M, Nam ES, Jeong AL, et al. Interleukin-32beta stimulates migration of MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells via the VEGF-STAT3 signaling pathway. Cell Oncol. 2013;36:493–503.
Tsai CY, Wang CS, Tsai MM, Chi HC, Cheng WL, Tseng YH, et al. Interleukin 32 increases human gastric cancer cell invasion associated with tumor progression and metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20:2276–88.
Zeng Q, Li S, Zhou Y, Ou W, Cai X, Zhang L, et al. Interleukin-32 contributes to invasion and metastasis of primary lung adenocarcinoma via NF-kappaB induced matrix metalloproteinases 2 and 9 expression. Cytokine. 2014;65:24–32.
Choo MK, Sakurai H, Kim DH, Saiki I. A ginseng saponin metabolite suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha-promoted metastasis by suppressing nuclear factor-kappaB signaling in murine colon cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 2008;19:595–600.
Popivanova BK, Kitamura K, Wu Y, Kondo T, Kagaya T, Kaneko S, et al. Blocking TNF-alpha in mice reduces colorectal carcinogenesis associated with chronic colitis. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:560–70.
Vendramini-Costa DB, Carvalho JE. Molecular link mechanisms between inflammation and cancer. Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18:3831–52.
Zhu F, Zhao H, Tian X, Meng X. Association between tumor necrosis factor-α rs1800629 polymorphism and risk of gastric cancer: a meta-analysis. Tumour Biol. 2014;35:1799–803.
Barrera L, Montes-Servín E, Barrera A, Ramírez-Tirado LA, Salinas-Parra F, Bañales-Méndez JL, et al. Cytokine profile determined by data-mining analysis set into clusters of non-small-cell lung cancer patients according to prognosis. Ann Oncol. 2015;26:428–35.
Naumnik W, Naumnik B, Niewiarowska K, Ossolinska M, Chyczewska E. Novel cytokines: IL-27, IL-29, IL-31 and IL-33. Can they be useful in clinical practice at the time diagnosis of lung cancer? Exp Oncol. 2012;34:348–53.
Guenterberg KD, Grignol VP, Raig ET, Zimmerer JM, Chan AN, Blaskovits FM, et al. Interleukin-29 binds to melanoma cells inducing Jak-STAT signal transduction and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2010;9:510–20.
Maher SG, Sheikh F, Scarzello AJ, Romero-Weaver AL, Baker DP, Donnelly RP, et al. IFNalpha and IFNlambda differ in their antiproliferative effects and duration of JAK/STAT signaling activity. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7:1109–15.
Sakitani K, Hirata Y, Hayakawa Y, Serizawa T, Nakata W, Takahashi R, et al. Role of interleukin-32 in Helicobacter pylori-induced gastric inflammation. Infect Immun. 2012;80:3795–803.
Fukamachi T, Ikeda S, Saito H, Tagawa M, Kobayashi H. Expression of acidosis-dependent genes in human cancer nests. Mol Clin Oncol. 2014;2:1160–6.
Suga H, Sugaya M, Miyagaki T, Kawaguchi M, Fujita H, Asano Y, et al. The role of IL-32 in cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. J Invest Dermatol. 2014;134:1428–35.
Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441:431–6.
Lin WW, Karin M. A cytokine-mediated link between innate immunity, inflammation and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2007;117:1175–83.
Tahara E. Molecular aspects of invasion and metastasis of stomach cancer. Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol. 2000;84:43–9.
Conti P, Youinou P, Theoharides TC. Modulation of autoimmunity by the latest interleukins (with special emphasis on IL-32). Autoimmun Rev. 2007;6:131–7.
Calabrese F, Baraldo S, Bazzan E, Lunardi F, Rea F, Maestrelli P, et al. IL-32, a novel proinflammatory cytokine in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2008;178:894–901.
Nold-Petry CA, Rudloff I, Baumer Y, Ruvo M, Marasco D, Botti P, et al. IL-32 promotes angiogenesis. J Immunol. 2014;192:589–602.
Yang Y, Wang Z, Zhou Y, Wang X, Xiang J, Chen Z. Dysregulation of over-expressed IL-32 in colorectal cancer induces metastasis. World J Surg Oncol. 2015;13:146.
Kagoya Y, Yoshimi A, Kataoka K, Nakagawa M, Kumano K, Arai S, et al. Positive feedback between NF-κB and TNF-α promotes leukemia-initiating cell capacity. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:528–42.
Wu Y, Zhou BP. TNF-alpha/NF-kappaB/Snail pathway in cancer cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer. 2010;102:639–44.
Kabir S, Daar GA. Serum levels of interleukin-1, interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor-alpha in patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 1995;95:207–12.
Macrì A, Versaci A, Loddo S, Scuderi G, Travagliante M, Trimarchi G, et al. Serum levels of interleukin 1beta, interleukin 8 and tumour necrosis factor alpha as markers of gastric cancer. Biomarkers. 2006;11:184–93.
Roselli M, Guadagni F, Martini F, Spila A, Mariotti S, D’Alessandro R, et al. Association between serum carcinoembryonic antigen and endothelial cell adhesion molecules in colorectal cancer. Oncology. 2003;65:132–8.
Wang YY, Lo GH, Lai KH, Cheng JS, Lin CK, Hsu PI. Increased serum concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-alpha are associated with disease progression and malnutrition in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Chin Med Assoc. 2003;66:593–8.
Forones NM, Mandowsky SV, Lourenço LG. Serum levels of interleukin-2 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha correlate to tumor progression in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 2001;48:1199–201.
Szaflarska A, Szczepanik A, Siedlar M, Czupryna A, Sierzega M, Popiela T, et al. Preoperative plasma level of IL-10 but not of proinflammatory cytokines is an independent prognostic factor in patients with gastric cancer. Anticancer Res. 2009;29:5005–12.
Guo L, Ou JL, Zhang T, Ma L, Qu LF. Effect of expressions of tumor necrosis factor α and interleukin 1B on peritoneal metastasis of gastric cancer. Tumour Biol. 2015.
Kim S, Choi MG, Lee HS, Lee SK, Kim SH, Kim WW, et al. Silibinin suppresses TNF-alpha-induced MMP-9 expression in gastric cancer cells through inhibition of the MAPK pathway. Molecules. 2009;14:4300–11.
Stanilov N, Miteva L, Dobreva Z, Stanilova S. Colorectal cancer severity and survival in correlation with tumour necrosis factor-alpha. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip. 2014;28:911–7.
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Erturk, K., Tastekin, D., Serilmez, M. et al. Clinical significance of serum interleukin-29, interleukin-32, and tumor necrosis factor alpha levels in patients with gastric cancer. Tumor Biol. 37, 405–412 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3829-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-015-3829-9