Abstract
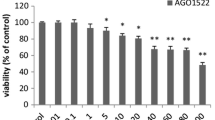
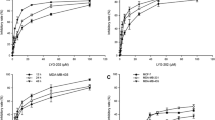
To explore the antitumor effect of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester (CADPE) on the breast cancer cell lines and illuminate the related mechanism. After treatment with different concentrations of CADPE for 24, 48, and 72 h, cell proliferation ability of the breast cancer cell lines MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-435 was analyzed by the MTT. Changes of the cell cycles were evaluated by PI staining. Cell apoptosis was examined by flow cytometry after Annexin V/7AAD double staining. Nuclear morphologic changes were observed under the inverted fluorescence microscope after staining with Hoechst 33342. Mitochondrial membrane potential and reactive oxygen species (ROS) level were estimated by JC-1 and DCFH-DA staining. In addition, the expression level of mitochondrial signaling pathway proteins Bcl-2, Bax, and caspase-3 were evaluated by Western blot. CADPE has the distinct cytotoxic effect to the breast cancer cells, and the effect is dose dependent. It did not change the cell cycles but induced the cell apoptosis of the breast cancer cells. At the same time, after CADPE treatment, the expression levels of caspase-3 and Bax in the breast cancer cells were upregulated and Bcl-2 expression was declined. The ROS level in the breast cancer cells was enhanced, and mitochondrial membrane potential of the cells was downregulated. CADPE has the antitumor functions. It can induce the cell apoptosis through downregulating Bcl-2 expression, enhancing Bax and caspase-3 expression levels, upregulating ROS level and reducing the mitochondrial membrane potential of the breast cancer cells to trigger the mitochondrial signal pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin MY, Evans MB, Kratt P, Pollack LA, Smith JL, Oster R, et al. Meeting the information needs of lower income cancer survivors: results of a randomized control trial evaluating the American Cancer Society's "I can cope". J Health Commun. 2014;19(4):441–59.
Jemal A. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011;61(2):69–90.
El-Mousallamy AM, Hawas UW, Hussein SA. Teucrol, a decarboxyrosmarinic acid and its 4′-O-triglycoside, teucroside from Teucrium pilosum. Phytochemistry. 2000;55(8):927–31.
Won C, Lee CS, Lee JK, Kim TJ, Lee KH, Yang YM, et al. CADPE suppresses cyclin D1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma by blocking IL-6-induced STAT3 activation. Anticancer Res. 2010;30(2):481–8.
Han H, Du B, Pan X, Liu J, Zhao Q, Lian X, et al. CADPE Inhibits PMA-stimulated gastric carcinoma cell invasion and matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression by FAK/MEK/ERK-mediated AP-1 activation. Mol Cancer Res. 2010;8(11):1477–88.
Zhang Z, Xiao B, Chen Q, Lian XY. Synthesis and biological evaluation of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester. J Nat Prod. 2010;73(2):252–4.
Yu SS, Spicer DV, Hawes D, Tseng CC, Yang CS, Pike MC, et al. Biological effects of green tea capsule supplementation in pre-surgery postmenopausal breast cancer patients. Front Oncol. 2013;3:298.
Chen YY, Hsu MJ, Sheu JR, Lee LW, Hsieh CY. Andrographolide, a novel NF- κ B inhibitor, induces vascular smooth muscle Cell apoptosis via a ceramide-p47phox-ROS signaling cascade. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:821813.
Lowe SW, Lin AW. Apoptosis in cancer. Carcinogenesis. 2000;21:485–95.
Mi Hye K, Sung-Hoon K, Woong Mo Y. Beneficial effects of astragaloside IV for hair loss via inhibition of Fas/Fas l-mediated apoptotic signaling. PLOS One. 2014;9(3):e92984.
Liu C, Yin L, Chen J, Chen J. The apoptotic effect of shikonin on human papillary thyroid carcinoma cells through mitochondrial pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014;35(3):1791–8.
Bu S, Xie Q, Chang W, Huo X, Chen F, Ma X. LukS-PV induces mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in human acute myeloid leukemia THP-1 cells. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2013;45(8):1531–7.
Zhang J, Park HS, Kim JA, Hong GE, Nagappan A, Park KI, et al. Flavonoids identified from Korean Scutellaria baicalensis induce apoptosis by ROS generation and caspase activation on human fibrosarcoma cells. Am J Chin Med. 2014;42(2):465–83.
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by Shanghai Municipal Health Bureau Foundation(2008021).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, J., Yang, M., Chen, Y. et al. Inducing apoptosis effect of caffeic acid 3,4-dihydroxy-phenethyl ester on the breast cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 35, 11781–11789 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2304-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-2304-3