Abstract
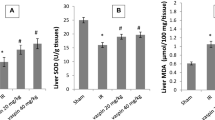
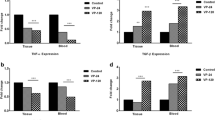
Ischemia-reperfusion (IR) has been reported to be associated with augmented reactive oxygen radicals and cytokines. Currently, we aimed to examine the influence of fluoxetine, which is already used as a preoperative anxiolytic, in the context of IR induced by occlusion of infrarenal abdominal aorta (60 min of ischemia) and its effects on renal oxidative status, inflammation, renal function, and cellular integrity in reperfusion (120 min post-ischemia). Male rats were randomly assigned as control, IR, and pretreated groups. The pretreated group animals received fluoxetine (20 mg/kg, i.p.) once daily for 3 days. Renal tissue oxidative stress, myeloperoxidase activity, proinflammatory cytokines (tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6), histology, and function were assessed. As an anti-inflammatory cytokine, interleukin-10 was also assessed. IR led to a significant increase in lipid hydroperoxide, malondialdehyde, and pro-oxidant antioxidant balance and decrease in superoxide dismutase activity and ferric reducing/antioxidant power level (p < 0.05), but fluoxetine was able to restore these parameters. High concentrations of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin-1β, interleukin-6, and myeloperoxidase activity caused by IR were significantly decreased in kidney tissue with fluoxetine. In addition, interleukin-10 levels were high in fluoxetine pretreated group. IR resulted in disrupted cellular integrity, infiltration of tissue with leukocytes, and decreased serum creatinine-urea levels (p < 0.05). Fluoxetine significantly restored impaired redox balance and inflammation parameters of rats subjected to IR to baseline values. This beneficial effect of fluoxetine on redox balance might be addressed to an improvement in renal function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aivatidi C, Vourliotakis G, Georgopoulos S, Sigala F, Bastounis E, Papalambros E (2011) Oxidative stress during abdominal aortic aneurysm repair biomarkers and antioxidant’s protective effect: a review. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 153:245–252
Aksu U, Demirci C, Ince C (2011) The pathogenesis of acute kidney injury and the toxic triangle of oxygen, reactive oxygen species and nitric oxide. Contrib Nephrol 174:119–128
Alamdari DH1, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Tavallaie S, Parizadeh MR, Moohebati M, Ghafoori F, Kazemi-Bajestani SM, Paletas K, Pegiou T, Koliakos G (2008) Prooxidant-antioxidant balance as a new risk factor in patients with angiographically defined coronary artery disease. Clin Biochem 41:375–380
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1999) Ferric reducing/antioxidant power assay: direct measure of total antioxidant activity of biological fluids and modified version for simultaneous measurement of total antioxidant power and ascorbic acid concentration. Methods Enzymol 299:15–27
Buege JA, Aust SD (1978) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Butterfield TA, Best TM, Merrick MA (2006) The dual roles of neutrophils and macrophages in inflammation: a critical balance between tissue damage and repair. J Athl Train 41:457–465
Chatterjee PK (2007) Novel pharmacological approaches to the treatment of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury: a comprehensive review. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 376(1–2):1–43
Guner I, Yaman MO, Aksu U, Uzun D, Erman H, Inceli M, Gelisgen R, Yelmen N, Uzun H, Sahin G (2014) The effect of fluoxetine on ischemia-reperfusion following aortic surgery in a rat model. J Surg Res 189(1):96–105. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2014.02.033
Han DD, Wang Y, Zhang XH, Liu JR, Wang HL (2012) Fluoxetine protects against monocrotaline-induced pulmonary arterial remodeling by inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and vascular endothelial growth factor. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 90:445
Hüttemann M, Helling S, Sanderson TH, Sinkler C, Samavati L, Mahapatra G, Varughese A, Lu G, Liu J, Ramzan R, Vogt S, Grossman LI, Doan JW, Marcus K, Lee I (2012) Regulation of mitochondrial respiration and apoptosis through cell signaling: cytochrome c oxidase and cytochrome c in ischemia/reperfusion injury and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1817(4):598–609
Kim H, Li H, Yoo KY, Lee BH, Hwang IK, Won MH (2007) Effects of fluoxetine on ischemic cells and expressions in BDNF and some antioxidants in the gerbil hippocampal CA1 region induced by transient ischemia. Exp Neurol 204(2):748–758
Kirkova M, Tzvetanova E, Vircheva S, Zamfirova R, Grygier B, Kubera M (2010) Antioxidant activity of fluoxetine: studies in mice melanoma model. Cell Biochem Funct 28(6):497–502
Koch A, Pernow M, Barthuber C, Mersmann J, Zacharowski K, Grotemeyer D (2012) Systemic inflammation after aortic cross clamping is influenced by Toll-like receptor 2 preconditioning and deficiency. J Surg Res 178(2):833–841
Kolla N, Wei Z, Richardson JS, Li XM (2005) Amitriptyline and fluoxetine protect PC12 cells from cell death induced by hydrogen peroxide. J Psychiatry Neurosci 30:196
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M (2009) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med 7:97
Li X, Mai J, Virtue A, Yin Y, Gong R, Sha X, Gutchigian S, Frisch A, Hodge I, Jiang X, Wang H, Yang XF (2012) IL-35 is a novel responsive anti-inflammatory cytokine—a new system of categorizing anti-inflammatory cytokines. PLoS One 7(3):e33628. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033628
Lim CM, Kim SW, Park JY, Kim C, Yoon SH, Lee JK (2009) Fluoxetine affords robust neuroprotection in the postischemic brain via its anti-inflammatory effect. J Neurosci Res 87(4):1037–1045
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR, White RF, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 25:1481–1488
Marcos E, Adnot S, Pham MH, Nosjean A, Raffestin B, Hamon M, Eddahibi S (2003) Serotonin transporter inhibitors protect against hypoxic pulmonary hypertension. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 168:487
Naito Y, Yoshikawa T, Matsuyama K, Yagi N, Arai M, Nakamura Y, Kaneko T, Yoshida N, Kondo M (1998) Neutrophils, lipid peroxidation, and nitric oxide in gastric reperfusion injury in rats. Free Radic Biol Med 24(3):494–502
Noiri E, Nakao A, Uchida K, Tsukahara H, Ohno M, Fujita T, Brodsky S, Goligorsky MS (2001) Oxidative and nitrosative stress in acute renal ischemia. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281(5):F948–F957
Nourooz-Zadeh J (1999) Ferrous ion oxidation in presence of xylenol orange for detection of lipid hydroperoxides in plasma. Methods Enzymol 300:58–62
Núñez MJ, Balboa J, Rodrigo E, Brenlla J, González-Peteiro M, Freire-Garabal M (2006) Effects of fluoxetine on cellular immune response in stressed mice. Neurosci Lett 396:247–251
Park Y, Hirose R, Dang K, Xu F, Behrends M, Tan V, Roberts JP, Niemann CU (2008) Increased severity of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury with venous clamping compared to arterial clamping in a rat model. Surgery 143(2):243–251
Patel NS, Chatterjee PK, Chatterjee BE, Cuzzocrea S, Serraino I, Brown PA, Stewart KN, Mota-Filipe H, Thiemermann C (2002) TEMPONE reduces renal dysfunction and injury mediated by oxidative stress of the rat kidney. Free Radic Biol Med 33(11):1575–1589
Roumestan C, Michel A, Bichon F, Portet F, Detoc M, Henriquet C, Jaffuel D, Mathieu M (2007) Anti-inflammatory properties of desipramine and fluoxetine. Respiratory Research 3:8:35
Sahin G, Guner I, Yelmen N, Yaman O, Mengi M, Simsek G, Sipahi S (2011) Alterations of central hypercapnic respiratory response induced by acute central administration of serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, fluoxetine. Chin J Physiol 54(5):356–366
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
van der Poll T, Keogh CV, Guirao X, Buurman WA, Kopf M, Lowry SF (1997) Interleukin-6 gene-deficient mice show impaired defense against pneumococcal pneumonia. J Infect Dis 176(2):439–444. doi:10.1086/514062
Vinas JL, Sola A, Hotter G (2006) Mitochondrial NOS upregulation during renal I/R causes apoptosis in a peroxynitrite-dependent manner. Kidney Int 69(8):1403–1409
Wu Y, Wan J, Zhen WZ, Chen LF, Zhan J, Ke JJ, Zhang ZZ, Wang YL (2014) The effect of butorphanol postconditioning on myocardial ischaemia reperfusion injury in rats. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 18(3):308–312
Zafir A, Ara A, Banu N (2009) In vivo antioxidant status: a putative target of antidepressant action. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:220–228
Zou C, Ding X, Flaherty JH, Dong B (2013) Clinical efficacy and safety of fluoxetine in generalized anxiety disorder in Chinese patients. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 9:1661-1670. Epub 2013 Nov 1. Review
Conflict of interest
All authors have disclosed potential conflicts of interest and all authors have read the journal’s policy on conflicts of interest and have none to declare. AS is a Ph.D. student at Istanbul University, Cerrahpasa Medical School, and no financial benefit was provided by Asfarma, International Pharmaceutical Marketing Company.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksu, U., Guner, I., Yaman, O.M. et al. Fluoxetine ameliorates imbalance of redox homeostasis and inflammation in an acute kidney injury model. J Physiol Biochem 70, 925–934 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0361-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13105-014-0361-0